scipy.special.voigt_profile#
- scipy.special.voigt_profile(x, sigma, gamma, out=None) = <ufunc 'voigt_profile'>#
Voigt 轮廓。
Voigt 轮廓是标准差为
sigma的一维正态分布与半高宽为gamma的一维柯西分布的卷积。如果
sigma = 0,则返回柯西分布的概率密度函数。相反,如果gamma = 0,则返回正态分布的概率密度函数。如果sigma = gamma = 0,则对于x = 0返回值为Inf,对于所有其他x返回值为0。- 参数:
- xarray_like
实际参数
- sigmaarray_like
正态分布部分的标准差
- gammaarray_like
柯西分布部分的半高宽
- 出ndarray,可选
函数值的可选输出数组
- 返回:
- 标量或ndarray
在给定参数下的Voigt轮廓
参见
wofzFaddeeva 函数
注释
它可以表示为 Faddeeva 函数的形式
\[V(x; \sigma, \gamma) = \frac{Re[w(z)]}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}},\]\[z = \frac{x + i\gamma}{\sqrt{2}\sigma}\]其中 \(w(z)\) 是 Faddeeva 函数。
参考文献
示例
计算函数在点 2 处,对于
sigma=1和gamma=1的值。>>> from scipy.special import voigt_profile >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> voigt_profile(2, 1., 1.) 0.09071519942627544
通过为 x 提供一个 NumPy 数组,在多个点上计算函数。
>>> values = np.array([-2., 0., 5]) >>> voigt_profile(values, 1., 1.) array([0.0907152 , 0.20870928, 0.01388492])
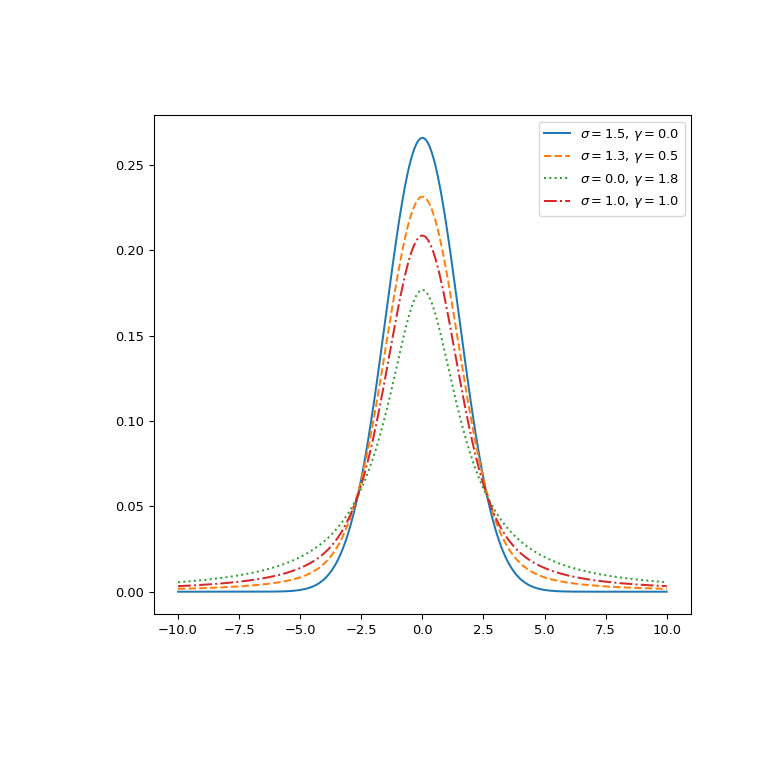
绘制不同参数集的函数图。
>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8)) >>> x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500) >>> parameters_list = [(1.5, 0., "solid"), (1.3, 0.5, "dashed"), ... (0., 1.8, "dotted"), (1., 1., "dashdot")] >>> for params in parameters_list: ... sigma, gamma, linestyle = params ... voigt = voigt_profile(x, sigma, gamma) ... ax.plot(x, voigt, label=rf"$\sigma={sigma},\, \gamma={gamma}$", ... ls=linestyle) >>> ax.legend() >>> plt.show()
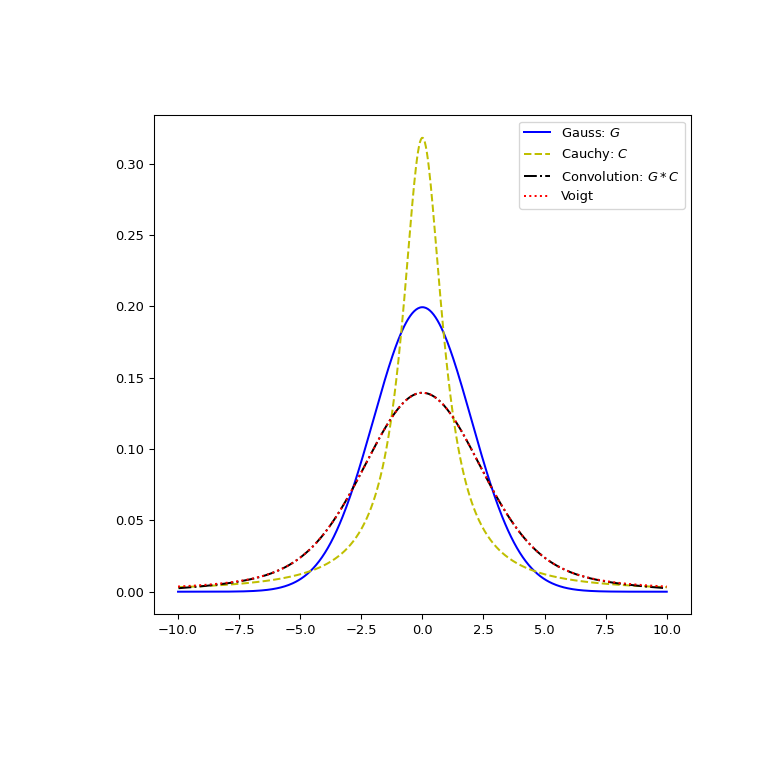
通过视觉验证,Voigt 轮廓确实是由正态分布和柯西分布的卷积产生的。
>>> from scipy.signal import convolve >>> x, dx = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500, retstep=True) >>> def gaussian(x, sigma): ... return np.exp(-0.5 * x**2/sigma**2)/(sigma * np.sqrt(2*np.pi)) >>> def cauchy(x, gamma): ... return gamma/(np.pi * (np.square(x)+gamma**2)) >>> sigma = 2 >>> gamma = 1 >>> gauss_profile = gaussian(x, sigma) >>> cauchy_profile = cauchy(x, gamma) >>> convolved = dx * convolve(cauchy_profile, gauss_profile, mode="same") >>> voigt = voigt_profile(x, sigma, gamma) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8)) >>> ax.plot(x, gauss_profile, label="Gauss: $G$", c='b') >>> ax.plot(x, cauchy_profile, label="Cauchy: $C$", c='y', ls="dashed") >>> xx = 0.5*(x[1:] + x[:-1]) # midpoints >>> ax.plot(xx, convolved[1:], label="Convolution: $G * C$", ls='dashdot', ... c='k') >>> ax.plot(x, voigt, label="Voigt", ls='dotted', c='r') >>> ax.legend() >>> plt.show()