从函数构建管道
pipeline_from_functions.py 示例脚本展示了如何使用PipelineController 类创建管道。
这个示例创建了一个包含四个任务的管道,其中三个任务是从一个函数创建的:
step_one- Download and process data.step_two- 进一步处理来自step_one的数据。step_three- 使用来自step_two的处理数据来训练模型。
第四个任务是管道任务,它在管道启动时创建。
当步骤函数被添加到管道控制器时,它们将被注册为管道步骤。
当管道步骤被执行时,相应的ClearML任务会被创建。请注意,函数内部的所有包导入将自动记录为管道执行步骤所需的包。
管道控制器
-
创建 PipelineController 对象:
pipe = PipelineController(
name='pipeline demo',
project='examples',
version='0.0.1',
add_pipeline_tags=False,
) -
设置一个执行队列,未明确指定执行队列的流水线步骤将通过该队列执行。这些流水线步骤将被排队在此队列中执行。
pipe.set_default_execution_queue('default') -
添加一个可以在管道中任何步骤引用的管道级别参数(参见下面的
step_one)。pipe.add_parameter(
name='url',
description='url to pickle file',
default='https://github.com/allegroai/events/raw/master/odsc20-east/generic/iris_dataset.pkl'
) -
构建管道(请参阅
PipelineController.add_function_step以获取完整参考)。管道中的第一步使用
step_one函数,并使用上面定义的管道级别参数作为其输入。其返回对象将作为名为data_frame的工件存储。pipe.add_function_step(
name='step_one',
function=step_one,
function_kwargs=dict(pickle_data_url='${pipeline.url}'),
function_return=['data_frame'],
cache_executed_step=True,
)管道中的第二步使用
step_two函数,并将第一步的输出作为其输入。这个引用隐式地定义了管道的结构,使step_one成为step_two的父步骤。它的返回对象将作为名为
processed_data的工件存储。pipe.add_function_step(
name='step_two',
# parents=['step_one'], # the pipeline will automatically detect the dependencies based on the kwargs inputs
function=step_two,
function_kwargs=dict(data_frame='${step_one.data_frame}'),
function_return=['processed_data'],
cache_executed_step=True,
)管道中的第三步使用
step_three函数,并将第二步的输出作为其输入。这个引用隐式地定义了管道的结构,使step_two成为step_three的父步骤。它的返回对象将作为名为
model的工件存储:pipe.add_function_step(
name='step_three',
# parents=['step_two'], # the pipeline will automatically detect the dependencies based on the kwargs inputs
function=step_three,
function_kwargs=dict(data='${step_two.processed_data}'),
function_return=['model'],
cache_executed_step=True,
) -
运行管道:
pipe.start()管道将通过
services队列远程启动,除非另有指定。
WebApp
当实验执行时,控制台输出显示任务ID,并链接到管道控制器任务页面和管道页面。
ClearML Task: created new task id=bc93610688f242ecbbe70f413ff2cf5f
ClearML results page: https://app.clear.ml/projects/462f48dba7b441ffb34bddb783711da7/experiments/bc93610688f242ecbbe70f413ff2cf5f/output/log
ClearML pipeline page: https://app.clear.ml/pipelines/462f48dba7b441ffb34bddb783711da7/experiments/bc93610688f242ecbbe70f413ff2cf5f
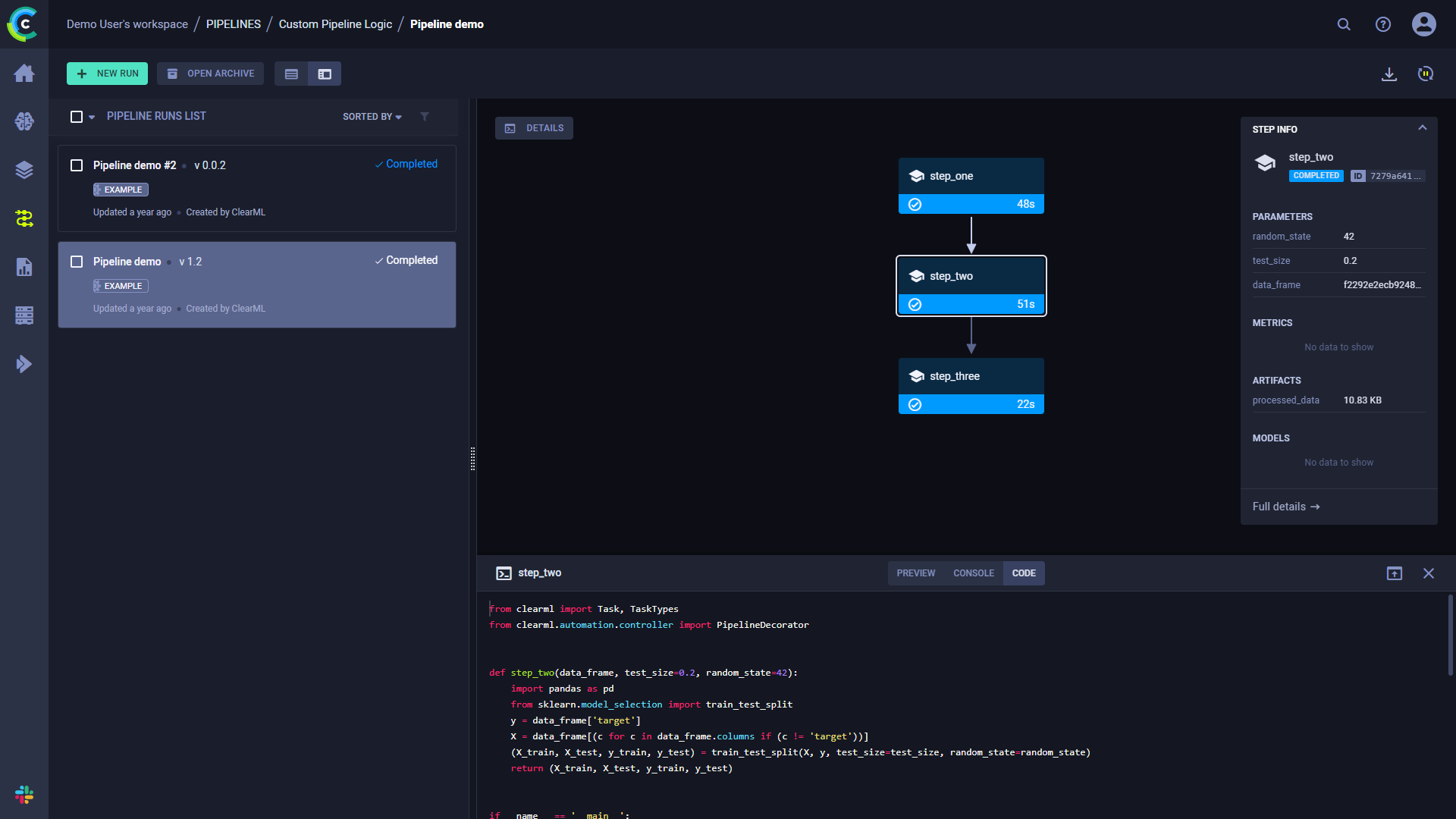
流水线运行的页面包含流水线的结构、每个步骤的执行状态,以及运行的配置参数和输出。
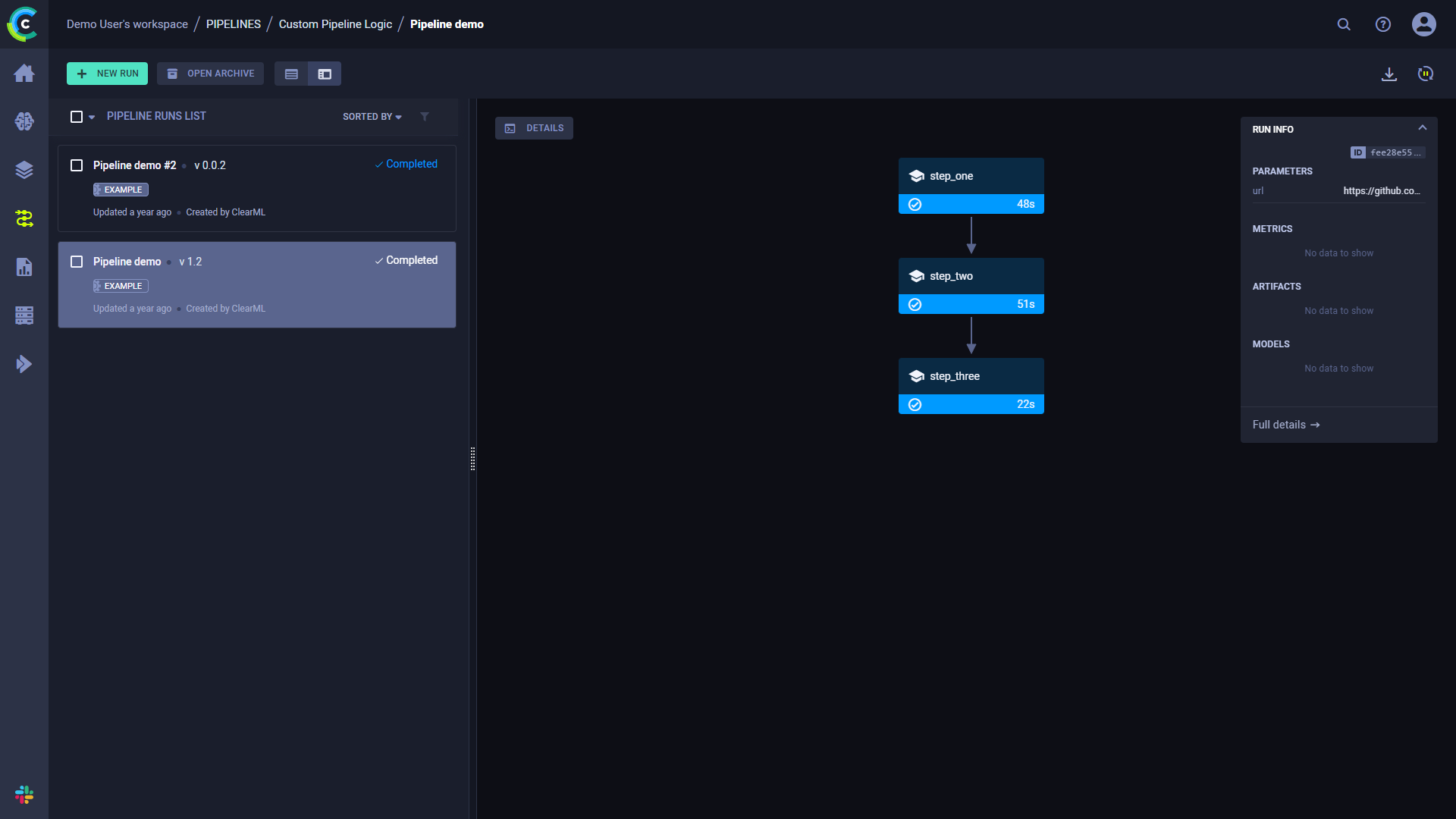
要查看运行的完整信息,请点击运行信息面板底部的完整详情,这将打开管道的控制器任务页面。
点击一个步骤以查看其详细概述。
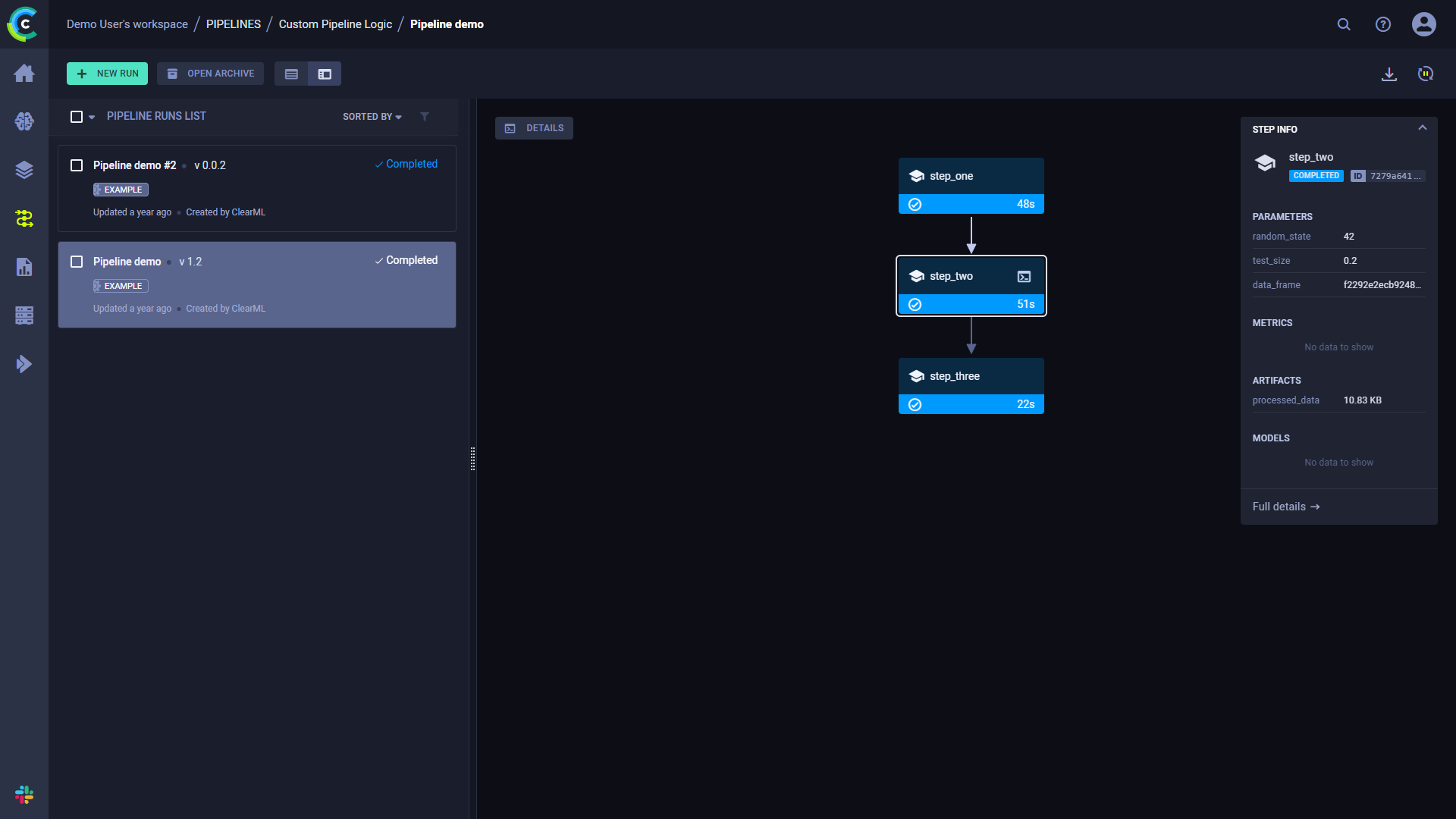
控制台和代码
点击详情查看管道控制器控制台输出的日志。
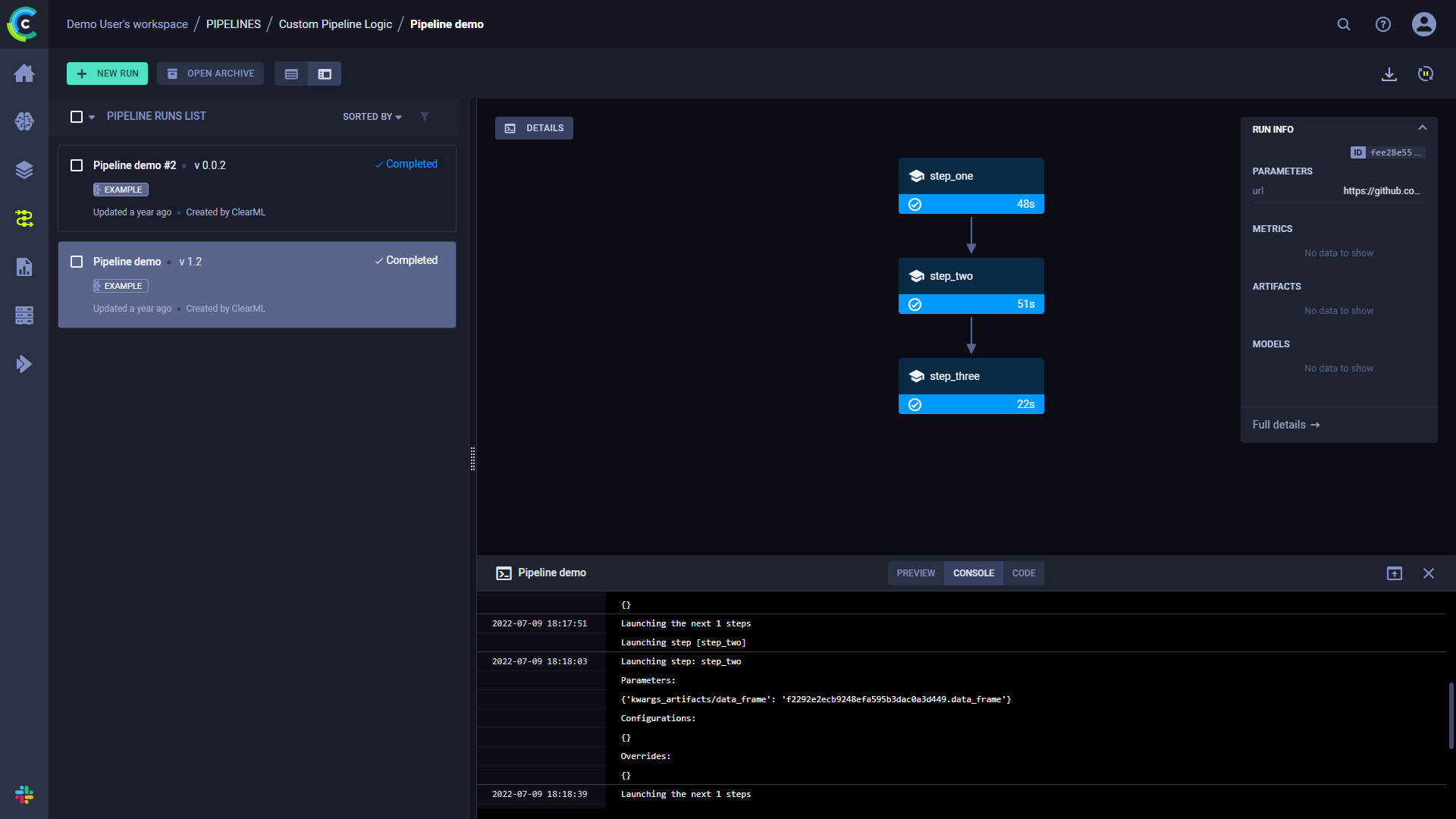
点击一个步骤以查看其控制台输出。您还可以通过点击控制台日志顶部的CODE来查看所选步骤的代码。