Grad-CAM 类激活可视化
作者: fchollet
创建日期: 2020/04/26
最后修改: 2021/03/07
描述: 如何为图像分类模型获取类激活热图。
改编自《深度学习与 Python》(2017)。
设置
import os
os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "tensorflow"
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
# 显示
from IPython.display import Image, display
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
可配置参数
您可以将这些更改为其他模型。
要获取 last_conv_layer_name 的值,请使用 model.summary()
查看模型中所有层的名称。
model_builder = keras.applications.xception.Xception
img_size = (299, 299)
preprocess_input = keras.applications.xception.preprocess_input
decode_predictions = keras.applications.xception.decode_predictions
last_conv_layer_name = "block14_sepconv2_act"
# 我们目标图像的本地路径
img_path = keras.utils.get_file(
"african_elephant.jpg", "https://i.imgur.com/Bvro0YD.png"
)
display(Image(img_path))

Grad-CAM 算法
def get_img_array(img_path, size):
# `img` 是大小为 299x299 的 PIL 图像
img = keras.utils.load_img(img_path, target_size=size)
# `array` 是形状为 (299, 299, 3) 的 float32 Numpy 数组
array = keras.utils.img_to_array(img)
# 我们添加一个维度将数组转换为 "批量"
# 形状为 (1, 299, 299, 3)
array = np.expand_dims(array, axis=0)
return array
def make_gradcam_heatmap(img_array, model, last_conv_layer_name, pred_index=None):
# 首先,我们创建一个模型,将输入图像映射到激活
# 的最后卷积层以及输出预测
grad_model = keras.models.Model(
model.inputs, [model.get_layer(last_conv_layer_name).output, model.output]
)
# 然后,我们计算输入图像的顶部预测类的梯度
# 相对于最后卷积层的激活
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
last_conv_layer_output, preds = grad_model(img_array)
if pred_index is None:
pred_index = tf.argmax(preds[0])
class_channel = preds[:, pred_index]
# 这是输出神经元(顶部预测或选择的)
# 相对于最后卷积层输出特征图的梯度
grads = tape.gradient(class_channel, last_conv_layer_output)
# 这是一个向量,其中每个条目是梯度在特定特征图通道上的平均强度
pooled_grads = tf.reduce_mean(grads, axis=(0, 1, 2))
# 我们将特征图数组中的每个通道乘以“该通道相对于顶部预测类的重要性”,
# 然后将所有通道相加以获得热图类激活
last_conv_layer_output = last_conv_layer_output[0]
heatmap = last_conv_layer_output @ pooled_grads[..., tf.newaxis]
heatmap = tf.squeeze(heatmap)
# 出于可视化目的,我们还将热图标准化到 0 到 1 之间
heatmap = tf.maximum(heatmap, 0) / tf.math.reduce_max(heatmap)
return heatmap.numpy()
让我们测试一下
# 准备图像
img_array = preprocess_input(get_img_array(img_path, size=img_size))
# 创建模型
model = model_builder(weights="imagenet")
# 移除最后一层的 softmax
model.layers[-1].activation = None
# 打印顶部预测的类别
preds = model.predict(img_array)
print("预测:", decode_predictions(preds, top=1)[0])
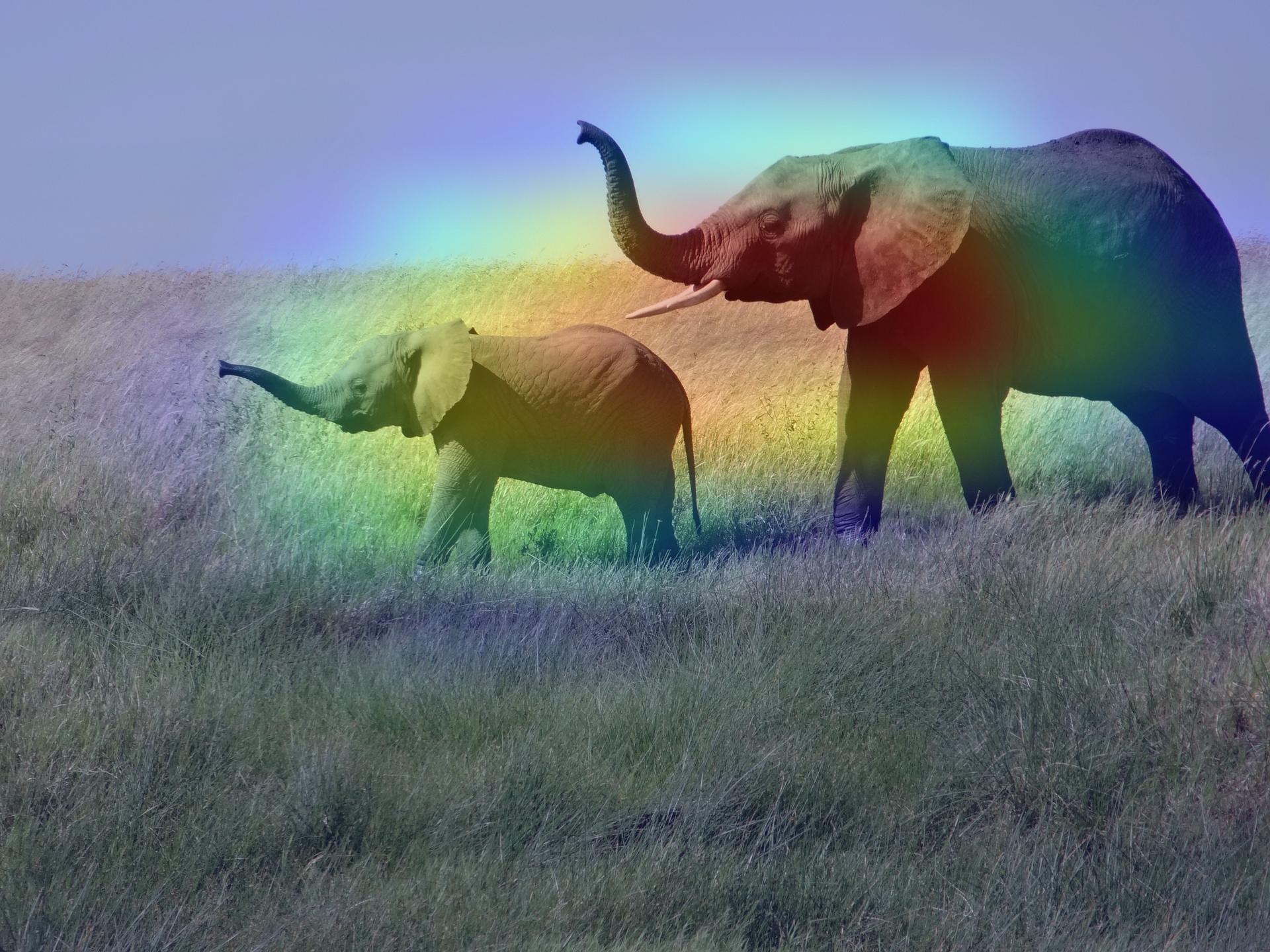
# 生成类激活热图
heatmap = make_gradcam_heatmap(img_array, model, last_conv_layer_name)
# 显示热图
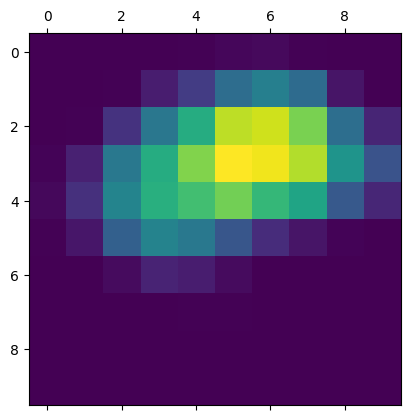
plt.matshow(heatmap)
plt.show()
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 3s 3s/step
预测: [('n02504458', 'African_elephant', 9.860664)]
创建叠加可视化
def save_and_display_gradcam(img_path, heatmap, cam_path="cam.jpg", alpha=0.4):
# 加载原始图像
img = keras.utils.load_img(img_path)
img = keras.utils.img_to_array(img)
# 将热图重新缩放到0-255范围
heatmap = np.uint8(255 * heatmap)
# 使用jet色图为热图上色
jet = mpl.colormaps["jet"]
# 使用色图的RGB值
jet_colors = jet(np.arange(256))[:, :3]
jet_heatmap = jet_colors[heatmap]
# 创建一个带RGB颜色热图的图像
jet_heatmap = keras.utils.array_to_img(jet_heatmap)
jet_heatmap = jet_heatmap.resize((img.shape[1], img.shape[0]))
jet_heatmap = keras.utils.img_to_array(jet_heatmap)
# 将热图叠加在原始图像上
superimposed_img = jet_heatmap * alpha + img
superimposed_img = keras.utils.array_to_img(superimposed_img)
# 保存叠加后的图像
superimposed_img.save(cam_path)
# 显示Grad CAM
display(Image(cam_path))
save_and_display_gradcam(img_path, heatmap)

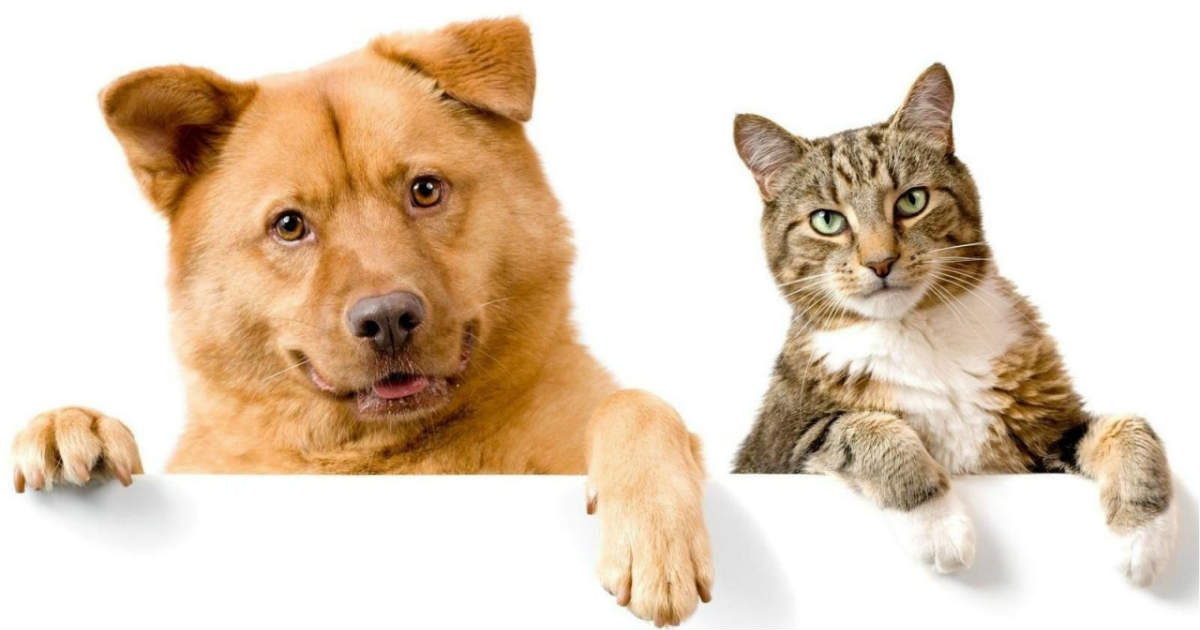
让我们试试另一张图片
我们将查看 Grad CAM 怎样解释模型对一张多标签图像的输出。让我们试一张有猫和狗在一起的图片,看看 Grad CAM 的表现如何。
img_path = keras.utils.get_file(
"cat_and_dog.jpg",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/petbacker/images/blog/2017/dog-and-cat-cover.jpg",
)
display(Image(img_path))
# 准备图像
img_array = preprocess_input(get_img_array(img_path, size=img_size))
# 打印前两个预测的类别
preds = model.predict(img_array)
print("Predicted:", decode_predictions(preds, top=2)[0])

1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 11ms/step
Predicted: [('n02112137', 'chow', 4.610808), ('n02124075', 'Egyptian_cat', 4.3835773)]
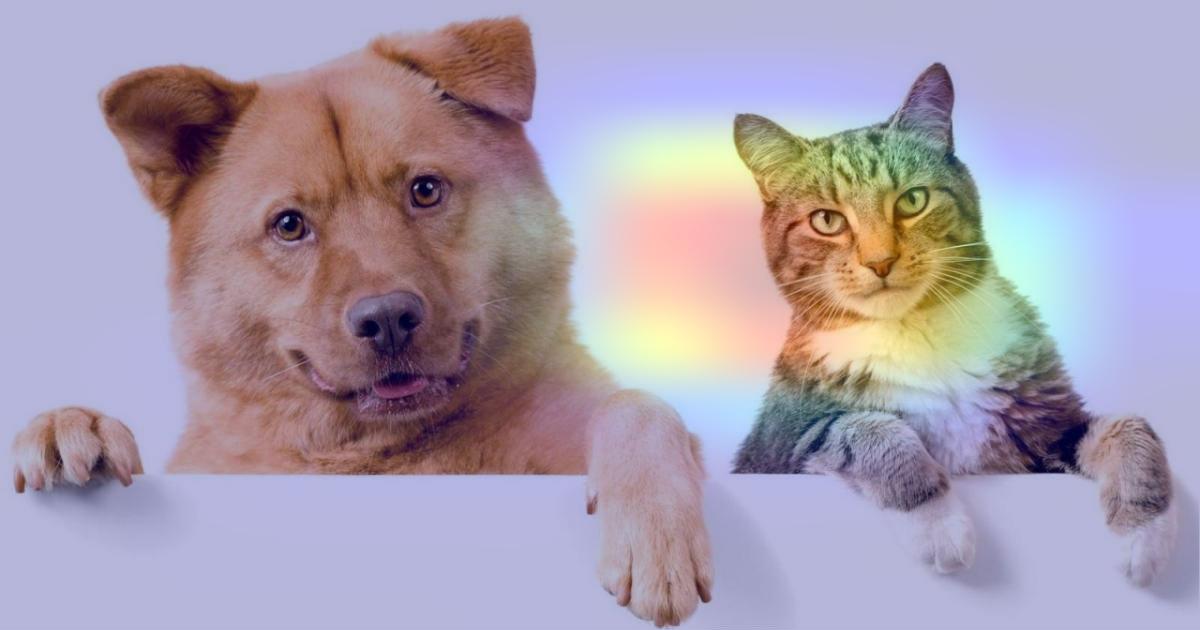
我们为“chow”生成类别激活热图,类别索引为 260
heatmap = make_gradcam_heatmap(img_array, model, last_conv_layer_name, pred_index=260)
save_and_display_gradcam(img_path, heatmap)
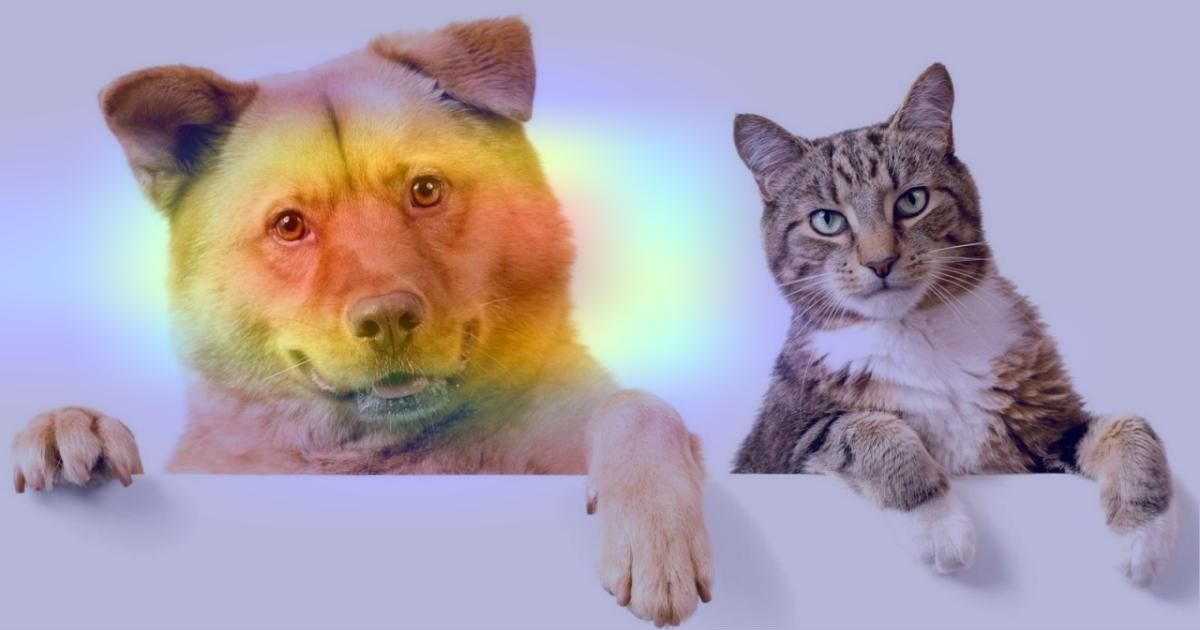

我们为“埃及猫”生成类别激活热图,类别索引为 285
heatmap = make_gradcam_heatmap(img_array, model, last_conv_layer_name, pred_index=285)
save_and_display_gradcam(img_path, heatmap)

