scipy.spatial.KDTree.
query_ball_tree#
- KDTree.query_ball_tree(other, r, p=2.0, eps=0)[源代码][源代码]#
找出 self 和 other 之间所有距离不超过 r 的点对。
- 参数:
- 其他KDTree 实例
包含用于搜索的点的树。
- r浮动
最大距离必须是正数。
- pfloat, 可选
使用哪种 Minkowski 范数。p 必须满足条件
1 <= p <= 无穷大。- epsfloat, 可选
近似搜索。如果树的分支的最近点比
r/(1+eps)更远,则不会探索这些分支,并且如果分支的最远点比r * (1+eps)更近,则这些分支会批量添加。eps 必须是非负的。
- 返回:
- 结果列表的列表
对于这棵树的每个元素
self.data[i],results[i]是其在other.data中邻居的索引列表。
示例
你可以在两个kd树之间搜索所有距离内的点对:
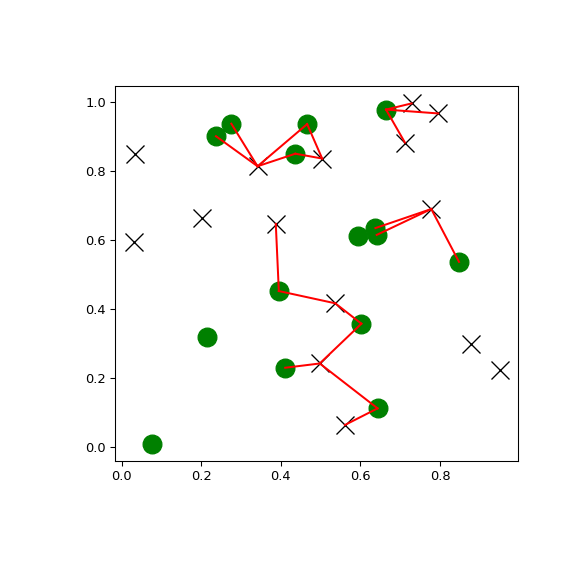
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.spatial import KDTree >>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> points1 = rng.random((15, 2)) >>> points2 = rng.random((15, 2)) >>> plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6)) >>> plt.plot(points1[:, 0], points1[:, 1], "xk", markersize=14) >>> plt.plot(points2[:, 0], points2[:, 1], "og", markersize=14) >>> kd_tree1 = KDTree(points1) >>> kd_tree2 = KDTree(points2) >>> indexes = kd_tree1.query_ball_tree(kd_tree2, r=0.2) >>> for i in range(len(indexes)): ... for j in indexes[i]: ... plt.plot([points1[i, 0], points2[j, 0]], ... [points1[i, 1], points2[j, 1]], "-r") >>> plt.show()