使用RetinaNet进行目标检测
作者: Srihari Humbarwadi
创建日期: 2020/05/17
最后修改日期: 2023/07/10
描述: 实现RetinaNet:用于密集目标检测的焦点损失。
引言
目标检测是计算机视觉中一个非常重要的问题。在这里,模型的任务是定位图像中存在的物体,同时将其分类为不同的类别。目标检测模型可以大致分为“单阶段”和“双阶段”检测器。双阶段检测器通常更准确,但速度较慢。在这个例子中,我们将实现RetinaNet,一种流行的单阶段检测器,它准确且运行快速。RetinaNet使用特征金字塔网络高效地检测多尺度的物体,并引入了一种新的损失,即焦点损失函数,以缓解极端前景-背景类别不平衡的问题。
参考文献:
import os
import re
import zipfile
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
下载COCO2017数据集
在整个COCO2017数据集上训练大约118k张图像需要很多时间,因此我们将在此示例中使用约500张图像的小子集进行训练。
url = "https://github.com/srihari-humbarwadi/datasets/releases/download/v0.1.0/data.zip"
filename = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "data.zip")
keras.utils.get_file(filename, url)
with zipfile.ZipFile("data.zip", "r") as z_fp:
z_fp.extractall("./")
从 https://github.com/srihari-humbarwadi/datasets/releases/download/v0.1.0/data.zip 下载数据
560529408/560525318 [==============================] - 7s 0us/step
560537600/560525318 [==============================] - 7s 0us/step
实现实用函数
边界框可以以多种方式表示,最常见的格式是:
- 存储角落的坐标
[xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax] - 存储中心坐标和框的尺寸
[x, y, width, height]
由于我们需要这两种格式,因此我们将实现转换格式的函数。
def swap_xy(boxes):
"""交换框的x和y坐标的顺序。
参数:
boxes: 形状为`(num_boxes, 4)`的张量,表示边界框。
返回:
交换后的框,形状与输入框相同。
"""
return tf.stack([boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 3], boxes[:, 2]], axis=-1)
def convert_to_xywh(boxes):
"""将框格式更改为中心、宽度和高度。
参数:
boxes: 形状为`(..., num_boxes, 4)`的二维或更高维张量,
表示边界框,每个框的格式为`[xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]`。
返回:
转换后的框,形状与输入框相同。
"""
return tf.concat(
[(boxes[..., :2] + boxes[..., 2:]) / 2.0, boxes[..., 2:] - boxes[..., :2]],
axis=-1,
)
def convert_to_corners(boxes):
"""将框格式更改为角坐标
参数:
boxes: 形状为`(..., num_boxes, 4)`的二维或更高维张量,
表示边界框,每个框的格式为`[x, y, width, height]`。
返回:
转换后的框,形状与输入框相同。
"""
return tf.concat(
[boxes[..., :2] - boxes[..., 2:] / 2.0, boxes[..., :2] + boxes[..., 2:] / 2.0],
axis=-1,
)
计算成对的交并比(IOU)
正如我们在示例中稍后将看到的,我们将根据重叠程度将真实框分配给锚框。这将需要我们计算所有锚框和真实框对之间的交并比(IOU)。
def compute_iou(boxes1, boxes2):
"""计算给定两组框的成对IOU矩阵
参数:
boxes1: 形状为 `(N, 4)` 的张量,表示边界框
每个框的格式为 `[x, y, width, height]`。
boxes2: 形状为 `(M, 4)` 的张量,表示边界框
每个框的格式为 `[x, y, width, height]`。
返回:
形状为 `(N, M)` 的成对IOU矩阵,其中第i行第j列的值表示
boxes1和boxes2中第i个框和第j个框之间的IOU。
"""
boxes1_corners = convert_to_corners(boxes1)
boxes2_corners = convert_to_corners(boxes2)
lu = tf.maximum(boxes1_corners[:, None, :2], boxes2_corners[:, :2])
rd = tf.minimum(boxes1_corners[:, None, 2:], boxes2_corners[:, 2:])
intersection = tf.maximum(0.0, rd - lu)
intersection_area = intersection[:, :, 0] * intersection[:, :, 1]
boxes1_area = boxes1[:, 2] * boxes1[:, 3]
boxes2_area = boxes2[:, 2] * boxes2[:, 3]
union_area = tf.maximum(
boxes1_area[:, None] + boxes2_area - intersection_area, 1e-8
)
return tf.clip_by_value(intersection_area / union_area, 0.0, 1.0)
def visualize_detections(
image, boxes, classes, scores, figsize=(7, 7), linewidth=1, color=[0, 0, 1]
):
"""可视化检测结果"""
image = np.array(image, dtype=np.uint8)
plt.figure(figsize=figsize)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(image)
ax = plt.gca()
for box, _cls, score in zip(boxes, classes, scores):
text = "{}: {:.2f}".format(_cls, score)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
patch = plt.Rectangle(
[x1, y1], w, h, fill=False, edgecolor=color, linewidth=linewidth
)
ax.add_patch(patch)
ax.text(
x1,
y1,
text,
bbox={"facecolor": color, "alpha": 0.4},
clip_box=ax.clipbox,
clip_on=True,
)
plt.show()
return ax
实现锚点生成器
锚框是固定大小的框,模型用它来预测物体的边界框。它通过回归物体中心位置与锚框中心之间的偏移量来完成这项任务,然后使用锚框的宽度和高度来预测物体的相对尺度。在 RetinaNet 中,给定特征图上的每个位置都有九个锚框(在三个尺度和三个比例下)。
class AnchorBox:
"""生成锚框。
该类具有生成特征图在步幅 `[8, 16, 32, 64, 128]` 上的锚框的操作。
每个锚框的格式为 `[x, y, width, height]`。
属性:
aspect_ratios: 表示每个特征图位置上的锚框的宽高比的浮点值列表
scales: 表示每个特征图位置上的锚框的尺度的浮点值列表。
num_anchors: 每个特征图位置上的锚框数量
areas: 表示特征金字塔中每个特征图的锚框面积的浮点值列表。
strides: 表示特征金字塔中每个特征图的步幅的浮点值列表。
"""
def __init__(self):
self.aspect_ratios = [0.5, 1.0, 2.0]
self.scales = [2 ** x for x in [0, 1 / 3, 2 / 3]]
self._num_anchors = len(self.aspect_ratios) * len(self.scales)
self._strides = [2 ** i for i in range(3, 8)]
self._areas = [x ** 2 for x in [32.0, 64.0, 128.0, 256.0, 512.0]]
self._anchor_dims = self._compute_dims()
def _compute_dims(self):
"""计算特征金字塔各级的所有比例和尺度的锚框尺寸。
"""
anchor_dims_all = []
for area in self._areas:
anchor_dims = []
for ratio in self.aspect_ratios:
anchor_height = tf.math.sqrt(area / ratio)
anchor_width = area / anchor_height
dims = tf.reshape(
tf.stack([anchor_width, anchor_height], axis=-1), [1, 1, 2]
)
for scale in self.scales:
anchor_dims.append(scale * dims)
anchor_dims_all.append(tf.stack(anchor_dims, axis=-2))
return anchor_dims_all
def _get_anchors(self, feature_height, feature_width, level):
"""为给定的特征图大小和级别生成锚框
参数:
feature_height: 表示特征图高度的整数。
feature_width: 表示特征图宽度的整数。
level: 表示特征图在特征金字塔中的级别的整数。
返回:
形状为 `(feature_height * feature_width * num_anchors, 4)` 的锚框
"""
rx = tf.range(feature_width, dtype=tf.float32) + 0.5
ry = tf.range(feature_height, dtype=tf.float32) + 0.5
centers = tf.stack(tf.meshgrid(rx, ry), axis=-1) * self._strides[level - 3]
centers = tf.expand_dims(centers, axis=-2)
centers = tf.tile(centers, [1, 1, self._num_anchors, 1])
dims = tf.tile(
self._anchor_dims[level - 3], [feature_height, feature_width, 1, 1]
)
anchors = tf.concat([centers, dims], axis=-1)
return tf.reshape(
anchors, [feature_height * feature_width * self._num_anchors, 4]
)
def get_anchors(self, image_height, image_width):
"""为特征金字塔的所有特征图生成锚框。
参数:
image_height: 输入图像的高度。
image_width: 输入图像的宽度。
返回:
所有特征图的锚框,堆叠为形状为 `(total_anchors, 4)` 的单个张量
"""
anchors = [
self._get_anchors(
tf.math.ceil(image_height / 2 ** i),
tf.math.ceil(image_width / 2 ** i),
i,
)
for i in range(3, 8)
]
return tf.concat(anchors, axis=0)
预处理数据
对图像的预处理包括两个步骤:
- 调整图像大小:图像被调整为最短边为 800 像素,调整后如果图像的最长边超过 1333 像素,则图像会调整为最长边不超过 1333 像素。
- 应用增强:随机缩放抖动和随机水平翻转是对图像应用的唯一增强。
在调整图像的同时,边界框也会在需要时进行重新缩放和翻转。
def random_flip_horizontal(image, boxes):
"""以50%的概率水平翻转图像和框
Arguments:
image: 形状为`(height, width, channels)`的3-D张量,表示一幅图像。
boxes: 形状为`(num_boxes, 4)`的张量,表示边界框,具有规范化坐标。
Returns:
随机翻转的图像和框
"""
if tf.random.uniform(()) > 0.5:
image = tf.image.flip_left_right(image)
boxes = tf.stack(
[1 - boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 1], 1 - boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 3]], axis=-1
)
return image, boxes
def resize_and_pad_image(
image, min_side=800.0, max_side=1333.0, jitter=[640, 1024], stride=128.0
):
"""调整图像大小并填充,同时保持宽高比。
1. 调整图像大小,以使较短的一边等于`min_side`
2. 如果较长的一边大于`max_side`,则调整图像大小,使较长的一边等于`max_side`
3. 在右侧和底部用零填充,使图像的形状可以被`stride`整除
Arguments:
image: 形状为`(height, width, channels)`的3-D张量,表示一幅图像。
min_side: 如果`jitter`设置为None,则图像的较短边调整为此值。
max_side: 如果图像调整大小后较长边超过此值,则图像调整大小,使较长边等于此值。
jitter: 一个包含最小和最大规模抖动大小的浮点列表。如果可用,图像的较短边将被调整为该范围内的随机值。
stride: 特征金字塔中最小特征图的步幅。可以通过`image_size / feature_map_size`计算。
Returns:
image: 调整大小并填充的图像。
image_shape: 填充前图像的形状。
ratio: 用于调整图像大小的缩放因子
"""
image_shape = tf.cast(tf.shape(image)[:2], dtype=tf.float32)
if jitter is not None:
min_side = tf.random.uniform((), jitter[0], jitter[1], dtype=tf.float32)
ratio = min_side / tf.reduce_min(image_shape)
if ratio * tf.reduce_max(image_shape) > max_side:
ratio = max_side / tf.reduce_max(image_shape)
image_shape = ratio * image_shape
image = tf.image.resize(image, tf.cast(image_shape, dtype=tf.int32))
padded_image_shape = tf.cast(
tf.math.ceil(image_shape / stride) * stride, dtype=tf.int32
)
image = tf.image.pad_to_bounding_box(
image, 0, 0, padded_image_shape[0], padded_image_shape[1]
)
return image, image_shape, ratio
def preprocess_data(sample):
"""对单个样本应用预处理步骤
Arguments:
sample: 一个表示单个训练样本的字典。
Returns:
image: 应用随机水平翻转的调整大小和填充的图像。
bbox: 形状为`(num_objects, 4)`的边界框,每个框的格式为`[x, y, width, height]`。
class_id: 一个表示对象类别ID的张量,形状为`(num_objects,)`。
"""
image = sample["image"]
bbox = swap_xy(sample["objects"]["bbox"])
class_id = tf.cast(sample["objects"]["label"], dtype=tf.int32)
image, bbox = random_flip_horizontal(image, bbox)
image, image_shape, _ = resize_and_pad_image(image)
bbox = tf.stack(
[
bbox[:, 0] * image_shape[1],
bbox[:, 1] * image_shape[0],
bbox[:, 2] * image_shape[1],
bbox[:, 3] * image_shape[0],
],
axis=-1,
)
bbox = convert_to_xywh(bbox)
return image, bbox, class_id
编码标签
原始标签,包括边界框和类别 ID,需要转换为训练目标。这个转换过程包括以下步骤:
- 为给定的图像维度生成锚框
- 将真实框分配给锚框
- 没有分配任何对象的锚框,依赖于 IOU 被分配背景类别或者被忽略
- 使用锚框生成分类和回归目标
class LabelEncoder:
"""将原始标签转换为训练目标。
该类具有为一批样本生成目标的操作,这些样本由输入图像、对象的边界框以及它们的类别 ID 组成。
属性:
anchor_box: 用于编码边界框的锚框生成器。
box_variance: 用于缩放边界框目标的缩放因子。
"""
def __init__(self):
self._anchor_box = AnchorBox()
self._box_variance = tf.convert_to_tensor(
[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2], dtype=tf.float32
)
def _match_anchor_boxes(
self, anchor_boxes, gt_boxes, match_iou=0.5, ignore_iou=0.4
):
"""根据 IOU 将真实框与锚框匹配。
1. 计算 M 个 `anchor_boxes` 和 N 个 `gt_boxes` 的成对 IOU
以获取一个形状为 `(M, N)` 的矩阵。
2. 每行中具有最大 IOU 的真实框会分配给锚框,前提是该 IOU 大于 `match_iou`。
3. 如果某行中的最大 IOU 小于 `ignore_iou`,则该锚框将分配为背景类。
4. 其余未分配类别的锚框在训练期间将被忽略。
参数:
anchor_boxes: 形状为 `(total_anchors, 4)` 的浮点张量
表示给定输入图像形状的所有锚框,其中每个锚框的格式为 `[x, y, 宽, 高]`。
gt_boxes: 形状为 `(num_objects, 4)` 的浮点张量表示
真实框,每个框的格式为 `[x, y, 宽, 高]`。
match_iou: 表示确定真实框是否可以分配给锚框的最小 IOU 阈值的浮点值。
ignore_iou: 表示锚框分配为背景类的 IOU 阈值的浮点值。
返回:
matched_gt_idx: 匹配对象的索引
positive_mask: 已分配真实框的锚框的掩码。
ignore_mask: 在训练期间需要被忽略的锚框的掩码
"""
iou_matrix = compute_iou(anchor_boxes, gt_boxes)
max_iou = tf.reduce_max(iou_matrix, axis=1)
matched_gt_idx = tf.argmax(iou_matrix, axis=1)
positive_mask = tf.greater_equal(max_iou, match_iou)
negative_mask = tf.less(max_iou, ignore_iou)
ignore_mask = tf.logical_not(tf.logical_or(positive_mask, negative_mask))
return (
matched_gt_idx,
tf.cast(positive_mask, dtype=tf.float32),
tf.cast(ignore_mask, dtype=tf.float32),
)
def _compute_box_target(self, anchor_boxes, matched_gt_boxes):
"""将真实框转换为训练目标"""
box_target = tf.concat(
[
(matched_gt_boxes[:, :2] - anchor_boxes[:, :2]) / anchor_boxes[:, 2:],
tf.math.log(matched_gt_boxes[:, 2:] / anchor_boxes[:, 2:]),
],
axis=-1,
)
box_target = box_target / self._box_variance
return box_target
def _encode_sample(self, image_shape, gt_boxes, cls_ids):
"""为单个样本创建框和分类目标"""
anchor_boxes = self._anchor_box.get_anchors(image_shape[1], image_shape[2])
cls_ids = tf.cast(cls_ids, dtype=tf.float32)
matched_gt_idx, positive_mask, ignore_mask = self._match_anchor_boxes(
anchor_boxes, gt_boxes
)
matched_gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, matched_gt_idx)
box_target = self._compute_box_target(anchor_boxes, matched_gt_boxes)
matched_gt_cls_ids = tf.gather(cls_ids, matched_gt_idx)
cls_target = tf.where(
tf.not_equal(positive_mask, 1.0), -1.0, matched_gt_cls_ids
)
cls_target = tf.where(tf.equal(ignore_mask, 1.0), -2.0, cls_target)
cls_target = tf.expand_dims(cls_target, axis=-1)
label = tf.concat([box_target, cls_target], axis=-1)
return label
def encode_batch(self, batch_images, gt_boxes, cls_ids):
"""为一批样本创建框和分类目标"""
images_shape = tf.shape(batch_images)
batch_size = images_shape[0]
labels = tf.TensorArray(dtype=tf.float32, size=batch_size, dynamic_size=True)
for i in range(batch_size):
label = self._encode_sample(images_shape, gt_boxes[i], cls_ids[i])
labels = labels.write(i, label)
batch_images = tf.keras.applications.resnet.preprocess_input(batch_images)
return batch_images, labels.stack()
构建 ResNet50 主干
RetinaNet 使用基于 ResNet 的主干,使用此主干构建特征金字塔网络。在示例中,我们使用 ResNet50 作为主干,并返回步幅为 8、16 和 32 的特征图。
def get_backbone():
"""构建带有预训练 imagenet 权重的 ResNet50"""
backbone = keras.applications.ResNet50(
include_top=False, input_shape=[None, None, 3]
)
c3_output, c4_output, c5_output = [
backbone.get_layer(layer_name).output
for layer_name in ["conv3_block4_out", "conv4_block6_out", "conv5_block3_out"]
]
return keras.Model(
inputs=[backbone.inputs], outputs=[c3_output, c4_output, c5_output]
)
将特征金字塔网络构建为自定义层
class FeaturePyramid(keras.layers.Layer):
"""根据主干构建特征金字塔的层。
属性:
num_classes: 数据集中的类别数量。
backbone: 用于构建特征金字塔的主干。
目前仅支持 ResNet50。
"""
def __init__(self, backbone=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(name="FeaturePyramid", **kwargs)
self.backbone = backbone if backbone else get_backbone()
self.conv_c3_1x1 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 1, 1, "same")
self.conv_c4_1x1 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 1, 1, "same")
self.conv_c5_1x1 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 1, 1, "same")
self.conv_c3_3x3 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, 1, "same")
self.conv_c4_3x3 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, 1, "same")
self.conv_c5_3x3 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, 1, "same")
self.conv_c6_3x3 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, 2, "same")
self.conv_c7_3x3 = keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, 2, "same")
self.upsample_2x = keras.layers.UpSampling2D(2)
def call(self, images, training=False):
c3_output, c4_output, c5_output = self.backbone(images, training=training)
p3_output = self.conv_c3_1x1(c3_output)
p4_output = self.conv_c4_1x1(c4_output)
p5_output = self.conv_c5_1x1(c5_output)
p4_output = p4_output + self.upsample_2x(p5_output)
p3_output = p3_output + self.upsample_2x(p4_output)
p3_output = self.conv_c3_3x3(p3_output)
p4_output = self.conv_c4_3x3(p4_output)
p5_output = self.conv_c5_3x3(p5_output)
p6_output = self.conv_c6_3x3(c5_output)
p7_output = self.conv_c7_3x3(tf.nn.relu(p6_output))
return p3_output, p4_output, p5_output, p6_output, p7_output
构建分类和框回归头
RetinaNet 模型具有单独的头部,用于边界框回归和预测物体的类别概率。这些头部在特征金字塔的所有特征图之间共享。
def build_head(output_filters, bias_init):
"""构建类/框预测头。
参数:
output_filters: 最后一层中的卷积滤波器数量。
bias_init: 最后一个卷积层的偏置初始化器。
返回:
一个代表分类或框回归头的 keras 顺序模型,具体取决于 `output_filters`。
"""
head = keras.Sequential([keras.Input(shape=[None, None, 256])])
kernel_init = tf.initializers.RandomNormal(0.0, 0.01)
for _ in range(4):
head.add(
keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding="same", kernel_initializer=kernel_init)
)
head.add(keras.layers.ReLU())
head.add(
keras.layers.Conv2D(
output_filters,
3,
1,
padding="same",
kernel_initializer=kernel_init,
bias_initializer=bias_init,
)
)
return head
使用子类模型构建 RetinaNet
class RetinaNet(keras.Model):
"""一个子类化的Keras模型,实现了RetinaNet架构。
Attributes:
num_classes: 数据集中类的数量。
backbone: 用于构建特征金字塔的主干网络。
当前仅支持ResNet50。
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes, backbone=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(name="RetinaNet", **kwargs)
self.fpn = FeaturePyramid(backbone)
self.num_classes = num_classes
prior_probability = tf.constant_initializer(-np.log((1 - 0.01) / 0.01))
self.cls_head = build_head(9 * num_classes, prior_probability)
self.box_head = build_head(9 * 4, "zeros")
def call(self, image, training=False):
features = self.fpn(image, training=training)
N = tf.shape(image)[0]
cls_outputs = []
box_outputs = []
for feature in features:
box_outputs.append(tf.reshape(self.box_head(feature), [N, -1, 4]))
cls_outputs.append(
tf.reshape(self.cls_head(feature), [N, -1, self.num_classes])
)
cls_outputs = tf.concat(cls_outputs, axis=1)
box_outputs = tf.concat(box_outputs, axis=1)
return tf.concat([box_outputs, cls_outputs], axis=-1)
实现自定义层以解码预测结果
class DecodePredictions(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
"""一个解码 RetinaNet 模型预测结果的 Keras 层。
Attributes:
num_classes: 数据集中的类别数量
confidence_threshold: 最小类别概率,低于该值的检测
将被修剪。
nms_iou_threshold: NMS 操作的 IOU 阈值
max_detections_per_class: 每个类别保留的最大检测数量。
max_detections: 所有类别中保留的最大检测数量。
box_variance: 用于缩放边界框预测的缩放因子。
"""
def __init__(
self,
num_classes=80,
confidence_threshold=0.05,
nms_iou_threshold=0.5,
max_detections_per_class=100,
max_detections=100,
box_variance=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],
**kwargs
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.confidence_threshold = confidence_threshold
self.nms_iou_threshold = nms_iou_threshold
self.max_detections_per_class = max_detections_per_class
self.max_detections = max_detections
self._anchor_box = AnchorBox()
self._box_variance = tf.convert_to_tensor(
[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2], dtype=tf.float32
)
def _decode_box_predictions(self, anchor_boxes, box_predictions):
boxes = box_predictions * self._box_variance
boxes = tf.concat(
[
boxes[:, :, :2] * anchor_boxes[:, :, 2:] + anchor_boxes[:, :, :2],
tf.math.exp(boxes[:, :, 2:]) * anchor_boxes[:, :, 2:],
],
axis=-1,
)
boxes_transformed = convert_to_corners(boxes)
return boxes_transformed
def call(self, images, predictions):
image_shape = tf.cast(tf.shape(images), dtype=tf.float32)
anchor_boxes = self._anchor_box.get_anchors(image_shape[1], image_shape[2])
box_predictions = predictions[:, :, :4]
cls_predictions = tf.nn.sigmoid(predictions[:, :, 4:])
boxes = self._decode_box_predictions(anchor_boxes[None, ...], box_predictions)
return tf.image.combined_non_max_suppression(
tf.expand_dims(boxes, axis=2),
cls_predictions,
self.max_detections_per_class,
self.max_detections,
self.nms_iou_threshold,
self.confidence_threshold,
clip_boxes=False,
)
实现 Smooth L1 损失和 Focal 损失作为 Keras 自定义损失函数
class RetinaNetBoxLoss(tf.losses.Loss):
"""Implements Smooth L1 loss"""
def __init__(self, delta):
super().__init__(
reduction="none", name="RetinaNetBoxLoss"
)
self._delta = delta
def call(self, y_true, y_pred):
difference = y_true - y_pred
absolute_difference = tf.abs(difference)
squared_difference = difference ** 2
loss = tf.where(
tf.less(absolute_difference, self._delta),
0.5 * squared_difference,
absolute_difference - 0.5,
)
return tf.reduce_sum(loss, axis=-1)
class RetinaNetClassificationLoss(tf.losses.Loss):
"""Implements Focal loss"""
def __init__(self, alpha, gamma):
super().__init__(
reduction="none", name="RetinaNetClassificationLoss"
)
self._alpha = alpha
self._gamma = gamma
def call(self, y_true, y_pred):
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=y_true, logits=y_pred
)
probs = tf.nn.sigmoid(y_pred)
alpha = tf.where(tf.equal(y_true, 1.0), self._alpha, (1.0 - self._alpha))
pt = tf.where(tf.equal(y_true, 1.0), probs, 1 - probs)
loss = alpha * tf.pow(1.0 - pt, self._gamma) * cross_entropy
return tf.reduce_sum(loss, axis=-1)
class RetinaNetLoss(tf.losses.Loss):
"""Wrapper to combine both the losses"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=80, alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0, delta=1.0):
super().__init__(reduction="auto", name="RetinaNetLoss")
self._clf_loss = RetinaNetClassificationLoss(alpha, gamma)
self._box_loss = RetinaNetBoxLoss(delta)
self._num_classes = num_classes
def call(self, y_true, y_pred):
y_pred = tf.cast(y_pred, dtype=tf.float32)
box_labels = y_true[:, :, :4]
box_predictions = y_pred[:, :, :4]
cls_labels = tf.one_hot(
tf.cast(y_true[:, :, 4], dtype=tf.int32),
depth=self._num_classes,
dtype=tf.float32,
)
cls_predictions = y_pred[:, :, 4:]
positive_mask = tf.cast(tf.greater(y_true[:, :, 4], -1.0), dtype=tf.float32)
ignore_mask = tf.cast(tf.equal(y_true[:, :, 4], -2.0), dtype=tf.float32)
clf_loss = self._clf_loss(cls_labels, cls_predictions)
box_loss = self._box_loss(box_labels, box_predictions)
clf_loss = tf.where(tf.equal(ignore_mask, 1.0), 0.0, clf_loss)
box_loss = tf.where(tf.equal(positive_mask, 1.0), box_loss, 0.0)
normalizer = tf.reduce_sum(positive_mask, axis=-1)
clf_loss = tf.math.divide_no_nan(tf.reduce_sum(clf_loss, axis=-1), normalizer)
box_loss = tf.math.divide_no_nan(tf.reduce_sum(box_loss, axis=-1), normalizer)
loss = clf_loss + box_loss
return loss
设置训练参数
model_dir = "retinanet/"
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
num_classes = 80
batch_size = 2
learning_rates = [2.5e-06, 0.000625, 0.00125, 0.0025, 0.00025, 2.5e-05]
learning_rate_boundaries = [125, 250, 500, 240000, 360000]
learning_rate_fn = tf.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries=learning_rate_boundaries, values=learning_rates
)
初始化并编译模型
resnet50_backbone = get_backbone()
loss_fn = RetinaNetLoss(num_classes)
model = RetinaNet(num_classes, resnet50_backbone)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.legacy.SGD(learning_rate=learning_rate_fn, momentum=0.9)
model.compile(loss=loss_fn, optimizer=optimizer)
从 https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/keras-applications/resnet/resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5 下载数据
94773248/94765736 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
94781440/94765736 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
设置回调
callbacks_list = [
tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath=os.path.join(model_dir, "weights" + "_epoch_{epoch}"),
monitor="loss",
save_best_only=False,
save_weights_only=True,
verbose=1,
)
]
使用 TensorFlow 数据集加载 COCO2017 数据集
# 设置 `data_dir=None` 以加载完整数据集
(train_dataset, val_dataset), dataset_info = tfds.load(
"coco/2017", split=["train", "validation"], with_info=True, data_dir="data"
)
设置 tf.data 管道
为了确保模型高效地获取数据,我们将使用
tf.data API 创建输入管道。输入管道
由以下主要处理步骤组成:
- 将预处理函数应用于样本
- 创建固定批次大小的批次。由于批次中的图像可以
具有不同的维度,并且可以有不同数量的
对象,我们使用
padded_batch来添加必要的填充以创建 矩形张量 - 使用
LabelEncoder为每个批次中的样本创建目标
autotune = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(preprocess_data, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(8 * batch_size)
train_dataset = train_dataset.padded_batch(
batch_size=batch_size, padding_values=(0.0, 1e-8, -1), drop_remainder=True
)
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(
label_encoder.encode_batch, num_parallel_calls=autotune
)
train_dataset = train_dataset.apply(tf.data.experimental.ignore_errors())
train_dataset = train_dataset.prefetch(autotune)
val_dataset = val_dataset.map(preprocess_data, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
val_dataset = val_dataset.padded_batch(
batch_size=1, padding_values=(0.0, 1e-8, -1), drop_remainder=True
)
val_dataset = val_dataset.map(label_encoder.encode_batch, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
val_dataset = val_dataset.apply(tf.data.experimental.ignore_errors())
val_dataset = val_dataset.prefetch(autotune)
训练模型
# 在全数据集上训练时取消注释以下行
# train_steps_per_epoch = dataset_info.splits["train"].num_examples // batch_size
# val_steps_per_epoch = \
# dataset_info.splits["validation"].num_examples // batch_size
# train_steps = 4 * 100000
# epochs = train_steps // train_steps_per_epoch
epochs = 1
# 运行 100 个训练和 50 个验证步骤,
# 在全数据集上训练时移除 `.take`
model.fit(
train_dataset.take(100),
validation_data=val_dataset.take(50),
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=callbacks_list,
verbose=1,
)
100/未知 - 290s 3s/步 - loss: 4.0817
第 1 轮:将模型保存到 retinanet/weights_epoch_1
100/100 [==============================] - 336s 3s/步 - loss: 4.0817 - val_loss: 4.1082
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f4c7e0428d0>
加载权重
# 在不使用下载权重时将此更改为 `model_dir`
weights_dir = "data"
latest_checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(weights_dir)
model.load_weights(latest_checkpoint)
<tensorflow.python.training.tracking.util.CheckpointLoadStatus at 0x7f4c6823d0d0>
构建推理模型
image = tf.keras.Input(shape=[None, None, 3], name="image")
predictions = model(image, training=False)
detections = DecodePredictions(confidence_threshold=0.5)(image, predictions)
inference_model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=image, outputs=detections)
生成检测结果
def prepare_image(image):
image, _, ratio = resize_and_pad_image(image, jitter=None)
image = tf.keras.applications.resnet.preprocess_input(image)
return tf.expand_dims(image, axis=0), ratio
val_dataset = tfds.load("coco/2017", split="validation", data_dir="data")
int2str = dataset_info.features["objects"]["label"].int2str
for sample in val_dataset.take(2):
image = tf.cast(sample["image"], dtype=tf.float32)
input_image, ratio = prepare_image(image)
detections = inference_model.predict(input_image)
num_detections = detections.valid_detections[0]
class_names = [
int2str(int(x)) for x in detections.nmsed_classes[0][:num_detections]
]
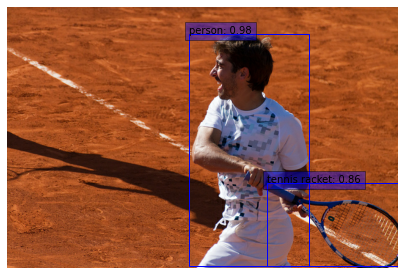
visualize_detections(
image,
detections.nmsed_boxes[0][:num_detections] / ratio,
class_names,
detections.nmsed_scores[0][:num_detections],
)

示例可在 HuggingFace 上获得。
| 训练模型 | 演示 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
