使用决策森林和预训练嵌入进行文本分类
作者: Gitesh Chawda
创建日期: 2022/05/09
最后修改日期: 2022/05/09
描述: 使用Tensorflow决策森林进行文本分类。
介绍
TensorFlow决策森林 (TF-DF) 是一组最先进的算法,用于决策森林模型,兼容Keras API。该模块包括随机森林、梯度提升树和CART,可用于回归、分类和排序任务。
在这个例子中,我们将使用带有预训练嵌入的梯度提升树来 分类与灾难相关的推文。
另见:
使用以下命令安装Tensorflow决策森林:
pip install tensorflow_decision_forests
导入
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import tensorflow_hub as hub
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import tensorflow_decision_forests as tfdf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
获取数据
数据集可在 Kaggle 找到
数据集描述:
文件:
- train.csv:训练集
列:
- id:每条推文的唯一标识符
- text:推文的文本
- location:发送推文的地点(可能为空)
- keyword:推文中的特定关键词(可能为空)
- target:仅在train.csv中,表示推文是否关于真实灾难(1)或不是(0)
# 将 .csv 文件转换为 pandas 数据框
df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IMvision12/Tweets-Classification-NLP/main/train.csv"
)
print(df.head())
id keyword location text \
0 1 NaN NaN Our Deeds are the Reason of this #earthquake M...
1 4 NaN NaN Forest fire near La Ronge Sask. Canada
2 5 NaN NaN All residents asked to 'shelter in place' are ...
3 6 NaN NaN 13,000 people receive #wildfires evacuation or...
4 7 NaN NaN Just got sent this photo from Ruby #Alaska as ...
target
0 1
1 1
2 1
3 1
4 1
数据集中包含7613个样本和5列:
print(f"训练数据集形状: {df.shape}")
训练数据集形状: (7613, 5)
打乱并删除不必要的列:
df_shuffled = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=42)
# 删除 id、keyword 和 location 列,因为这些列大多数值为 nan
# 我们将仅使用 text 和 target 列
df_shuffled.drop(["id", "keyword", "location"], axis=1, inplace=True)
df_shuffled.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)
print(df_shuffled.head())
text target
0 So you have a new weapon that can cause un-ima... 1
1 The f$&@ing things I do for #GISHWHES Just... 0
2 DT @georgegalloway: RT @Galloway4Mayor: ÛÏThe... 1
3 Aftershock back to school kick off was great. ... 0
4 in response to trauma Children of Addicts deve... 0
打印关于打乱后的数据框的信息:
print(df_shuffled.info())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 7613 entries, 0 to 7612
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 text 7613 non-null object
1 target 7613 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 119.1+ KB
None
“灾难”和“非灾难”推文的总数:
print(
"灾难和非灾难推文的总数:"
f"{df_shuffled.target.value_counts()}"
)
灾难和非灾难推文的总数: 0 4342
1 3271
Name: target, dtype: int64
让我们预览一些样本:
for index, example in df_shuffled[:5].iterrows():
print(f"示例 #{index}")
print(f"\t目标 : {example['target']}")
print(f"\t文本 : {example['text']}")
示例 #0
目标 : 1
文本 : 所以你有了一种新的武器,可以造成无法想象的毁灭。
示例 #1
目标 : 0
文本 : 我为#GISHWHES所做的事情真是太@#! 我淋成了落汤鸡,只为去拿护垫和卫生棉条。 谢谢 @mishacollins @/@
示例 #2
目标 : 1
文本 : DT @georgegalloway: RT @Galloway4Mayor: ÛÏ科尔警方可以在利物浦街上抓到扒手... http://t.co/vXIn1gOq4Q
示例 #3
目标 : 0
文本 : 余震上学的启动仪式非常棒。 我想感谢每一个使这成为可能的人。 真是一个美妙的夜晚。
示例 #4
目标 : 0
文本 : 对于创伤的反应 上瘾者的孩子们发展出一种防御性的自我——这种自我是降低脆弱性的。 (3
拆分数据集为训练集和测试集:
test_df = df_shuffled.sample(frac=0.1, random_state=42)
train_df = df_shuffled.drop(test_df.index)
print(f"使用 {len(train_df)} 个样本进行训练,{len(test_df)} 个样本进行验证")
使用 6852 个样本进行训练,761 个样本进行验证
训练数据中“灾难”和“非灾难”推文的总数:
print(train_df["target"].value_counts())
0 3929
1 2923
名称: target, dtype: int64
测试数据中“灾难”和“非灾难”推文的总数:
print(test_df["target"].value_counts())
0 413
1 348
名称: target, dtype: int64
将数据转换为 tf.data.Dataset
def create_dataset(dataframe):
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(dataframe["text"].to_numpy(), dataframe["target"].to_numpy())
)
dataset = dataset.batch(100)
dataset = dataset.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
return dataset
train_ds = create_dataset(train_df)
test_ds = create_dataset(test_df)
下载预训练的嵌入
通用句子编码器嵌入将文本编码为高维向量,可用于文本分类、语义相似性、聚类等自然语言任务。它们在各种数据源和不同任务上进行了训练。它们的输入是可变长度的英语文本,输出是一个512维的向量。
要了解有关这些预训练嵌入的更多信息,请访问 Universal Sentence Encoder。
sentence_encoder_layer = hub.KerasLayer(
"https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder/4"
)
创建我们的模型
我们创建两个模型。在第一个模型(model_1)中,原始文本将首先通过预训练嵌入进行编码,然后传递给用于分类的梯度提升树模型。在第二个模型(model_2)中,原始文本将直接传递给梯度提升树模型。
构建 model_1
inputs = layers.Input(shape=(), dtype=tf.string)
outputs = sentence_encoder_layer(inputs)
preprocessor = keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
model_1 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(preprocessing=preprocessor)
使用 /tmp/tmpsp7fmsyk 作为临时训练目录
构建 model_2
model_2 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel()
使用 /tmp/tmpl0zj3vw0 作为临时训练目录
训练模型
我们通过传递指标 Accuracy、Recall、Precision 和 AUC 来编译我们的模型。对于损失,TF-DF 会自动检测最佳的损失函数(分类或回归)。这会在模型摘要中打印。
此外,由于它们是批量训练模型,而不是小批量梯度下降模型,TF-DF 模型不需要验证数据集来监控过拟合或提前停止训练。有些算法不使用验证数据集(例如随机森林),而有些算法则会使用(例如梯度提升树)。如果需要验证数据集,它将从训练数据集中自动提取。
# 编译 model_1
model_1.compile(metrics=["Accuracy", "Recall", "Precision", "AUC"])
# 这里我们不指定 epochs,因为,TF-DF 精确训练数据集的一轮
model_1.fit(train_ds)
# 编译 model_2
model_2.compile(metrics=["Accuracy", "Recall", "Precision", "AUC"])
# 这里我们不指定 epochs,因为,TF-DF 精确训练数据集的一轮
model_2.fit(train_ds)
读取训练数据集...
训练数据集读取时间为 0:00:06.473683。找到 6852 个示例。
训练模型...
模型训练时间为 0:00:41.461477
编译模型...
模型编译完成。
读取训练数据集...
训练数据集读取时间为 0:00:00.087930。找到 6852 个示例。
训练模型...
模型训练时间为 0:00:00.367492
编译模型...
模型编译完成。
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fe09ded1b40>
打印 model_1 的训练日志
logs_1 = model_1.make_inspector().training_logs() # 获取训练日志
print(logs_1) # 打印日志
打印模型_2的训练日志
logs_2 = model_2.make_inspector().training_logs()
print(logs_2)
model.summary() 方法打印关于你的决策树模型的各种信息,包括模型类型、任务、输入特征和特征重要性。
print("model_1 summary: ")
print(model_1.summary())
print()
print("model_2 summary: ")
print(model_2.summary())
model_1 summary:
Model: "gradient_boosted_trees_model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
model (Functional) (None, 512) 256797824
=================================================================
Total params: 256,797,825
Trainable params: 0
Non-trainable params: 256,797,825
_________________________________________________________________
Type: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
Task: CLASSIFICATION
Label: "__LABEL"
无权重
损失: BINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
验证损失值: 0.806777
每次迭代的树木数量: 1
节点格式: NOT_SET
树木数量: 137
总节点数: 6671
每棵树的节点数:
数量: 137 平均: 48.6934 标准偏差: 9.91023
最小: 21 最大: 63 忽略: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 21, 23) 1 0.73% 0.73%
[ 23, 25) 1 0.73% 1.46%
[ 25, 27) 0 0.00% 1.46%
[ 27, 29) 1 0.73% 2.19%
[ 29, 31) 3 2.19% 4.38% #
[ 31, 33) 3 2.19% 6.57% #
[ 33, 36) 9 6.57% 13.14% ####
[ 36, 38) 4 2.92% 16.06% ##
[ 38, 40) 4 2.92% 18.98% ##
[ 40, 42) 8 5.84% 24.82% ####
[ 42, 44) 8 5.84% 30.66% ####
[ 44, 46) 9 6.57% 37.23% ####
[ 46, 48) 7 5.11% 42.34% ###
[ 48, 51) 10 7.30% 49.64% #####
[ 51, 53) 13 9.49% 59.12% ######
[ 53, 55) 10 7.30% 66.42% #####
[ 55, 57) 10 7.30% 73.72% #####
[ 57, 59) 6 4.38% 78.10% ###
[ 59, 61) 8 5.84% 83.94% ####
[ 61, 63] 22 16.06% 100.00% ##########
叶子的深度:
数量: 3404 平均: 4.81052 标准偏差: 0.557183
最小: 1 最大: 5 忽略: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 1, 2) 6 0.18% 0.18%
[ 2, 3) 38 1.12% 1.29%
[ 3, 4) 117 3.44% 4.73%
[ 4, 5) 273 8.02% 12.75% #
[ 5, 5] 2970 87.25% 100.00% ##########
每个叶子中的训练观察数量:
数量: 3404 平均: 248.806 标准偏差: 517.403
最小: 5 最大: 4709 忽略: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 5, 240) 2615 76.82% 76.82% ##########
[ 240, 475) 243 7.14% 83.96% #
[ 475, 710) 162 4.76% 88.72% #
[ 710, 946) 104 3.06% 91.77%
[ 946, 1181) 80 2.35% 94.12%
[ 1181, 1416) 48 1.41% 95.53%
[ 1416, 1651) 44 1.29% 96.83%
[ 1651, 1887) 27 0.79% 97.62%
[ 1887, 2122) 18 0.53% 98.15%
[ 2122, 2357) 19 0.56% 98.71%
[ 2357, 2592) 10 0.29% 99.00%
[ 2592, 2828) 6 0.18% 99.18%
[ 2828, 3063) 8 0.24% 99.41%
[ 3063, 3298) 7 0.21% 99.62%
[ 3298, 3533) 3 0.09% 99.71%
[ 3533, 3769) 5 0.15% 99.85%
[ 3769, 4004) 2 0.06% 99.91%
[ 4004, 4239) 1 0.03% 99.94%
[ 4239, 4474) 1 0.03% 99.97%
[ 4474, 4709] 1 0.03% 100.00%
节点中的条件类型:
3267 : HigherCondition
深度 <= 0 的节点中的条件类型:
137 : HigherCondition
深度 <= 1 的节点中的条件类型:
405 : HigherCondition
深度 <= 2 的节点中的条件类型:
903 : HigherCondition
深度 <= 3 的节点中的条件类型:
1782 : HigherCondition
深度 <= 5 的节点中的条件类型:
3267 : HigherCondition
无
model_2 摘要:
模型: "gradient_boosted_trees_model_1"
_________________________________________________________________
层 (类型) 输出形状 参数 #
=================================================================
=================================================================
总参数: 1
可训练参数: 0
非可训练参数: 1
_________________________________________________________________
类型: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
任务: 分类
标签: "__LABEL"
输入特征 (1):
data:0
无权重
变量重要性: MEAN_MIN_DEPTH:
1. "__LABEL" 2.250000 ################
2. "data:0" 0.000000
变量重要性: NUM_AS_ROOT:
1. "data:0" 117.000000
变量重要性: NUM_NODES:
1. "data:0" 351.000000
变量重要性: SUM_SCORE:
1. "data:0" 32.035971
损失: BINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
验证损失值: 1.36429
每次迭代的树数量: 1
节点格式: NOT_SET
树的数量: 117
节点总数: 819
每棵树的节点数量:
计数: 117 平均: 7 标准差: 0
最小: 7 最大: 7 被忽略: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 7, 7] 117 100.00% 100.00% ##########
按叶子的深度:
计数: 468 平均: 2.25 标准差: 0.829156
最小: 1 最大: 3 被忽略: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 1, 2) 117 25.00% 25.00% #####
[ 2, 3) 117 25.00% 50.00% #####
[ 3, 3] 234 50.00% 100.00% ##########
按叶子训练观察数:
计数: 468 平均: 1545.5 标准差: 2660.15
最小: 5 最大: 6153 被忽略: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 5, 312) 351 75.00% 75.00% ##########
[ 312, 619) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 619, 927) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 927, 1234) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 1234, 1542) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 1542, 1849) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 1849, 2157) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 2157, 2464) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 2464, 2772) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 2772, 3079) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 3079, 3386) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 3386, 3694) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 3694, 4001) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 4001, 4309) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 4309, 4616) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 4616, 4924) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 4924, 5231) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 5231, 5539) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 5539, 5846) 0 0.00% 75.00%
[ 5846, 6153] 117 25.00% 100.00% ###
节点中的属性:
351 : data:0 [分类]
深度 <= 0 的节点中的属性:
117 : data:0 [分类]
深度 <= 1 的节点中的属性:
234 : data:0 [分类]
深度 <= 2 的节点中的属性:
351 : data:0 [分类]
深度 <= 3 的节点中的属性:
351 : data:0 [分类]
深度 <= 5 的节点中的属性:
351 : data:0 [分类]
节点中的条件类型:
351 : ContainsBitmapCondition
深度 <= 0 的节点中的条件类型:
117 : ContainsBitmapCondition
深度 <= 1 的节点中的条件类型:
234 : ContainsBitmapCondition
深度 <= 2 的节点中的条件类型:
351 : ContainsBitmapCondition
深度 <= 3 的节点中的条件类型:
351 : ContainsBitmapCondition
深度 <= 5 的节点中的条件类型:
351 : ContainsBitmapCondition
无
绘制训练指标
def plot_curve(logs):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot([log.num_trees for log in logs], [log.evaluation.accuracy for log in logs])
plt.xlabel("树的数量")
plt.ylabel("准确率")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot([log.num_trees for log in logs], [log.evaluation.loss for log in logs])
plt.xlabel("树的数量")
plt.ylabel("损失")
plt.show()
plot_curve(logs_1)
plot_curve(logs_2)
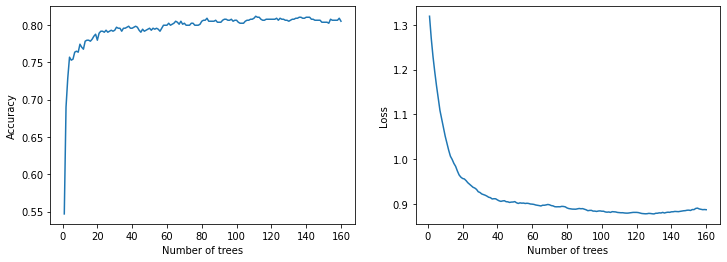
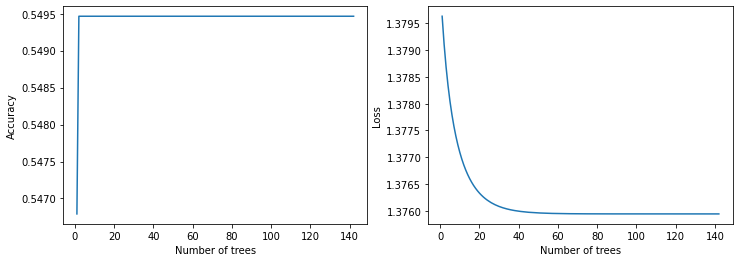
在测试数据上进行评估
results = model_1.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True, verbose=0)
print("model_1 评估: \n")
for name, value in results.items():
print(f"{name}: {value:.4f}")
results = model_2.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True, verbose=0)
print("model_2 评估: \n")
for name, value in results.items():
print(f"{name}: {value:.4f}")
model_1 评估:
损失: 0.0000
准确率: 0.8160
召回率: 0.7241
精准率: 0.8514
auc: 0.8700
model_2 评估:
损失: 0.0000
准确率: 0.5440
召回率: 0.0029
精准率: 1.0000
auc: 0.5026
在验证数据上进行预测
test_df.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)
for index, row in test_df.iterrows():
text = tf.expand_dims(row["text"], axis=0)
preds = model_1.predict_step(text)
preds = tf.squeeze(tf.round(preds))
print(f"文本: {row['text']}")
print(f"预测: {int(preds)}")
print(f"真实值: {row['target']}")
if index == 10:
break
文本: DFR EP016 Monthly Meltdown - On Dnbheaven 2015.08.06 http://t.co/EjKRf8N8A8 #Drum and Bass #heavy #nasty http://t.co/SPHWE6wFI5
预测: 0
真实值: 0
文本: FedEx no longer to transport bioterror germs in wake of anthrax lab mishaps http://t.co/qZQc8WWwcN via @usatoday
预测: 1
真实值: 0
文本: Gunmen kill four in El Salvador bus attack: Suspected Salvadoran gang members killed four people and wounded s... http://t.co/CNtwB6ScZj
预测: 1
真实值: 1
文本: @camilacabello97 Internally and externally screaming
预测: 0
真实值: 1
文本: Radiation emergency #preparedness starts with knowing to: get inside stay inside and stay tuned http://t.co/RFFPqBAz2F via @CDCgov
预测: 1
真实值: 1
文本: Investigators rule catastrophic structural failure resulted in 2014 Virg.. Related Articles: http://t.co/Cy1LFeNyV8
预测: 1
真实值: 1
文本: How the West was burned: Thousands of wildfires ablaze in #California alone http://t.co/iCSjGZ9tE1 #climate #energy http://t.co/9FxmN0l0Bd
预测: 1
真实值: 1
文本: Map: Typhoon Soudelor's predicted path as it approaches Taiwan; expected to make landfall over southern China by SÛ_ http://t.co/JDVSGVhlIs
预测: 1
真实值: 1
文本: Ûª93 blasts accused Yeda Yakub dies in Karachi of heart attack http://t.co/mfKqyxd8XG #Mumbai
预测: 1
真实值: 1
文本: My ears are bleeding https://t.co/k5KnNwugwT
预测: 0
真实值: 0
文本: @RedCoatJackpot *如同他们的典型表现,他们的子弹相撞,没人成功达到目标;这就是那种“诅咒” --
预测: 0
真实值: 0
结论
TensorFlow 决策森林包提供了强大的模型,尤其适用于结构化数据。在我们的实验中,使用预训练嵌入的梯度提升树模型达到了 81.6% 的测试准确率,而普通的梯度提升树模型的准确率为 54.4%。
