使用对比损失的联结网络进行图像相似度估计
作者: Mehdi
创建日期: 2021/05/06
最后修改: 2022/09/10
描述: 使用训练有素的联结网络进行相似性学习,采用对比损失。
介绍
联结网络是共享权重的神经网络,通常由两个或多个姊妹网络组成,每个网络生成其各自输入的嵌入向量。
在监督相似性学习中,网络的训练目的是最大化不同类别输入嵌入之间的对比(距离),同时最小化相似类别嵌入之间的距离,从而生成反映训练输入类别分割的嵌入空间。
设置
import random
import numpy as np
import keras
from keras import ops
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
超参数
epochs = 10
batch_size = 16
margin = 1 # 对比损失的边际。
加载 MNIST 数据集
(x_train_val, y_train_val), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
# 将数据类型更改为浮点格式
x_train_val = x_train_val.astype("float32")
x_test = x_test.astype("float32")
定义训练和验证集
# 保留 50% 的训练集作为验证集
x_train, x_val = x_train_val[:30000], x_train_val[30000:]
y_train, y_val = y_train_val[:30000], y_train_val[30000:]
del x_train_val, y_train_val
创建图像对
我们将训练模型区分不同类别的数字。例如,数字 0 需要与其他数字(1 到 9)区分开,数字 1 需要与 0 和 2 到 9 区分,依此类推。为了实现这一点,我们将从类别 A(例如,数字 0)中随机选择 N 张图像,并与类别 B(例如,数字 1)中的 N 张随机图像配对。然后,我们可以对所有数字类别(直到数字 9)重复此过程。一旦我们将数字 0 与其他数字配对,我们就可以对剩余数字(从 1 到 9)进行相同的操作。
def make_pairs(x, y):
"""创建一个包含图像对及其对应标签的元组。
参数:
x: 包含图像的列表,每个索引对应一张图像。
y: 包含标签的列表,每个标签的数据类型为 `int`。
返回:
包含两个 numpy 数组的元组 (pairs_of_samples, labels),
其中 pairs_of_samples 的形状为 (2len(x), 2,n_features_dims),
labels 是形状为 (2len(x)) 的二进制数组。
"""
num_classes = max(y) + 1
digit_indices = [np.where(y == i)[0] for i in range(num_classes)]
pairs = []
labels = []
for idx1 in range(len(x)):
# 添加一个匹配的示例
x1 = x[idx1]
label1 = y[idx1]
idx2 = random.choice(digit_indices[label1])
x2 = x[idx2]
pairs += [[x1, x2]]
labels += [0]
# 添加一个不匹配的示例
label2 = random.randint(0, num_classes - 1)
while label2 == label1:
label2 = random.randint(0, num_classes - 1)
idx2 = random.choice(digit_indices[label2])
x2 = x[idx2]
pairs += [[x1, x2]]
labels += [1]
return np.array(pairs), np.array(labels).astype("float32")
# 创建训练对
pairs_train, labels_train = make_pairs(x_train, y_train)
# 创建验证对
pairs_val, labels_val = make_pairs(x_val, y_val)
# 创建测试对
pairs_test, labels_test = make_pairs(x_test, y_test)
我们得到:
pairs_train.shape = (60000, 2, 28, 28)
- 我们有 60,000 对
- 每对包含 2 张图像
- 每张图像的形状为
(28, 28)
拆分训练对
x_train_1 = pairs_train[:, 0] # x_train_1.shape 是 (60000, 28, 28)
x_train_2 = pairs_train[:, 1]
拆分验证对
x_val_1 = pairs_val[:, 0] # x_val_1.shape = (60000, 28, 28)
x_val_2 = pairs_val[:, 1]
拆分测试对
x_test_1 = pairs_test[:, 0] # x_test_1.shape = (20000, 28, 28)
x_test_2 = pairs_test[:, 1]
可视化对及其标签
def visualize(pairs, labels, to_show=6, num_col=3, predictions=None, test=False):
"""创建一个对偶和标签的图,并在其是测试数据集时显示预测。
参数:
pairs: Numpy Array,待可视化的对偶数组,形状为
(对偶的数量, 2, 28, 28)。
to_show: 整数,待可视化的示例数量(默认为6)
`to_show` 必须是 `num_col` 的整数倍。
否则如果大于 num_col 则会被截短,
如果小于 num_col 则会增加。
num_col: 整数,一行中的图像数量 - (默认为3)
对于测试和训练,分别不应超过 3 和 7。
predictions: 形状为 (to_show, 1) 的 Numpy Array 预测 -
(默认为 None)
当 test=True 时必须传入。
test: 布尔值,指示可视化的数据集是
训练数据集还是测试数据集 - (默认为 False)。
返回:
无。
"""
# 定义 num_row
# 如果 to_show % num_col != 0
# 截短 to_show,
# 将 to_show 截短到 num_row 的限制点,以使
# to_show % num_col == 0
#
# 如果 to_show//num_col == 0
# 那么它表示 num_col 大于 to_show
# 增加 to_show
# 增加 to_show 将 num_row 设置为 1
num_row = to_show // num_col if to_show // num_col != 0 else 1
# `to_show` 必须是 `num_col` 的整数倍
# 我们找到了 num_row 并且有 num_col
# 增加或减少 to_show
# 使之成为 `num_col` 的整数倍
# 只需将其设置为 num_row * num_col
to_show = num_row * num_col
# 绘制图像
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_row, num_col, figsize=(5, 5))
for i in range(to_show):
# 如果行数为 1,则 axes 数组是一维的
if num_row == 1:
ax = axes[i % num_col]
else:
ax = axes[i // num_col, i % num_col]
ax.imshow(ops.concatenate([pairs[i][0], pairs[i][1]], axis=1), cmap="gray")
ax.set_axis_off()
if test:
ax.set_title("真实: {} | 预测: {:.5f}".format(labels[i], predictions[i][0]))
else:
ax.set_title("标签: {}".format(labels[i]))
if test:
plt.tight_layout(rect=(0, 0, 1.9, 1.9), w_pad=0.0)
else:
plt.tight_layout(rect=(0, 0, 1.5, 1.5))
plt.show()
Inspect training pairs
visualize(pairs_train[:-1], labels_train[:-1], to_show=4, num_col=4)
Inspect validation pairs
visualize(pairs_val[:-1], labels_val[:-1], to_show=4, num_col=4)
Inspect test pairs
visualize(pairs_test[:-1], labels_test[:-1], to_show=4, num_col=4)
定义模型
有两个输入层,各自连接到自己的网络,生成嵌入。然后一个Lambda层使用欧几里得距离合并它们,合并后的输出被送入最终网络。
# 提供两个张量 t1 和 t2
# 欧几里得距离 = sqrt(sum(square(t1-t2)))
def euclidean_distance(vects):
"""查找两个向量之间的欧几里得距离。
参数:
vects: 包含两个相同长度张量的列表。
返回:
包含两个向量之间的欧几里得距离的张量
(作为浮点值)。
"""
x, y = vects
sum_square = ops.sum(ops.square(x - y), axis=1, keepdims=True)
return ops.sqrt(ops.maximum(sum_square, keras.backend.epsilon()))
input = keras.layers.Input((28, 28, 1))
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(input)
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(4, (5, 5), activation="tanh")(x)
x = keras.layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
x = keras.layers.Conv2D(16, (5, 5), activation="tanh")(x)
x = keras.layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
x = keras.layers.Flatten()(x)
x = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="tanh")(x)
embedding_network = keras.Model(input, x)
input_1 = keras.layers.Input((28, 28, 1))
input_2 = keras.layers.Input((28, 28, 1))
# 如上所述,连体网络在
# 塔式网络(姐妹网络)之间共享权重。为此,我们将使用
# 相同的嵌入网络来构建两个塔式网络。
tower_1 = embedding_network(input_1)
tower_2 = embedding_network(input_2)
merge_layer = keras.layers.Lambda(euclidean_distance, output_shape=(1,))(
[tower_1, tower_2]
)
normal_layer = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(merge_layer)
output_layer = keras.layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(normal_layer)
siamese = keras.Model(inputs=[input_1, input_2], outputs=output_layer)
定义对比损失
def loss(margin=1):
"""提供'contrastive_loss'一个包裹范围和变量'margin'。
参数:
margin: 整数,定义距离的基线,成对
应被分类为不相似的。-(默认值为1)。
返回:
附带数据('margin')的'contrastive_loss'函数。
"""
# 对比损失 = mean( (1-true_value) * square(prediction) +
# true_value * square( max(margin-prediction, 0) ))
def contrastive_loss(y_true, y_pred):
"""计算对比损失。
参数:
y_true: 标签列表,每个标签类型为float32。
y_pred: 与y_true长度相同的预测列表,
每个标签类型为float32。
返回:
包含对比损失作为浮点值的张量。
"""
square_pred = ops.square(y_pred)
margin_square = ops.square(ops.maximum(margin - (y_pred), 0))
return ops.mean((1 - y_true) * square_pred + (y_true) * margin_square)
return contrastive_loss
使用对比损失编译模型
siamese.compile(loss=loss(margin=margin), optimizer="RMSprop", metrics=["accuracy"])
siamese.summary()
模型: "functional_3"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ 层 (类型) ┃ 输出形状 ┃ 参数 # ┃ 连接到 ┃ ┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩ │ input_layer_1 │ (None, 28, 28, 1) │ 0 │ - │ │ (InputLayer) │ │ │ │ ├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼─────────┼──────────────────────┤ │ input_layer_2 │ (None, 28, 28, 1) │ 0 │ - │ │ (InputLayer) │ │ │ │ ├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼─────────┼──────────────────────┤ │ functional_1 │ (None, 10) │ 5,318 │ input_layer_1[0][0], │ │ (Functional) │ │ │ input_layer_2[0][0] │ ├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼─────────┼──────────────────────┤ │ lambda (Lambda) │ (None, 1) │ 0 │ functional_1[0][0], │ │ │ │ │ functional_1[1][0] │ ├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼─────────┼──────────────────────┤ │ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 1) │ 4 │ lambda[0][0] │ │ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │ ├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼─────────┼──────────────────────┤ │ dense_1 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 2 │ batch_normalization… │ └─────────────────────┴───────────────────┴─────────┴──────────────────────┘
总参数: 5,324 (20.80 KB)
可训练参数: 4,808 (18.78 KB)
不可训练参数: 516 (2.02 KB)
训练模型
history = siamese.fit(
[x_train_1, x_train_2],
labels_train,
validation_data=([x_val_1, x_val_2], labels_val),
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
)
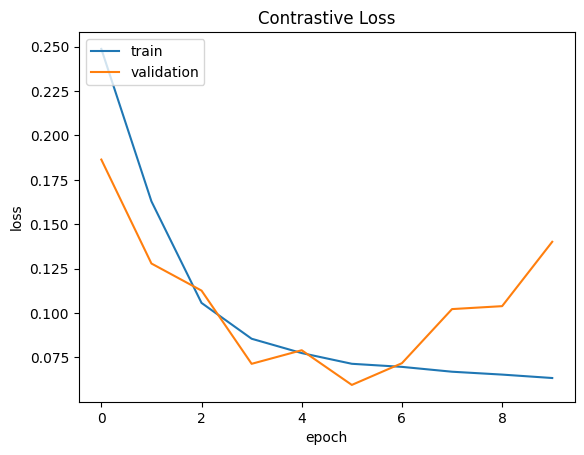
纪元 1/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 16s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.4802 - 损失: 0.2768 - 验证准确率: 0.7363 - 验证损失: 0.1864
纪元 2/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.7368 - 损失: 0.1827 - 验证准确率: 0.8193 - 验证损失: 0.1279
纪元 3/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.8480 - 损失: 0.1117 - 验证准确率: 0.8420 - 验证损失: 0.1126
纪元 4/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.8834 - 损失: 0.0871 - 验证准确率: 0.9037 - 验证损失: 0.0714
纪元 5/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.8932 - 损失: 0.0797 - 验证准确率: 0.8952 - 验证损失: 0.0791
纪元 6/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.9047 - 损失: 0.0721 - 验证准确率: 0.9223 - 验证损失: 0.0595
纪元 7/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.9070 - 损失: 0.0704 - 验证准确率: 0.9032 - 验证损失: 0.0718
纪元 8/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.9122 - 损失: 0.0680 - 验证准确率: 0.8615 - 验证损失: 0.1022
纪元 9/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.9132 - 损失: 0.0664 - 验证准确率: 0.8630 - 验证损失: 0.1039
纪元 10/10
3750/3750 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 3ms/step - 准确率: 0.9187 - 损失: 0.0621 - 验证准确率: 0.8117 - 验证损失: 0.1401
可视化结果
def plt_metric(history, metric, title, has_valid=True):
"""绘制 'history' 中给定的 'metric'。
参数:
history: 从 Model.fit 返回的 History 对象的 history 属性。
metric: 要绘制的度量,'history' 中的字符串值作为键出现。
title: 用作图表标题的字符串。
has_valid: 布尔值,如果有效数据传递给 Model.fit 则为真,否则为假。
返回:
无。
"""
plt.plot(history[metric])
if has_valid:
plt.plot(history["val_" + metric])
plt.legend(["训练", "验证"], loc="upper left")
plt.title(title)
plt.ylabel(metric)
plt.xlabel("纪元")
plt.show()
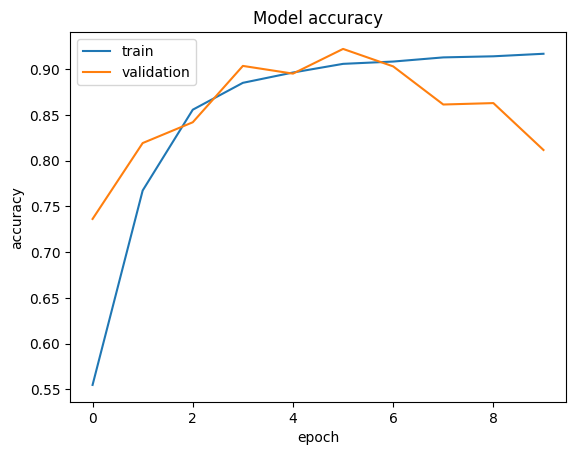
# 绘制准确率
plt_metric(history=history.history, metric="accuracy", title="模型准确率")
# 绘制对比损失
plt_metric(history=history.history, metric="loss", title="对比损失")
评估模型
results = siamese.evaluate([x_test_1, x_test_2], labels_test)
print("测试损失,测试准确率:", results)
625/625 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 1ms/step - 准确率: 0.8068 - 损失: 0.1439
测试损失,测试准确率: [0.13836927711963654, 0.8143500089645386]
可视化预测结果
predictions = siamese.predict([x_test_1, x_test_2])
visualize(pairs_test, labels_test, to_show=3, predictions=predictions, test=True)
625/625 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 619us/step

