解析PDF文档用于RAG应用
本笔记展示如何利用GPT-4V将丰富的PDF文档(如幻灯片演示或从网页导出的文档)转换为可用于RAG应用的内容。
如果您有大量包含有价值信息的非结构化数据,并希望能够在RAG流程的一部分中检索这些信息,那么可以使用这种技术。
例如,您可以构建一个知识助手,根据PDF文档中包含的信息回答用户关于您公司或产品的查询。
本笔记中使用的示例文档位于data/example_pdfs。它们与OpenAI的API以及作为LLM项目一部分可以使用的各种技术相关。
数据准备
在本部分中,我们将处理我们的输入数据,以便为检索做准备。
我们将通过两种方式进行此操作:
- 使用pdfminer提取文本
- 将PDF页面转换为图像,以便用GPT-4V分析
如果您只想使用从图像分析中推断出的内容,可以跳过第一种方法。
设置
我们需要安装一些库来将PDF转换为图像并提取文本(可选)。
注意:您需要在计算机上安装poppler才能使pdf2image库正常工作。您可以按照这里的说明进行安装。
%pip install pdf2image
%pip install pdfminer
%pip install openai
%pip install scikit-learn
%pip install rich
%pip install tqdm
%pip install concurrent
# 进口
from pdf2image import convert_from_path
from pdf2image.exceptions import (
PDFInfoNotInstalledError,
PDFPageCountError,
PDFSyntaxError
)
from pdfminer.high_level import extract_text
import base64
from io import BytesIO
import os
import concurrent
from tqdm import tqdm
from openai import OpenAI
import re
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
import json
import numpy as np
from rich import print
from ast import literal_eval
文件处理
def convert_doc_to_images(path):
images = convert_from_path(path)
return images
def extract_text_from_doc(path):
text = extract_text(path)
page_text = []
return text
使用示例进行测试
file_path = "data/example_pdfs/fine-tuning-deck.pdf"
images = convert_doc_to_images(file_path)
text = extract_text_from_doc(file_path)
for img in images:
display(img)






使用GPT-4V进行图像分析
在将PDF文件转换为多个图像后,我们将使用GPT-4V根据这些图像来分析内容。
# 正在初始化OpenAI客户端 - 请参阅 https://platform.openai.com/docs/quickstart?context=python
client = OpenAI()
# 将图像转换为数据URI格式的base64编码图像,以便与ChatCompletions API一起使用
def get_img_uri(img):
buffer = BytesIO()
img.save(buffer, format="jpeg")
base64_image = base64.b64encode(buffer.getvalue()).decode("utf-8")
data_uri = f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{base64_image}"
return data_uri
system_prompt = '''
You will be provided with an image of a pdf page or a slide. Your goal is to talk about the content that you see, in technical terms, as if you were delivering a presentation.
If there are diagrams, describe the diagrams and explain their meaning.
For example: if there is a diagram describing a process flow, say something like "the process flow starts with X then we have Y and Z..."
If there are tables, describe logically the content in the tables
For example: if there is a table listing items and prices, say something like "the prices are the following: A for X, B for Y..."
DO NOT include terms referring to the content format
DO NOT mention the content type - DO focus on the content itself
For example: if there is a diagram/chart and text on the image, talk about both without mentioning that one is a chart and the other is text.
Simply describe what you see in the diagram and what you understand from the text.
You should keep it concise, but keep in mind your audience cannot see the image so be exhaustive in describing the content.
Exclude elements that are not relevant to the content:
DO NOT mention page numbers or the position of the elements on the image.
------
If there is an identifiable title, identify the title to give the output in the following format:
{TITLE}
{Content description}
If there is no clear title, simply return the content description.
'''
def analyze_image(img_url):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-vision-preview",
temperature=0,
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": system_prompt
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": img_url,
},
],
}
],
max_tokens=300,
top_p=0.1
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
通过示例进行测试
img = images[2]
data_uri = get_img_uri(img)
res = analyze_image(data_uri)
print(res)
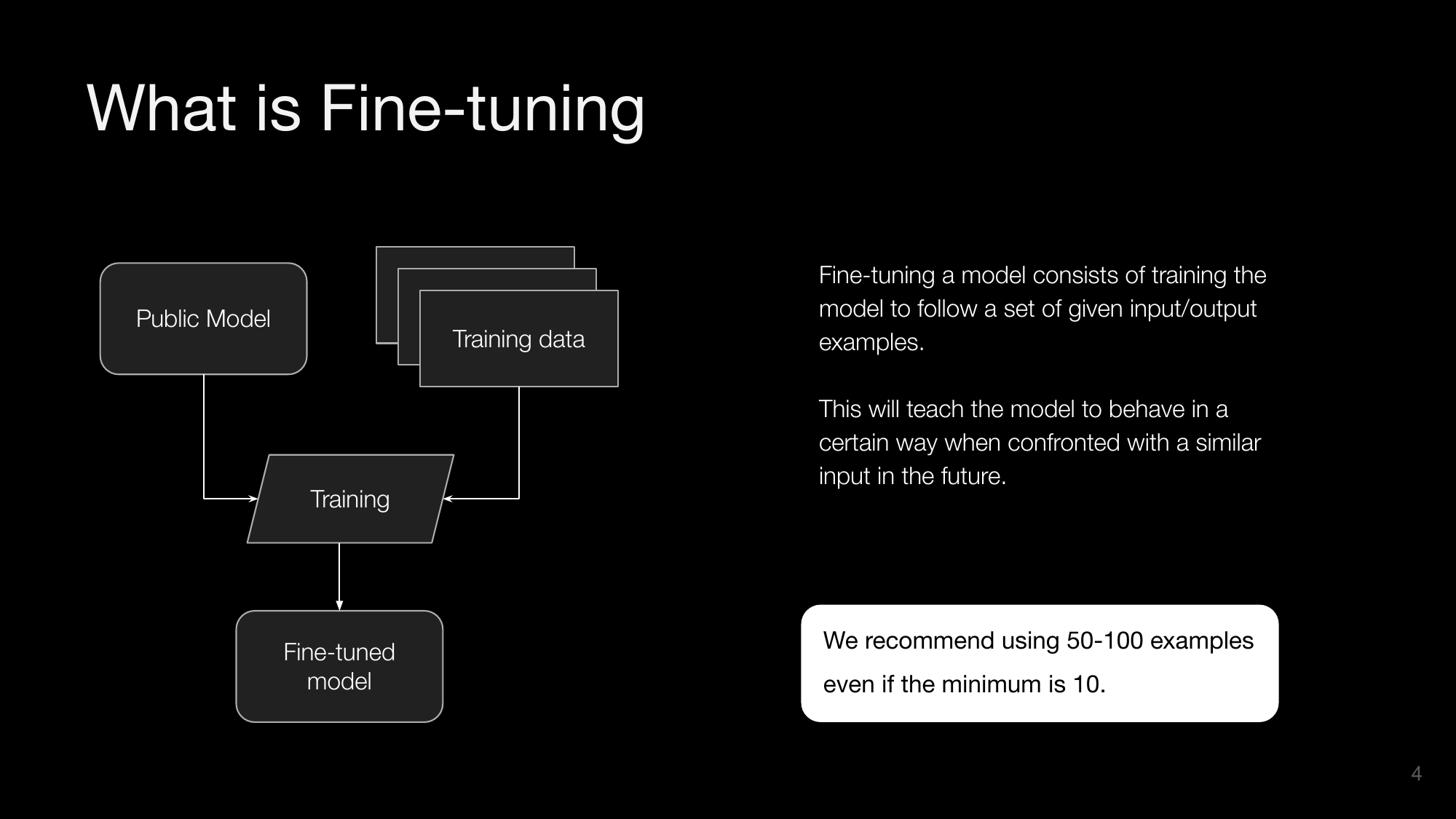
What is Fine-tuning
Fine-tuning a model consists of training the model to follow a set of given input/output examples. This will teach the model to behave in a certain way when confronted with a similar input in the future.
We recommend using 50-100 examples even if the minimum is 10.
The process involves starting with a public model, using training data to train the model, and resulting in a fine-tuned model.
处理所有文档
files_path = "data/example_pdfs"
all_items = os.listdir(files_path)
files = [item for item in all_items if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(files_path, item))]
def analyze_doc_image(img):
img_uri = get_img_uri(img)
data = analyze_image(img_uri)
return data
我们将列出示例文件夹中的所有文件,并按以下步骤处理它们: 1. 提取文本 2. 将文档转换为图像 3. 使用GPT-4V分析页面
注意:这个过程大约需要~2分钟才能完成。如果愿意,可以跳过这一步,直接加载结果文件(见下文)。
docs = []
for f in files:
path = f"{files_path}/{f}"
doc = {
"filename": f
}
text = extract_text_from_doc(path)
doc['text'] = text
imgs = convert_doc_to_images(path)
pages_description = []
print(f"Analyzing pages for doc {f}")
# 并发执行
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=8) as executor:
# Removing 1st slide as it's usually just an intro
futures = [
executor.submit(analyze_doc_image, img)
for img in imgs[1:]
]
with tqdm(total=len(imgs)-1) as pbar:
for _ in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
pbar.update(1)
for f in futures:
res = f.result()
pages_description.append(res)
doc['pages_description'] = pages_description
docs.append(doc)
Analyzing pages for doc rag-deck.pdf
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 19/19 [00:32<00:00, 1.72s/it]
Analyzing pages for doc models-page.pdf
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 9/9 [00:25<00:00, 2.80s/it]
Analyzing pages for doc evals-decks.pdf
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 12/12 [00:29<00:00, 2.44s/it]
Analyzing pages for doc fine-tuning-deck.pdf
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 6/6 [00:19<00:00, 3.32s/it]
# 将结果保存到文件以备后用
json_path = "data/parsed_pdf_docs.json"
with open(json_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(docs, f)
# 可选:从保存的文件中加载内容
with open(json_path, 'r') as f:
docs = json.load(f)
嵌入内容
在嵌入内容之前,我们将通过页面逻辑地对其进行分块。 对于实际场景,您可以探索更高级的方式来对内容进行分块: - 将其分割成更小的片段 - 在每个内容片段的开头添加数据 - 如幻灯片标题、文档标题和/或文档描述。这样,每个独立的块就可以在上下文中使用。
为简洁起见,我们将使用非常简单的分块策略,并依赖于分隔符来按页面拆分文本。
# 按页面分块内容,并在适用情况下合并幻灯片文本与描述
content = []
for doc in docs:
# 删除第一张幻灯片
text = doc['text'].split('\f')[1:]
description = doc['pages_description']
description_indexes = []
for i in range(len(text)):
slide_content = text[i] + '\n'
# 努力寻找匹配的幻灯片描述
slide_title = text[i].split('\n')[0]
for j in range(len(description)):
description_title = description[j].split('\n')[0]
if slide_title.lower() == description_title.lower():
slide_content += description[j].replace(description_title, '')
# 跟踪添加的描述
description_indexes.append(j)
# 将幻灯片内容与相应的内容片段描述相结合
content.append(slide_content)
# 添加未使用的幻灯片描述
for j in range(len(description)):
if j not in description_indexes:
content.append(description[j])
for c in content:
print(c)
print("\n\n-------------------------------\n\n")
# 清理内容
# 去除尾随空格、多余的换行符、页码以及对内容为幻灯片的引用。
clean_content = []
for c in content:
text = c.replace(' \n', '').replace('\n\n', '\n').replace('\n\n\n', '\n').strip()
text = re.sub(r"(?<=\n)\d{1,2}", "", text)
text = re.sub(r"\b(?:the|this)\s*slide\s*\w+\b", "", text, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
clean_content.append(text)
for c in clean_content:
print(c)
print("\n\n-------------------------------\n\n")
# 生成嵌入向量
# We'll save to a csv file here for testing purposes but this is where you should load content in your vectorDB.
df = pd.DataFrame(clean_content, columns=['content'])
print(df.shape)
df.head()
(64, 1)
| content | |
|---|---|
| 0 | Overview Retrieval-Augmented Generationenhanc... |
| 1 | What is RAG Retrieve information to Augment t... |
| 2 | When to use RAG Good for ✅ Not good for ❌... |
| 3 | Technical patterns Data preparation Input pr... |
| 4 | Technical patterns Data preparation chunk do... |
embeddings_model = "text-embedding-3-large"
def get_embeddings(text):
embeddings = client.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-3-small",
input=text,
encoding_format="float"
)
return embeddings.data[0].embedding
df['embeddings'] = df['content'].apply(lambda x: get_embeddings(x))
df.head()
| content | embeddings | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Overview Retrieval-Augmented Generationenhanc... | [-0.014744381, 0.03017278, 0.06353764, 0.02110... |
| 1 | What is RAG Retrieve information to Augment t... | [-0.024337867, 0.022921458, -0.00971687, 0.010... |
| 2 | When to use RAG Good for ✅ Not good for ❌... | [-0.011084231, 0.021158217, -0.00430421, 0.017... |
| 3 | Technical patterns Data preparation Input pr... | [-0.0058343858, 0.0408407, 0.054318383, 0.0190... |
| 4 | Technical patterns Data preparation chunk do... | [-0.010359385, 0.03736894, 0.052995477, 0.0180... |
# 本地保存以供稍后使用
data_path = "data/parsed_pdf_docs_with_embeddings.csv"
df.to_csv(data_path, index=False)
# 可选:从保存的文件加载数据
df = pd.read_csv(data_path)
df["embeddings"] = df.embeddings.apply(literal_eval).apply(np.array)
检索增强生成
该过程的最后一步是在检索内容作为上下文回复之后,根据输入查询生成输出。
system_prompt = '''
You will be provided with an input prompt and content as context that can be used to reply to the prompt.
You will do 2 things:
1. First, you will internally assess whether the content provided is relevant to reply to the input prompt.
2a. If that is the case, answer directly using this content. If the content is relevant, use elements found in the content to craft a reply to the input prompt.
2b. If the content is not relevant, use your own knowledge to reply or say that you don't know how to respond if your knowledge is not sufficient to answer.
Stay concise with your answer, replying specifically to the input prompt without mentioning additional information provided in the context content.
'''
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview"
def search_content(df, input_text, top_k):
embedded_value = get_embeddings(input_text)
df["similarity"] = df.embeddings.apply(lambda x: cosine_similarity(np.array(x).reshape(1,-1), np.array(embedded_value).reshape(1, -1)))
res = df.sort_values('similarity', ascending=False).head(top_k)
return res
def get_similarity(row):
similarity_score = row['similarity']
if isinstance(similarity_score, np.ndarray):
similarity_score = similarity_score[0][0]
return similarity_score
def generate_output(input_prompt, similar_content, threshold = 0.5):
content = similar_content.iloc[0]['content']
# Adding more matching content if the similarity is above threshold
if len(similar_content) > 1:
for i, row in similar_content.iterrows():
similarity_score = get_similarity(row)
if similarity_score > threshold:
content += f"\n\n{row['content']}"
prompt = f"INPUT PROMPT:\n{input_prompt}\n-------\nCONTENT:\n{content}"
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
temperature=0.5,
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": system_prompt
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt
}
]
)
return completion.choices[0].message.content
# 与内容相关的用户查询示例
example_inputs = [
'What are the main models you offer?',
'Do you have a speech recognition model?',
'Which embedding model should I use for non-English use cases?',
'Can I introduce new knowledge in my LLM app using RAG?',
'How many examples do I need to fine-tune a model?',
'Which metric can I use to evaluate a summarization task?',
'Give me a detailed example for an evaluation process where we are looking for a clear answer to compare to a ground truth.',
]
# 对每个示例运行RAG管道
for ex in example_inputs:
print(f"[deep_pink4][bold]QUERY:[/bold] {ex}[/deep_pink4]\n\n")
matching_content = search_content(df, ex, 3)
print(f"[grey37][b]Matching content:[/b][/grey37]\n")
for i, match in matching_content.iterrows():
print(f"[grey37][i]Similarity: {get_similarity(match):.2f}[/i][/grey37]")
print(f"[grey37]{match['content'][:100]}{'...' if len(match['content']) > 100 else ''}[/[grey37]]\n\n")
reply = generate_output(ex, matching_content)
print(f"[turquoise4][b]REPLY:[/b][/turquoise4]\n\n[spring_green4]{reply}[/spring_green4]\n\n--------------\n\n")
QUERY: What are the main models you offer?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.43
Models - OpenAI API The content lists various API endpoints and their corresponding latest models: -...[/]
Similarity: 0.39
26/02/2024, 17:58 Models - OpenAI API The Moderation models are designed to check whether content co...[/]
Similarity: 0.39
The content describes various models provided by OpenAI, focusing on moderation models and GPT base ...[/]
REPLY: The main models we offer include: - For completions: gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct, babbage-002, and davinci-002. - For embeddings: text-embedding-3-small, text-embedding-3-large, and text-embedding-ada-002. - For fine-tuning jobs: gpt-3.5-turbo, babbage-002, and davinci-002. - For moderations: text-moderation-stable and text-moderation. Additionally, we have the latest models like gpt-3.5-turbo-16k and fine-tuned versions of gpt-3.5-turbo. --------------
QUERY: Do you have a speech recognition model?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.53
The content describes various models related to text-to-speech, speech recognition, embeddings, and ...[/]
Similarity: 0.50
26/02/2024, 17:58 Models - OpenAI API MODEL DE S CRIPTION tts-1 New Text-to-speech 1 The latest tex...[/]
Similarity: 0.44
26/02/2024, 17:58 Models - OpenAI API ENDP OINT DATA USED FOR TRAINING DEFAULT RETENTION ELIGIBLE FO...[/]
REPLY: Yes, the Whisper model is a general-purpose speech recognition model mentioned in the content, capable of multilingual speech recognition, speech translation, and language identification. The v2-large model, referred to as "whisper-1", is available through an API and is optimized for faster performance. --------------
QUERY: Which embedding model should I use for non-English use cases?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.57
The content describes various models related to text-to-speech, speech recognition, embeddings, and ...[/]
Similarity: 0.46
26/02/2024, 17:58 Models - OpenAI API MODEL DE S CRIPTION tts-1 New Text-to-speech 1 The latest tex...[/]
Similarity: 0.40
26/02/2024, 17:58 Models - OpenAI API Multilingual capabilities GPT-4 outperforms both previous larg...[/]
REPLY: For non-English use cases, you should use the "V3 large" embedding model, as it is described as the most capable for both English and non-English tasks, with an output dimension of 3,072. --------------
QUERY: Can I introduce new knowledge in my LLM app using RAG?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.50
What is RAG Retrieve information to Augment the model’s knowledge and Generate the output “What is y...[/]
Similarity: 0.49
When to use RAG Good for ✅ Not good for ❌ ● ● Introducing new information to the model ● Teaching ...[/]
Similarity: 0.43
Technical patterns Data preparation: augmenting content What does “Augmentingcontent” mean? Augmenti...[/]
REPLY: Yes, you can introduce new knowledge in your LLM app using RAG by retrieving information from a knowledge base or external sources to augment the model's knowledge and generate outputs relevant to the queries posed. --------------
QUERY: How many examples do I need to fine-tune a model?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.68
What is Fine-tuning Public Model Training data Training Fine-tunedmodel Fine-tuning a model consists...[/]
Similarity: 0.62
When to fine-tune Fine-tuning is good for: - Following a given format or tone for the output - Proce...[/]
Similarity: 0.57
Overview Fine-tuning involves adjusting theparameters of pre-trained models on aspecific dataset or t...[/]
REPLY: We recommend using 50-100 examples for fine-tuning a model, even though the minimum is 10. --------------
QUERY: Which metric can I use to evaluate a summarization task?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.53
Technical patterns Metric-based evaluations ROUGE is a common metric for evaluating machine summariz...[/]
Similarity: 0.49
Technical patterns Metric-based evaluations Component evaluations Subjective evaluations ● ● Compari...[/]
Similarity: 0.48
Technical patterns Metric-based evaluations BLEU score is another standard metric, this time focusin...[/]
REPLY: ROUGE is a common metric you can use to evaluate a summarization task. --------------
QUERY: Give me a detailed example for an evaluation process where we are looking for a clear answer to compare to a ground truth.
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.60
What are evals Example Our ground truth matches the predicted answer, so the evaluation passes! Eval...[/]
Similarity: 0.59
What are evals Example An evaluation contains a question and a correct answer. We call this the grou...[/]
Similarity: 0.50
Technical patterns Metric-based evaluations What they’re good for What to be aware of ● ● A good sta...[/]
REPLY: The content provided is relevant and offers a detailed example for an evaluation process comparing to a ground truth. Here's a concise explanation based on the content: In the given example, the evaluation process involves a question-and-answer scenario to verify the accuracy of information retrieved by a tool or system in response to a query. The question posed is, "What is the population of Canada?" The ground truth, or the correct answer, is established as "The population of Canada in 2023 is 39,566,248 people." A tool labeled "LLM" is then used to search for the answer, which predicts "The current population of Canada is 39,566,248 as of Tuesday, May 23, 2023." This predicted answer matches the ground truth exactly, indicating that the evaluation passes. This process demonstrates how an evaluation can be used to verify the accuracy of information retrieved by a tool, comparing the predicted answer to the ground truth to ensure correctness. --------------
总结
在这个笔记本中,我们学习了如何基于PDF文档开发一个基本的RAG流水线。具体包括:
- 如何解析pdf文档,以幻灯片和从HTML页面导出的内容为例,使用python库以及GPT-4V来解释其中的可视化内容
- 如何处理提取的内容,清洗并将其分块处理
- 如何使用OpenAI嵌入来嵌入处理过的内容
- 如何检索与输入查询相关的内容
- 如何使用GPT-4-turbo生成答案,使用检索到的内容作为上下文
如果您想进一步探索,可以考虑以下优化:
- 尝试使用提供的示例提示
- 进一步分块内容,并为每个块添加元数据作为上下文
- 在检索结果上添加基于规则的过滤,或重新排名结果以展示最相关的内容
您可以将本笔记本中涵盖的技术应用于多种用例,例如可以访问您专有数据的助手,可以阅读您内部政策的客服或FAQ机器人,或者任何需要利用丰富文档的情况,这些文档最好被理解为图像。