%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2分析训练后的模型
在拟合后访问并解释模型
数据准备
from mlforecast.utils import generate_daily_seriesseries = generate_daily_series(10)
series.head()| unique_id | ds | y | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | id_0 | 2000-01-01 | 0.322947 |
| 1 | id_0 | 2000-01-02 | 1.218794 |
| 2 | id_0 | 2000-01-03 | 2.445887 |
| 3 | id_0 | 2000-01-04 | 3.481831 |
| 4 | id_0 | 2000-01-05 | 4.191721 |
训练
假设您想使用星期几和滞后1作为特征来训练一个线性回归模型。
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from mlforecast import MLForecastfcst = MLForecast(
freq='D',
models={'lr': LinearRegression()},
lags=[1],
date_features=['dayofweek'],
)fcst.fit(series)MLForecast(models=[lr], freq=<Day>, lag_features=['lag1'], date_features=['dayofweek'], num_threads=1)MLForecast.fit 的作用是保存预测步骤所需的数据,并同时训练模型(在本例中为线性回归)。训练好的模型可以在 MLForecast.models_ 属性中找到,它是一个字典,其中键是模型名称,值是模型本身。
fcst.models_{'lr': LinearRegression()}检查参数
我们可以通过以下方式访问线性回归系数:
fcst.models_['lr'].intercept_, fcst.models_['lr'].coef_(3.2476337167384415, array([ 0.19896416, -0.21441331]))SHAP
import shap训练集
如果您需要生成训练数据,可以使用 MLForecast.preprocess。
prep = fcst.preprocess(series)
prep.head()| unique_id | ds | y | lag1 | dayofweek | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | id_0 | 2000-01-02 | 1.218794 | 0.322947 | 6 |
| 2 | id_0 | 2000-01-03 | 2.445887 | 1.218794 | 0 |
| 3 | id_0 | 2000-01-04 | 3.481831 | 2.445887 | 1 |
| 4 | id_0 | 2000-01-05 | 4.191721 | 3.481831 | 2 |
| 5 | id_0 | 2000-01-06 | 5.395863 | 4.191721 | 3 |
我们提取X,这涉及去掉信息列(id + times)和目标值。
X = prep.drop(columns=['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
X.head()| lag1 | dayofweek | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.322947 | 6 |
| 2 | 1.218794 | 0 |
| 3 | 2.445887 | 1 |
| 4 | 3.481831 | 2 |
| 5 | 4.191721 | 3 |
我们现在可以计算shap值。
X100 = shap.utils.sample(X, 100)
explainer = shap.Explainer(fcst.models_['lr'].predict, X100)
shap_values = explainer(X)并对其进行可视化
shap.plots.beeswarm(shap_values)
预测
有时你想要确定模型为什么给出了特定的预测。为了做到这一点,你需要输入特征,而这些特征默认不会返回,但你可以通过回调来获取它们。
from mlforecast.callbacks import SaveFeaturessave_feats = SaveFeatures()
preds = fcst.predict(1, before_predict_callback=save_feats)
preds.head()| unique_id | ds | lr | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | id_0 | 2000-08-10 | 3.468643 |
| 1 | id_1 | 2000-04-07 | 3.016877 |
| 2 | id_2 | 2000-06-16 | 2.815249 |
| 3 | id_3 | 2000-08-30 | 4.048894 |
| 4 | id_4 | 2001-01-08 | 3.524532 |
您现在可以通过使用 SaveFeatures.get_features 来获取特征。
features = save_feats.get_features()
features.head()| lag1 | dayofweek | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.343744 | 3 |
| 1 | 3.150799 | 4 |
| 2 | 2.137412 | 4 |
| 3 | 6.182456 | 2 |
| 4 | 1.391698 | 0 |
并使用这些特征计算SHAP值。
shap_values_predictions = explainer(features)我们现在可以分析影响 'id_4' 预测的因素。
round(preds.loc[4, 'lr'], 3)3.525shap.plots.waterfall(shap_values_predictions[4])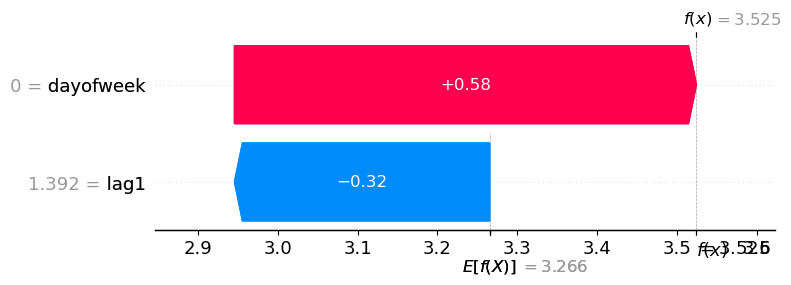
Give us a ⭐ on Github