%%capture
!pip install hierarchicalforecast statsforecastPERMBU
在许多情况下,只有层次结构中最低级别的时间序列(底层时间序列)可用。HierarchicalForecast 具有创建所有层次结构时间序列的工具,并且还允许您计算所有层次结构的预测区间。在本笔记本中,我们将看到如何完成这一切。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 计算基准预测无一致性
from statsforecast.models import AutoARIMA
from statsforecast.core import StatsForecast
#获取层次协调方法及评估
from hierarchicalforecast.methods import BottomUp, MinTrace
from hierarchicalforecast.utils import aggregate, HierarchicalPlot
from hierarchicalforecast.core import HierarchicalReconciliation
from hierarchicalforecast.evaluation import HierarchicalEvaluation/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/statsforecast/core.py:21: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm聚合底层时间序列
在这个例子中,我们将使用来自《预测:原则与实践》一书的旅游数据集。该数据集仅包含最低层级的时间序列,因此我们需要为所有层级创建时间序列。
Y_df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/tourism.csv')
Y_df = Y_df.rename({'Trips': 'y', 'Quarter': 'ds'}, axis=1)
Y_df.insert(0, 'Country', 'Australia')
Y_df = Y_df[['Country', 'Region', 'State', 'Purpose', 'ds', 'y']]
Y_df['ds'] = Y_df['ds'].str.replace(r'(\d+) (Q\d)', r'\1-\2', regex=True)
Y_df['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(Y_df['ds'])
Y_df.head()| Country | Region | State | Purpose | ds | y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Australia | Adelaide | South Australia | Business | 1998-01-01 | 135.077690 |
| 1 | Australia | Adelaide | South Australia | Business | 1998-04-01 | 109.987316 |
| 2 | Australia | Adelaide | South Australia | Business | 1998-07-01 | 166.034687 |
| 3 | Australia | Adelaide | South Australia | Business | 1998-10-01 | 127.160464 |
| 4 | Australia | Adelaide | South Australia | Business | 1999-01-01 | 137.448533 |
数据集可以按照以下严格的层级结构进行分组。
spec = [
['Country'],
['Country', 'State'],
['Country', 'State', 'Region']
]使用 HierarchicalForecast 中的 aggregate 函数,我们可以获得完整的时间序列集合。
Y_df, S_df, tags = aggregate(df=Y_df, spec=spec)
Y_df = Y_df.reset_index()/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(Y_df.head()| unique_id | ds | y | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Australia | 1998-01-01 | 23182.197269 |
| 1 | Australia | 1998-04-01 | 20323.380067 |
| 2 | Australia | 1998-07-01 | 19826.640511 |
| 3 | Australia | 1998-10-01 | 20830.129891 |
| 4 | Australia | 1999-01-01 | 22087.353380 |
S_df.iloc[:5, :5]| Australia/ACT/Canberra | Australia/New South Wales/Blue Mountains | Australia/New South Wales/Capital Country | Australia/New South Wales/Central Coast | Australia/New South Wales/Central NSW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Australia/ACT | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Australia/New South Wales | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Australia/Northern Territory | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Australia/Queensland | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
tags['Country/State']array(['Australia/ACT', 'Australia/New South Wales',
'Australia/Northern Territory', 'Australia/Queensland',
'Australia/South Australia', 'Australia/Tasmania',
'Australia/Victoria', 'Australia/Western Australia'], dtype=object)我们可以使用 HierarchicalPlot 类可视化 S 矩阵和数据,如下所示。
hplot = HierarchicalPlot(S=S_df, tags=tags)hplot.plot_summing_matrix()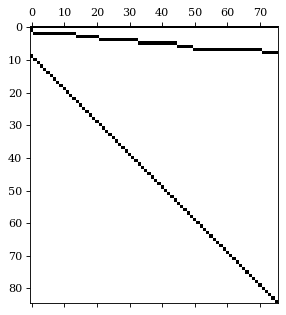
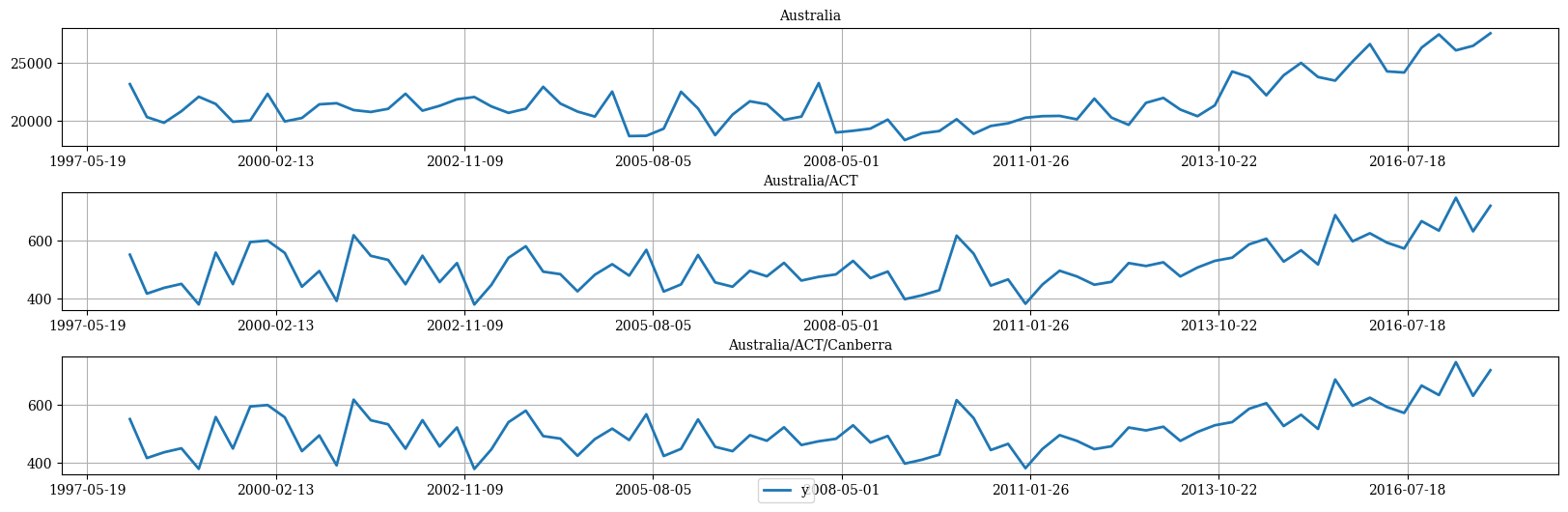
hplot.plot_hierarchically_linked_series(
bottom_series='Australia/ACT/Canberra',
Y_df=Y_df.set_index('unique_id')
)
拆分训练/测试集
我们使用最后两年(8个季度)作为测试集。
Y_test_df = Y_df.groupby('unique_id').tail(8)
Y_train_df = Y_df.drop(Y_test_df.index)Y_test_df = Y_test_df.set_index('unique_id')
Y_train_df = Y_train_df.set_index('unique_id')Y_train_df.groupby('unique_id').size()unique_id
Australia 72
Australia/ACT 72
Australia/ACT/Canberra 72
Australia/New South Wales 72
Australia/New South Wales/Blue Mountains 72
..
Australia/Western Australia/Australia's Coral Coast 72
Australia/Western Australia/Australia's Golden Outback 72
Australia/Western Australia/Australia's North West 72
Australia/Western Australia/Australia's South West 72
Australia/Western Australia/Experience Perth 72
Length: 85, dtype: int64计算基线预测
以下单元格使用 AutoARIMA 模型计算 Y_df 中每个时间序列的 基线预测。注意到 Y_hat_df 包含预测结果,但它们并不一致。为了调和预测区间,我们需要使用 StatsForecast 的 level 参数计算不一致的区间。
fcst = StatsForecast(df=Y_train_df,
models=[AutoARIMA(season_length=4)],
freq='QS', n_jobs=-1)
Y_hat_df = fcst.forecast(h=8, fitted=True, level=[80, 90])
Y_fitted_df = fcst.forecast_fitted_values()使预测一致并使用PERMBU计算预测区间
以下单元使用HierarchicalReconciliation类使之前的预测保持一致。在这个例子中,我们使用BottomUp和MinTrace。如果您想计算预测区间,您必须使用level参数,并且还要将intervals_method='permbu'。
reconcilers = [
BottomUp(),
MinTrace(method='mint_shrink'),
MinTrace(method='ols')
]
hrec = HierarchicalReconciliation(reconcilers=reconcilers)
Y_rec_df = hrec.reconcile(Y_hat_df=Y_hat_df, Y_df=Y_fitted_df,
S=S_df, tags=tags,
level=[80, 90], intervals_method='permbu')/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(
/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(
/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(
/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(
/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(
/Users/fedex/miniconda3/envs/hierarchicalforecast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/_encoders.py:828: FutureWarning: `sparse` was renamed to `sparse_output` in version 1.2 and will be removed in 1.4. `sparse_output` is ignored unless you leave `sparse` to its default value.
warnings.warn(数据框 Y_rec_df 包含经过调整的预测结果。
Y_rec_df.head()| ds | AutoARIMA | AutoARIMA-lo-90 | AutoARIMA-lo-80 | AutoARIMA-hi-80 | AutoARIMA-hi-90 | AutoARIMA/BottomUp | AutoARIMA/BottomUp-lo-90 | AutoARIMA/BottomUp-lo-80 | AutoARIMA/BottomUp-hi-80 | ... | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-mint_shrink | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-mint_shrink-lo-90 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-mint_shrink-lo-80 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-mint_shrink-hi-80 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-mint_shrink-hi-90 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols-lo-90 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols-lo-80 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols-hi-80 | AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols-hi-90 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unique_id | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Australia | 2016-01-01 | 26212.554688 | 24694.224609 | 25029.580078 | 27395.527344 | 27730.884766 | 24865.636719 | 24106.802510 | 24373.962043 | 25423.566450 | ... | 25395.411928 | 24733.046633 | 24824.274681 | 25939.345007 | 25998.692460 | 26133.758953 | 25516.484518 | 25600.644926 | 26662.923204 | 26855.585562 |
| Australia | 2016-04-01 | 25033.667969 | 23324.066406 | 23701.669922 | 26365.666016 | 26743.269531 | 23247.097656 | 22696.597930 | 22821.256357 | 23830.632567 | ... | 23986.272540 | 23289.811432 | 23525.630785 | 24563.998645 | 24739.826238 | 24934.260399 | 24402.570904 | 24481.968560 | 25567.085565 | 25696.312229 |
| Australia | 2016-07-01 | 24507.027344 | 22625.500000 | 23041.076172 | 25972.978516 | 26388.554688 | 22658.207031 | 21816.988906 | 22011.905035 | 23158.311619 | ... | 23345.821184 | 22688.605574 | 22780.602574 | 23934.244609 | 24033.906220 | 24374.026569 | 23539.673724 | 23797.836651 | 24893.463090 | 25098.321828 |
| Australia | 2016-10-01 | 25598.929688 | 23559.919922 | 24010.281250 | 27187.578125 | 27637.937500 | 23330.804688 | 22567.948299 | 22694.449708 | 23850.068162 | ... | 24275.423420 | 23392.040447 | 23626.165662 | 24828.207813 | 24958.926002 | 25477.951913 | 24793.436993 | 24911.271547 | 26006.244161 | 26152.362329 |
| Australia | 2017-01-01 | 26982.578125 | 24651.535156 | 25166.396484 | 28798.757812 | 29313.619141 | 24497.001953 | 23578.418503 | 23731.657437 | 25114.564017 | ... | 25485.433879 | 24549.969625 | 24802.819691 | 26073.792872 | 26284.826386 | 26842.564741 | 26037.725561 | 26248.171831 | 27436.222761 | 27668.067666 |
5 rows × 21 columns
绘制预测结果
然后我们可以使用以下函数绘制概率预测。
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_df.set_index(['unique_id', 'ds']),
Y_rec_df.set_index('ds', append=True)], axis=1)
plot_df = plot_df.reset_index('ds')绘制单个时间序列
hplot.plot_series(
series='Australia',
Y_df=plot_df,
models=['y', 'AutoARIMA',
'AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols',
'AutoARIMA/BottomUp'
],
level=[80]
)
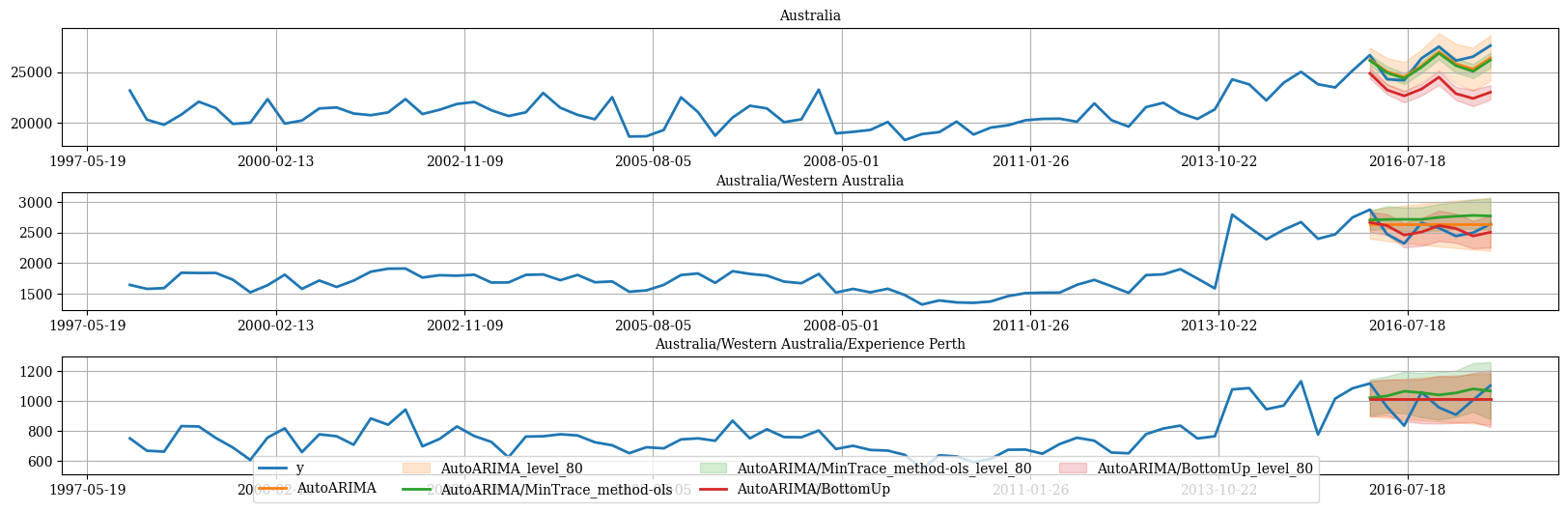
绘制层次链接的时间序列
hplot.plot_hierarchically_linked_series(
bottom_series='Australia/Western Australia/Experience Perth',
Y_df=plot_df,
models=['y', 'AutoARIMA', 'AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-ols', 'AutoARIMA/BottomUp'],
level=[80]
)
# ACT仅拥有堪培拉
hplot.plot_hierarchically_linked_series(
bottom_series='Australia/ACT/Canberra',
Y_df=plot_df,
models=['y', 'AutoARIMA/MinTrace_method-mint_shrink'],
level=[80, 90]
)
参考文献
- Hyndman, R.J., & Athanasopoulos, G. (2021). “预测:原理与实践, 第3版: 第11章: 预测层次和分组系列。” OTexts: 澳大利亚墨尔本。 OTexts.com/fpp3 于2022年7月访问。
- Shanika L. Wickramasuriya, George Athanasopoulos, and Rob J. Hyndman. 通过迹最小化对层次和分组时间序列进行最佳预测调和. 美国统计协会杂志, 114(526):804–819, 2019. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2018.1448825. URL https://robjhyndman.com/publications/mint/.
If you find the code useful, please ⭐ us on Github