scipy.signal.
gammatone#
- scipy.signal.gammatone(freq, ftype, order=None, numtaps=None, fs=None)[源代码][源代码]#
伽马通滤波器设计。
此函数计算 FIR 或 IIR 伽马音数字滤波器的系数 [1]。
- 参数:
- 频率浮动
滤波器的中心频率(以与 fs 相同的单位表示)。
- ftype{‘fir’, ‘iir’}
该函数生成的滤波器类型。如果为 ‘fir’,函数将生成一个 N 阶 FIR 伽马通滤波器。如果为 ‘iir’,函数将生成一个 8 阶数字 IIR 滤波器,模拟为 4 阶伽马通滤波器。
- 顺序int, 可选
滤波器的顺序。仅在
ftype='fir'时使用。默认值为 4,以模拟人类听觉系统。必须在 0 到 24 之间。- numtapsint, 可选
滤波器的长度。仅在
ftype='fir'时使用。如果 fs 大于 1000,默认值为fs*0.015;如果 fs 小于或等于 1000,默认值为 15。- fsfloat, 可选
信号的采样频率。freq 必须在 0 和
fs/2之间。默认值为 2。
- 返回:
- b, andarray, ndarray
滤波器的分子 (
b) 和分母 (a) 多项式。
- Raises:
- ValueError
如果 freq 小于或等于 0 或大于或等于
fs/2,如果 ftype 不是 ‘fir’ 或 ‘iir’,如果 order 小于或等于 0 或当ftype='fir'时大于 24
参考文献
[1]Slaney, Malcolm, “帕特森-霍尔沃斯听觉滤波器组的高效实现”, Apple Computer 技术报告 35, 1993, 第3-8页, 34-39页。
示例
16-样本 4阶 FIR 伽马通滤波器,中心频率为 440 Hz
>>> from scipy import signal >>> signal.gammatone(440, 'fir', numtaps=16, fs=16000) (array([ 0.00000000e+00, 2.22196719e-07, 1.64942101e-06, 4.99298227e-06, 1.01993969e-05, 1.63125770e-05, 2.14648940e-05, 2.29947263e-05, 1.76776931e-05, 2.04980537e-06, -2.72062858e-05, -7.28455299e-05, -1.36651076e-04, -2.19066855e-04, -3.18905076e-04, -4.33156712e-04]), [1.0])
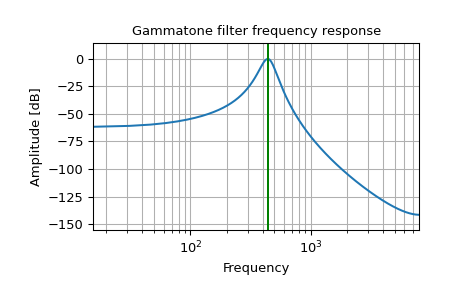
IIR Gammatone 滤波器,中心频率为 440 Hz
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np
>>> b, a = signal.gammatone(440, 'iir', fs=16000) >>> w, h = signal.freqz(b, a) >>> plt.plot(w / ((2 * np.pi) / 16000), 20 * np.log10(abs(h))) >>> plt.xscale('log') >>> plt.title('Gammatone filter frequency response') >>> plt.xlabel('Frequency') >>> plt.ylabel('Amplitude [dB]') >>> plt.margins(0, 0.1) >>> plt.grid(which='both', axis='both') >>> plt.axvline(440, color='green') # cutoff frequency >>> plt.show()