示例¶
特色教程¶
PyOD 已经得到了机器学习社区的广泛认可,有几篇特色文章和教程。
Analytics Vidhya: 一个使用PyOD库在Python中学习异常检测的精彩教程
KDnuggets: 异常检测方法的直观可视化
数据科学之路: 傻瓜也能懂的异常检测
awesome-machine-learning: 通用机器学习
kNN 示例¶
完整示例: knn_example.py
导入模型
from pyod.models.knn import KNN # kNN detector
使用
pyod.utils.data.generate_data()生成样本数据:contamination = 0.1 # percentage of outliers n_train = 200 # number of training points n_test = 100 # number of testing points X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = generate_data( n_train=n_train, n_test=n_test, contamination=contamination)
初始化一个
pyod.models.knn.KNN检测器,拟合模型,并进行预测。# train kNN detector clf_name = 'KNN' clf = KNN() clf.fit(X_train) # get the prediction labels and outlier scores of the training data y_train_pred = clf.labels_ # binary labels (0: inliers, 1: outliers) y_train_scores = clf.decision_scores_ # raw outlier scores # get the prediction on the test data y_test_pred = clf.predict(X_test) # outlier labels (0 or 1) y_test_scores = clf.decision_function(X_test) # outlier scores # it is possible to get the prediction confidence as well y_test_pred, y_test_pred_confidence = clf.predict(X_test, return_confidence=True) # outlier labels (0 or 1) and confidence in the range of [0,1]
使用 ROC 和 Precision @ Rank n 评估预测
pyod.utils.data.evaluate_print()。from pyod.utils.data import evaluate_print # evaluate and print the results print("\nOn Training Data:") evaluate_print(clf_name, y_train, y_train_scores) print("\nOn Test Data:") evaluate_print(clf_name, y_test, y_test_scores)
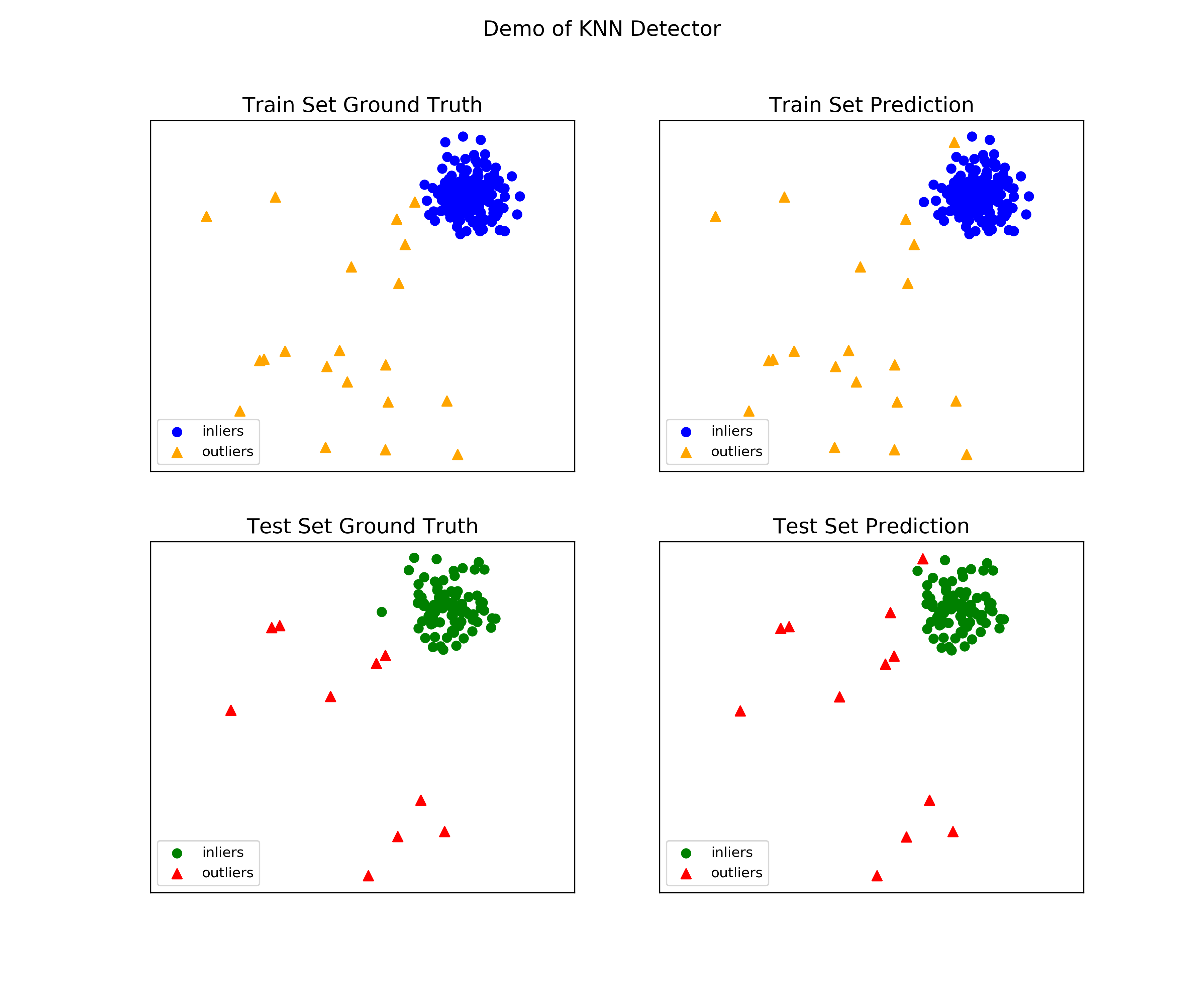
查看训练和测试数据上的样本输出。
On Training Data: KNN ROC:1.0, precision @ rank n:1.0 On Test Data: KNN ROC:0.9989, precision @ rank n:0.9
通过所有示例中包含的 visualize 函数生成可视化。
visualize(clf_name, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, y_train_pred, y_test_pred, show_figure=True, save_figure=False)
模型组合示例¶
由于其无监督的特性,异常检测常常受到模型不稳定性的影响。因此,建议通过平均等方式结合多种检测器的输出,以提高其鲁棒性。检测器组合是异常检测集成的一个子领域;更多信息请参考 [BKalayciE18]。
本演示展示了四种得分组合机制:
平均值: 所有检测器的平均分数。
最大化:所有检测器中的最高分数。
最大值的平均值 (AOM):将基础检测器分成子组,并为每个子组取最大分数。最终分数是所有子组分数的平均值。
最大平均值 (MOA):将基础检测器分成子组,并对每个子组取平均分。最终得分是所有子组得分的最大值。
“examples/comb_example.py” 展示了组合多个基础检测器输出的API(comb_example.py, Jupyter Notebooks)。对于Jupyter Notebooks,请导航至 “/notebooks/Model Combination.ipynb”
导入模型并生成示例数据。
from pyod.models.knn import KNN # kNN detector from pyod.models.combination import aom, moa, average, maximization from pyod.utils.data import generate_data X, y= generate_data(train_only=True) # load data
初始化20个不同的k(从10到200)的kNN异常检测器,并获取异常分数。
# initialize 20 base detectors for combination k_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200] n_clf = len(k_list) # Number of classifiers being trained train_scores = np.zeros([X_train.shape[0], n_clf]) test_scores = np.zeros([X_test.shape[0], n_clf]) for i in range(n_clf): k = k_list[i] clf = KNN(n_neighbors=k, method='largest') clf.fit(X_train_norm) train_scores[:, i] = clf.decision_scores_ test_scores[:, i] = clf.decision_function(X_test_norm)
然后,输出分数在组合之前被标准化为零平均值和单位标准差。这一步对于将检测器输出调整为相同尺度至关重要。
from pyod.utils.utility import standardizer # scores have to be normalized before combination train_scores_norm, test_scores_norm = standardizer(train_scores, test_scores)
如上所述,应用了四种不同的组合算法:
comb_by_average = average(test_scores_norm) comb_by_maximization = maximization(test_scores_norm) comb_by_aom = aom(test_scores_norm, 5) # 5 groups comb_by_moa = moa(test_scores_norm, 5) # 5 groups
最后,所有四种组合方法都通过ROC和Precision @ Rank n进行评估:
Combining 20 kNN detectors Combination by Average ROC:0.9194, precision @ rank n:0.4531 Combination by Maximization ROC:0.9198, precision @ rank n:0.4688 Combination by AOM ROC:0.9257, precision @ rank n:0.4844 Combination by MOA ROC:0.9263, precision @ rank n:0.4688
阈值化示例¶
完整示例:threshold_example.py
导入模型
from pyod.models.knn import KNN # kNN detector from pyod.models.thresholds import FILTER # Filter thresholder
使用
pyod.utils.data.generate_data()生成样本数据:contamination = 0.1 # percentage of outliers n_train = 200 # number of training points n_test = 100 # number of testing points X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = generate_data( n_train=n_train, n_test=n_test, contamination=contamination)
初始化一个
pyod.models.knn.KNN检测器,拟合模型,并进行预测。# train kNN detector and apply FILTER thresholding clf_name = 'KNN' clf = KNN(contamination=FILTER()) clf.fit(X_train) # get the prediction labels and outlier scores of the training data y_train_pred = clf.labels_ # binary labels (0: inliers, 1: outliers) y_train_scores = clf.decision_scores_ # raw outlier scores
参考文献