VideoMAE
概述
VideoMAE模型由Zhan Tong、Yibing Song、Jue Wang和Limin Wang在VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training中提出。 VideoMAE将掩码自编码器(MAE)扩展到视频领域,声称在多个视频分类基准上达到了最先进的性能。
论文的摘要如下:
在超大规模数据集上进行预训练视频变换器通常是为了在相对较小的数据集上实现最佳性能。在本文中,我们展示了视频掩码自编码器(VideoMAE)是自监督视频预训练(SSVP)的数据高效学习者。我们受到最近ImageMAE的启发,提出了定制的视频管掩码和重建。这些简单的设计被证明对于克服视频重建过程中由时间相关性引起的信息泄漏是有效的。我们在SSVP上获得了三个重要发现:(1)极高的掩码比例(即90%到95%)仍然能够使VideoMAE表现出色。时间冗余的视频内容使得掩码比例高于图像。(2)VideoMAE在非常小的数据集(即大约3k-4k视频)上取得了令人印象深刻的结果,而无需使用任何额外数据。这在一定程度上归因于视频重建任务的挑战性,以强制高级结构学习。(3)VideoMAE表明,对于SSVP来说,数据质量比数据数量更重要。预训练和目标数据集之间的领域转移是SSVP中的重要问题。值得注意的是,我们的VideoMAE使用普通的ViT骨干网络,在不使用任何额外数据的情况下,可以在Kinects-400上达到83.9%,在Something-Something V2上达到75.3%,在UCF101上达到90.8%,在HMDB51上达到61.1%。
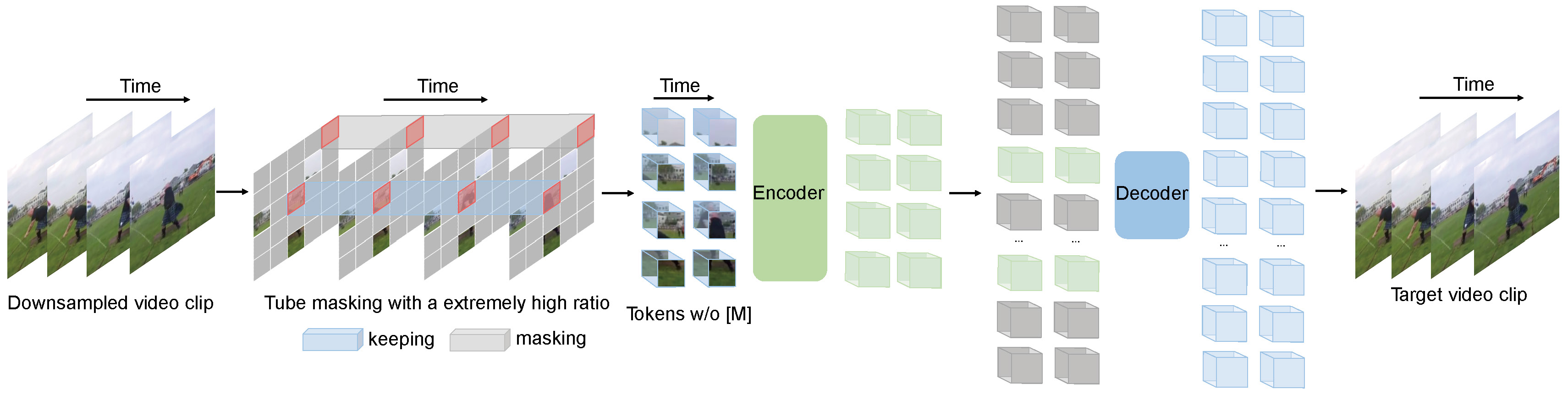 VideoMAE pre-training. Taken from the original paper.
VideoMAE pre-training. Taken from the original paper. 使用缩放点积注意力 (SDPA)
PyTorch 包含一个原生的缩放点积注意力(SDPA)操作符,作为 torch.nn.functional 的一部分。这个函数
包含了几种实现,可以根据输入和使用的硬件进行应用。更多信息请参阅
官方文档
或 GPU 推理
页面。
默认情况下,当有可用实现时,SDPA 用于 torch>=2.1.1,但你也可以在 from_pretrained() 中设置 attn_implementation="sdpa" 来明确请求使用 SDPA。
from transformers import VideoMAEForVideoClassification
model = VideoMAEForVideoClassification.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
...为了获得最佳加速效果,我们建议以半精度加载模型(例如 torch.float16 或 torch.bfloat16)。
在本地基准测试(A100-40GB,PyTorch 2.3.0,操作系统 Ubuntu 22.04)中,使用float32和MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics模型,我们在推理过程中看到了以下加速效果。
| 批量大小 | 平均推理时间(毫秒),eager模式 | 平均推理时间(毫秒),sdpa模型 | 加速比,Sdpa / Eager(倍) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37 | 10 | 3.7 |
| 2 | 24 | 18 | 1.33 |
| 4 | 43 | 32 | 1.34 |
| 8 | 84 | 60 | 1.4 |
资源
以下是官方Hugging Face和社区(由🌎表示)提供的资源列表,帮助您开始使用VideoMAE。如果您有兴趣提交资源以包含在此处,请随时打开一个Pull Request,我们将进行审核!理想情况下,资源应展示一些新内容,而不是重复现有资源。
视频分类
- A notebook 展示了如何在自定义数据集上微调 VideoMAE 模型。
- 视频分类任务指南
- A 🤗 Space 展示如何使用视频分类模型进行推理。
VideoMAEConfig
类 transformers.VideoMAEConfig
< source >( image_size = 224 patch_size = 16 num_channels = 3 num_frames = 16 tubelet_size = 2 hidden_size = 768 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 intermediate_size = 3072 hidden_act = 'gelu' hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 qkv_bias = True use_mean_pooling = True decoder_num_attention_heads = 6 decoder_hidden_size = 384 decoder_num_hidden_layers = 4 decoder_intermediate_size = 1536 norm_pix_loss = True **kwargs )
参数
- image_size (
int, optional, 默认为 224) — 每张图像的大小(分辨率)。 - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — 每个补丁的大小(分辨率)。 - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — 输入通道的数量。 - num_frames (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — 每个视频中的帧数。 - tubelet_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2) — 管状体的数量。 - hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, 可选, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数量。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 3072) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu","relu","selu"和"gelu_new". - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 嵌入层、编码器和池化器中所有全连接层的 dropout 概率。 - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比例。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的截断正态初始化器的标准差。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - qkv_bias (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否向查询、键和值添加偏置。 - use_mean_pooling (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否对最终的隐藏状态进行平均池化,而不是使用[CLS]标记的最终隐藏状态。 - decoder_num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 6) — 解码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - decoder_hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 384) — 解码器的维度。 - decoder_num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, 默认为 4) — 解码器中的隐藏层数。 - decoder_intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 1536) — 解码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - norm_pix_loss (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否对目标补丁像素进行归一化。
这是用于存储VideoMAEModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化一个VideoMAE模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生类似于VideoMAE MCG-NJU/videomae-base架构的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import VideoMAEConfig, VideoMAEModel
>>> # Initializing a VideoMAE videomae-base style configuration
>>> configuration = VideoMAEConfig()
>>> # Randomly initializing a model from the configuration
>>> model = VideoMAEModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configVideoMAEFeatureExtractor
预处理一张图像或一批图像。
VideoMAEImageProcessor
类 transformers.VideoMAEImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Dict[str, int] = None resample: Resampling =
参数
- do_resize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否将图像的(高度,宽度)尺寸调整为指定的size。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_resize参数覆盖此设置。 - size (
Dict[str, int]可选, 默认为{"shortest_edge" -- 224}): 调整大小后输出图像的尺寸。图像的短边将被调整为size["shortest_edge"],同时保持原始图像的宽高比。可以在preprocess方法中通过size覆盖此设置。 - resample (
PILImageResampling, 可选, 默认为Resampling.BILINEAR) — 如果调整图像大小,则使用的重采样过滤器。可以在preprocess方法中通过resample参数覆盖。 - do_center_crop (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否将图像中心裁剪到指定的crop_size。可以通过preprocess方法中的do_center_crop参数进行覆盖。 - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为{"height" -- 224, "width": 224}): 应用中心裁剪后图像的大小。可以通过preprocess方法中的crop_size参数进行覆盖。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否通过指定的比例rescale_factor来重新缩放图像。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_rescale参数进行覆盖。 - rescale_factor (
int或float, 可选, 默认为1/255) — 定义在重新缩放图像时使用的比例因子。可以在preprocess方法中通过rescale_factor参数覆盖此设置。 - do_normalize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否对图像进行归一化。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_normalize参数进行覆盖。 - image_mean (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — 如果对图像进行归一化,则使用的均值。这是一个浮点数或与图像通道数长度相同的浮点数列表。可以通过preprocess方法中的image_mean参数进行覆盖。 - image_std (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — 如果对图像进行归一化,则使用的标准差。这是一个浮点数或与图像通道数长度相同的浮点数列表。可以通过preprocess方法中的image_std参数进行覆盖。
构建一个VideoMAE图像处理器。
预处理
< source >( videos: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]] do_resize: bool = None size: typing.Dict[str, int] = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: bool = None crop_size: typing.Dict[str, int] = None do_rescale: bool = None rescale_factor: float = None do_normalize: bool = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: ChannelDimension =
参数
- 图像 (
ImageInput) — 要预处理的图像。期望输入单个或批量的图像,像素值范围从0到255。如果传入的图像像素值在0到1之间,请设置do_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — 是否调整图像大小. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — 应用调整大小后的图像尺寸。 - resample (
PILImageResampling, 可选, 默认为self.resample) — 如果调整图像大小,则使用的重采样过滤器。这可以是枚举PILImageResampling中的一个,只有在do_resize设置为True时才会生效。 - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_centre_crop) — 是否对图像进行中心裁剪。 - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — 应用中心裁剪后图像的大小。 - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — 是否将图像值缩放到 [0 - 1] 之间。 - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — 如果do_rescale设置为True,则用于重新缩放图像的重新缩放因子。 - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — 是否对图像进行归一化处理。 - image_mean (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为self.image_mean) — 图像均值. - image_std (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为self.image_std) — 图像标准差. - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选) — 返回的张量类型。可以是以下之一:- 未设置:返回一个
np.ndarray列表。 TensorType.TENSORFLOW或'tf':返回一个类型为tf.Tensor的批次。TensorType.PYTORCH或'pt':返回一个类型为torch.Tensor的批次。TensorType.NUMPY或'np':返回一个类型为np.ndarray的批次。TensorType.JAX或'jax':返回一个类型为jax.numpy.ndarray的批次。
- 未设置:返回一个
- data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选, 默认为ChannelDimension.FIRST) — 输出图像的通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。- 未设置:使用输入图像的推断通道维度格式。
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:"channels_first"或ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。"channels_last"或ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。"none"或ChannelDimension.NONE: 图像格式为 (height, width)。
预处理一张图像或一批图像。
VideoMAEModel
类 transformers.VideoMAEModel
< source >( config )
参数
- config (VideoMAEConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
裸的VideoMAE模型转换器输出原始隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。 该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其用作常规的PyTorch模块,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有事项。
前进
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor bool_masked_pos: typing.Optional[torch.BoolTensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 VideoMAEImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length), 可选) — 布尔掩码位置。指示哪些补丁被掩码(1)和哪些没有被掩码(0)。批次中的每个视频必须具有相同数量的掩码补丁。如果为None,则考虑所有补丁。序列长度为(num_frames // tubelet_size) * (image_size // patch_size) ** 2.
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(VideoMAEConfig)和输入。
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
VideoMAEModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import av
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, VideoMAEModel
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>> def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
... '''
... Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
... Args:
... container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
... indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
... Returns:
... result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
... '''
... frames = []
... container.seek(0)
... start_index = indices[0]
... end_index = indices[-1]
... for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
... if i > end_index:
... break
... if i >= start_index and i in indices:
... frames.append(frame)
... return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
>>> def sample_frame_indices(clip_len, frame_sample_rate, seg_len):
... '''
... Sample a given number of frame indices from the video.
... Args:
... clip_len (`int`): Total number of frames to sample.
... frame_sample_rate (`int`): Sample every n-th frame.
... seg_len (`int`): Maximum allowed index of sample's last frame.
... Returns:
... indices (`List[int]`): List of sampled frame indices
... '''
... converted_len = int(clip_len * frame_sample_rate)
... end_idx = np.random.randint(converted_len, seg_len)
... start_idx = end_idx - converted_len
... indices = np.linspace(start_idx, end_idx, num=clip_len)
... indices = np.clip(indices, start_idx, end_idx - 1).astype(np.int64)
... return indices
>>> # video clip consists of 300 frames (10 seconds at 30 FPS)
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(
... repo_id="nielsr/video-demo", filename="eating_spaghetti.mp4", repo_type="dataset"
... )
>>> container = av.open(file_path)
>>> # sample 16 frames
>>> indices = sample_frame_indices(clip_len=16, frame_sample_rate=1, seg_len=container.streams.video[0].frames)
>>> video = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base")
>>> model = VideoMAEModel.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base")
>>> # prepare video for the model
>>> inputs = image_processor(list(video), return_tensors="pt")
>>> # forward pass
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 1568, 768]VideoMAEForPreTraining
VideoMAEForPreTraining 包括顶部的解码器,用于自监督预训练。
类 transformers.VideoMAEForPreTraining
< source >( config )
参数
- config (VideoMAEConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
VideoMAE模型变压器,顶部带有解码器,用于自监督预训练。 该模型是PyTorch torch.nn.Module的子类。将其用作常规的PyTorch模块,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor bool_masked_pos: BoolTensor head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.videomae.modeling_videomae.VideoMAEForPreTrainingOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 VideoMAEImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — 布尔掩码位置。指示哪些补丁被掩码(1)和哪些没有被掩码(0)。批次中的每个视频必须具有相同数量的掩码补丁。序列长度为(num_frames // tubelet_size) * (image_size // patch_size) ** 2.
返回
transformers.models.videomae.modeling_videomae.VideoMAEForPreTrainingOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.videomae.modeling_videomae.VideoMAEForPreTrainingOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(VideoMAEConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,)) — 像素重建损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, patch_size ** 2 * num_channels)) — 像素重建的 logits。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每一层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。
VideoMAEForPreTraining 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, VideoMAEForPreTraining
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import torch
>>> num_frames = 16
>>> video = list(np.random.randint(0, 256, (num_frames, 3, 224, 224)))
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base")
>>> model = VideoMAEForPreTraining.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base")
>>> pixel_values = image_processor(video, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> num_patches_per_frame = (model.config.image_size // model.config.patch_size) ** 2
>>> seq_length = (num_frames // model.config.tubelet_size) * num_patches_per_frame
>>> bool_masked_pos = torch.randint(0, 2, (1, seq_length)).bool()
>>> outputs = model(pixel_values, bool_masked_pos=bool_masked_pos)
>>> loss = outputs.lossVideoMAEForVideoClassification
类 transformers.VideoMAEForVideoClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (VideoMAEConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
VideoMAE 模型转换器,顶部带有视频分类头(在所有标记的平均池化隐藏状态之上的线性层),例如用于 ImageNet。 该模型是 PyTorch torch.nn.Module 的子类。将其用作常规的 PyTorch 模块,并参考 PyTorch 文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有事项。
前进
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 VideoMAEImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor形状为(batch_size,), 可选) — 用于计算图像分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(VideoMAEConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,), 可选, 当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)分数(在 SoftMax 之前)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每个阶段的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每个阶段输出的隐藏状态(也称为特征图)。 -
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每个层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
VideoMAEForVideoClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import av
>>> import torch
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, VideoMAEForVideoClassification
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>> def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
... '''
... Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
... Args:
... container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
... indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
... Returns:
... result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
... '''
... frames = []
... container.seek(0)
... start_index = indices[0]
... end_index = indices[-1]
... for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
... if i > end_index:
... break
... if i >= start_index and i in indices:
... frames.append(frame)
... return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
>>> def sample_frame_indices(clip_len, frame_sample_rate, seg_len):
... '''
... Sample a given number of frame indices from the video.
... Args:
... clip_len (`int`): Total number of frames to sample.
... frame_sample_rate (`int`): Sample every n-th frame.
... seg_len (`int`): Maximum allowed index of sample's last frame.
... Returns:
... indices (`List[int]`): List of sampled frame indices
... '''
... converted_len = int(clip_len * frame_sample_rate)
... end_idx = np.random.randint(converted_len, seg_len)
... start_idx = end_idx - converted_len
... indices = np.linspace(start_idx, end_idx, num=clip_len)
... indices = np.clip(indices, start_idx, end_idx - 1).astype(np.int64)
... return indices
>>> # video clip consists of 300 frames (10 seconds at 30 FPS)
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(
... repo_id="nielsr/video-demo", filename="eating_spaghetti.mp4", repo_type="dataset"
... )
>>> container = av.open(file_path)
>>> # sample 16 frames
>>> indices = sample_frame_indices(clip_len=16, frame_sample_rate=1, seg_len=container.streams.video[0].frames)
>>> video = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics")
>>> model = VideoMAEForVideoClassification.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics")
>>> inputs = image_processor(list(video), return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
... logits = outputs.logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 400 Kinetics-400 classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
eating spaghetti