scipy.ndimage.
gaussian_laplace#
- scipy.ndimage.gaussian_laplace(input, sigma, output=None, mode='reflect', cval=0.0, **kwargs)[源代码][源代码]#
使用高斯二阶导数的多元拉普拉斯滤波器。
- 参数:
- 输入array_like
输入数组。
- sigma标量或标量序列
高斯滤波器的标准偏差作为序列给出,每个轴对应一个值,或者作为一个单独的数字给出,在这种情况下,它对所有轴都是相同的。
- 输出数组或数据类型,可选
要放置输出的数组,或返回数组的 dtype。默认情况下,将创建一个与输入具有相同 dtype 的数组。
- 模式str 或 序列, 可选
mode 参数决定了当滤波器跨越边界时输入数组如何扩展。通过传递一个长度等于输入数组维数的模式序列,可以沿着每个轴指定不同的模式。默认值是 ‘reflect’。有效值及其行为如下:
- ‘reflect’ (d c b a | a b c d | d c b a)
输入通过反射最后一个像素的边缘来扩展。这种模式有时也被称为半样本对称。
- ‘常量’ (k k k k | a b c d | k k k k)
输入通过填充边缘以外的所有值来扩展,这些值由 cval 参数定义为相同的常数值。
- ‘nearest’ (a a a a | a b c d | d d d d)
输入通过复制最后一个像素来扩展。
- ‘mirror’ (d c b | a b c d | c b a)
输入通过围绕最后一个像素的中心进行反射来扩展。这种模式有时也被称为全样本对称。
- ‘wrap’ (a b c d | a b c d | a b c d)
输入通过环绕到相对的边缘来扩展。
为了与插值函数保持一致,也可以使用以下模式名称:
- ‘网格常数’
这是“常量”的同义词。
- ‘grid-mirror’
这是“reflect”的同义词。
- ‘grid-wrap’
这是 ‘wrap’ 的同义词。
- cval标量,可选
如果 mode 是 ‘constant’,则用于填充输入边缘之外的值。默认值为 0.0。
- 额外的关键字参数将被传递给 gaussian_filter()。
- 返回:
- 高斯拉普拉斯ndarray
过滤后的数组。与 input 具有相同的形状。
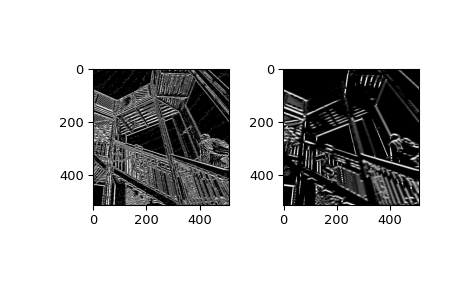
示例
>>> from scipy import ndimage, datasets >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> ascent = datasets.ascent()
>>> fig = plt.figure() >>> plt.gray() # show the filtered result in grayscale >>> ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121) # left side >>> ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122) # right side
>>> result = ndimage.gaussian_laplace(ascent, sigma=1) >>> ax1.imshow(result)
>>> result = ndimage.gaussian_laplace(ascent, sigma=3) >>> ax2.imshow(result) >>> plt.show()