Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
使用Girvan-Newman方法的社区检测#
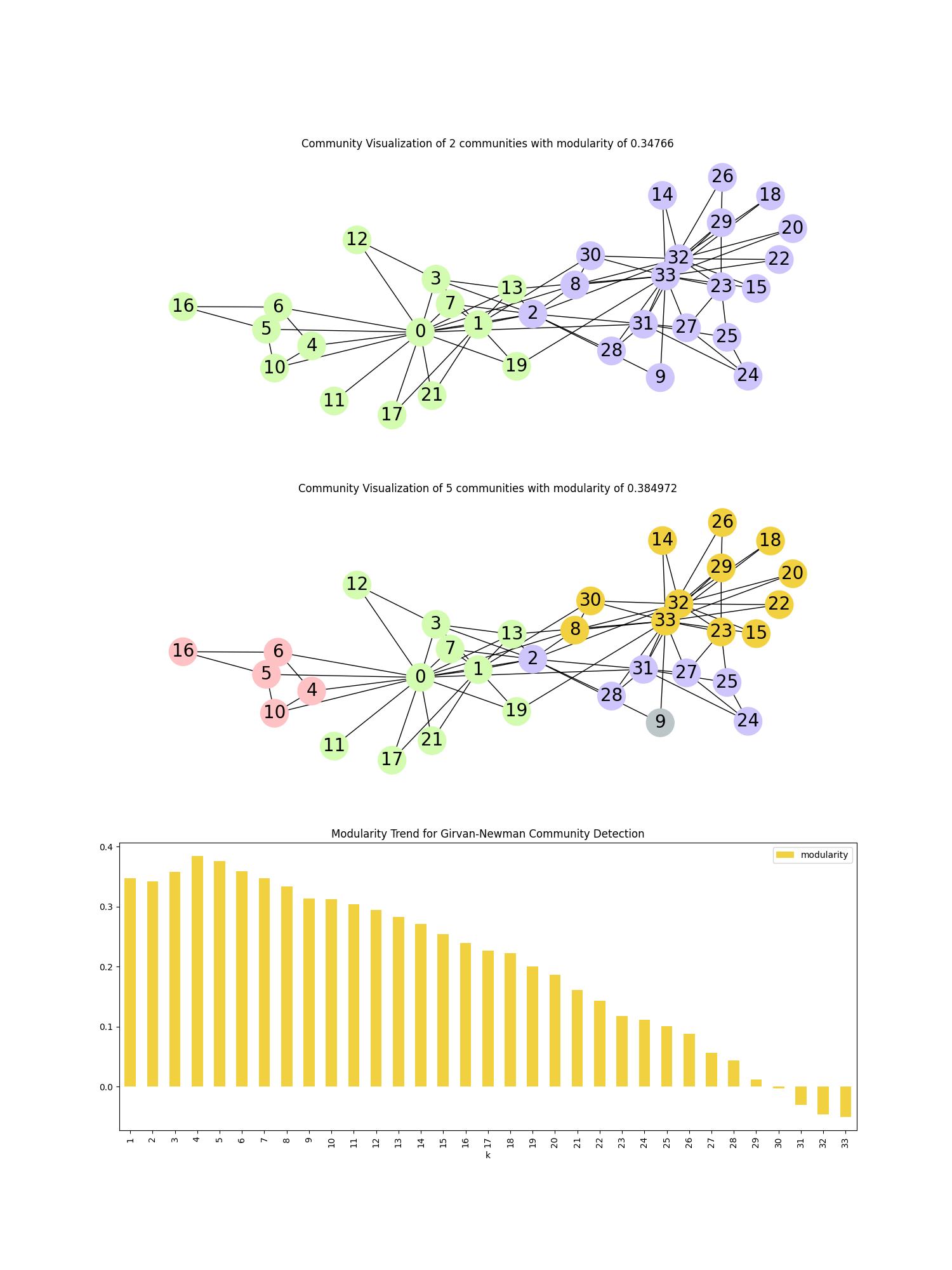
这个示例展示了使用Girvan-Newman方法在Zachary空手道俱乐部数据集中检测社区的情况。
我们绘制了随着重要边被移除时模块度的变化。 根据社区检测结果,当迭代次数分别为1和4时,图的颜色和绘制方式会有所不同。
import networkx as nx
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载空手道图并使用Girvan-Newman方法寻找社区
G = nx.karate_club_graph()
communities = list(nx.community.girvan_newman(G))
# 模块化 -> 衡量网络划分成模块的强度
modularity_df = pd.DataFrame(
[
[k + 1, nx.community.modularity(G, communities[k])]
for k in range(len(communities))
],
columns=["k", "modularity"],
)
# 创建节点颜色列表的函数
def create_community_node_colors(graph, communities):
number_of_colors = len(communities[0])
colors = ["#D4FCB1", "#CDC5FC", "#FFC2C4", "#F2D140", "#BCC6C8"][:number_of_colors]
node_colors = []
for node in graph:
current_community_index = 0
for community in communities:
if node in community:
node_colors.append(colors[current_community_index])
break
current_community_index += 1
return node_colors
# 根据社区对节点进行着色的绘图函数
def visualize_communities(graph, communities, i):
node_colors = create_community_node_colors(graph, communities)
modularity = round(nx.community.modularity(graph, communities), 6)
title = f"Community Visualization of {len(communities)} communities with modularity of {modularity}"
pos = nx.spring_layout(graph, k=0.3, iterations=50, seed=2)
plt.subplot(3, 1, i)
plt.title(title)
nx.draw(
graph,
pos=pos,
node_size=1000,
node_color=node_colors,
with_labels=True,
font_size=20,
font_color="black",
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, figsize=(15, 20))
# 根据社区着色绘制图表
visualize_communities(G, communities[0], 1)
visualize_communities(G, communities[3], 2)
# 绘制重要边被移除时模块度变化的情况
modularity_df.plot.bar(
x="k",
ax=ax[2],
color="#F2D140",
title="Modularity Trend for Girvan-Newman Community Detection",
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.458 seconds)
