! [ -e /content ] && pip install -Uqq fastai # 在Colab上升级fastaiTorch Core
from __future__ import annotations
from fastai.imports import *
from fastai.torch_imports import *
from packaging.version import parsefrom PIL import Imagefrom nbdev.showdoc import *_all_ = ['progress_bar','master_bar']defaults.benchmark = Truedef setup_cuda(benchmark=defaults.benchmark):
"Sets the main cuda device and sets `cudnn.benchmark` to `benchmark`"
if torch.cuda.is_available():
if torch.cuda.current_device()==0:
def_gpu = int(os.environ.get('DEFAULT_GPU') or 0)
if torch.cuda.device_count()>=def_gpu: torch.cuda.set_device(def_gpu)
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = benchmarkfastai库中使用的基本pytorch函数
数组和显示
@delegates(plt.subplots, keep=True)
def subplots(
nrows:int=1, # 返回的轴网格中的行数
ncols:int=1, # 返回的轴网格中的列数
figsize:tuple=None, # 返回图形的长、宽(英寸)
imsize:int=3, # 返回图形中将显示的图像尺寸(以英寸为单位)
suptitle:str=None, # 标题将设置为返回的图形
**kwargs
) -> (plt.Figure, plt.Axes): # 返回 fig 和 ax 作为元组
"Returns a figure and set of subplots to display images of `imsize` inches"
if figsize is None:
h=nrows*imsize if suptitle is None or imsize>2 else nrows*imsize+0.6 #https://github.com/matplotlib/matplotlib/issues/5355
figsize=(ncols*imsize, h)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize, **kwargs)
if suptitle is not None: fig.suptitle(suptitle)
if nrows*ncols==1: ax = array([ax])
return fig,ax这在 get_grid 中使用。suptitle、sharex、sharey、squeeze、subplot_kw 和 gridspec_kw 都会传递给 plt.subplots。
_,axs = subplots()
test_eq(axs.shape,[1])
plt.close()
_,axs = subplots(2,3)
test_eq(axs.shape,[2,3])
plt.close()def _fig_bounds(x):
r = x//32
return min(5, max(1,r))@delegates(plt.Axes.imshow, keep=True, but=['shape', 'imlim'])
def show_image(im, ax=None, figsize=None, title=None, ctx=None, **kwargs):
"Show a PIL or PyTorch image on `ax`."
# 处理PyTorch轴顺序
if hasattrs(im, ('data','cpu','permute')):
im = im.data.cpu()
if im.shape[0]<5: im=im.permute(1,2,0)
elif not isinstance(im,np.ndarray): im=array(im)
# 处理单通道图像
if im.shape[-1]==1: im=im[...,0]
ax = ifnone(ax,ctx)
if figsize is None: figsize = (_fig_bounds(im.shape[0]), _fig_bounds(im.shape[1]))
if ax is None: _,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
ax.imshow(im, **kwargs)
if title is not None: ax.set_title(title)
ax.axis('off')
return axshow_image 可以显示PIL图像……
im = Image.open(TEST_IMAGE_BW)
ax = show_image(im, cmap="Greys")
…和具有标准 CHW 维度顺序的彩色图像…
im2 = np.array(Image.open(TEST_IMAGE))
ax = show_image(im2, figsize=(2,2))
…以及维度顺序为HWC的彩色图像…
im3 = torch.as_tensor(im2).permute(2,0,1)
ax = show_image(im3, figsize=(2,2))
@delegates(show_image, keep=True)
def show_titled_image(o, **kwargs):
"Call `show_image` destructuring `o` to `(img,title)`"
show_image(o[0], title=str(o[1]), **kwargs)show_titled_image((im3,'A puppy'), figsize=(2,2))
显示所有图像 ims 作为子图,并使用 titles 进行标注。suptitle 提供了一种为所有图像创建图形标题的方法。如果使用 suptitle,则默认使用 constrained_layout,除非将 constrained_layout 设置为 False。
@delegates(subplots)
def show_images(ims, nrows=1, ncols=None, titles=None, **kwargs):
"Show all images `ims` as subplots with `rows` using `titles`."
if ncols is None: ncols = int(math.ceil(len(ims)/nrows))
if titles is None: titles = [None]*len(ims)
axs = subplots(nrows, ncols, **kwargs)[1].flat
for im,t,ax in zip(ims, titles, axs): show_image(im, ax=ax, title=t)show_images((im,im3),titles=('number','puppy'),suptitle='Number Puppy', imsize=3)
ArrayImage、ArrayImageBW 和 ArrayMask 是 ndarray 的子类,能够自我展示。
class ArrayBase(ndarray):
"An `ndarray` that can modify casting behavior"
@classmethod
def _before_cast(cls, x): return x if isinstance(x,ndarray) else array(x)class ArrayImageBase(ArrayBase):
"Base class for arrays representing images"
_show_args = {'cmap':'viridis'}
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
return show_image(self, ctx=ctx, **{**self._show_args, **kwargs})class ArrayImage(ArrayImageBase):
"An array representing an image"
passclass ArrayImageBW(ArrayImage):
"An array representing an image"
_show_args = {'cmap':'Greys'}class ArrayMask(ArrayImageBase):
"An array representing an image mask"
_show_args = {'alpha':0.5, 'cmap':'tab20', 'interpolation':'nearest'}im = Image.open(TEST_IMAGE)im_t = cast(im, ArrayImage)
test_eq(type(im_t), ArrayImage)ax = im_t.show(figsize=(2,2))
test_fig_exists(ax)基础知识
@patch
def __array_eq__(self:Tensor,b):
return torch.equal(self,b) if self.dim() else self==bdef _array2tensor(x, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False, **kwargs):
if x.dtype==np.uint16: x = x.astype(np.float32)
# Windows 默认的 numpy 整数数据类型是 int32,而 torch 张量的默认整数数据类型是 int64。
# https://github.com/numpy/numpy/issues/9464
if sys.platform == "win32" and x.dtype==int: x = x.astype(np.int64)
t = torch.as_tensor(x, **kwargs)
t.requires_grad_(requires_grad)
if pin_memory: t.pin_memory()
return t@use_kwargs_dict(dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)
def tensor(x, *rest, **kwargs):
"Like `torch.as_tensor`, but handle lists too, and can pass multiple vector elements directly."
if len(rest): x = (x,)+rest
# There was a Pytorch bug in dataloader using num_workers>0. Haven't confirmed if fixed
# if isinstance(x, (tuple,list)) and len(x)==0: return tensor(0)
res = (x if isinstance(x, Tensor)
else torch.tensor(x, **kwargs) if isinstance(x, (tuple,list,numbers.Number))
else _array2tensor(x, **kwargs) if isinstance(x, ndarray)
else as_tensor(x.values, **kwargs) if isinstance(x, (pd.Series, pd.DataFrame))
# else as_tensor(array(x, **kwargs)) if hasattr(x, '__array__') or is_iter(x)
else _array2tensor(array(x), **kwargs))
if res.dtype is torch.float64: return res.float()
return restest_eq(tensor(torch.tensor([1,2,3])), torch.tensor([1,2,3]))
test_eq(tensor(array([1,2,3])), torch.tensor([1,2,3]))
test_eq(tensor(1,2,3), torch.tensor([1,2,3]))
test_eq_type(tensor(1.0), torch.tensor(1.0))set_seed 对于运行之间的可重现性非常有用。需要记住的是,某些类,例如 Dataloaders,具有内部随机数生成器,这不受此函数的影响,因此必须在创建此类对象之前运行,以确保可重现性。
def set_seed(s, reproducible=False):
"Set random seed for `random`, `torch`, and `numpy` (where available)"
try: torch.manual_seed(s)
except NameError: pass
try: torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(s)
except NameError: pass
try: np.random.seed(s%(2**32-1))
except NameError: pass
random.seed(s)
if reproducible:
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False这是一个如何使用 set_seed 来重置随机数生成器状态的示例。
set_seed(2*33)
a1 = np.random.random()
a2 = torch.rand(())
a3 = random.random()
set_seed(2*33)
b1 = np.random.random()
b2 = torch.rand(())
b3 = random.random()
print('a\'s: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(a1,a2,a3))
print('b\'s: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(b1,b2,a3))a's: 0.154 0.498 0.071
b's: 0.154 0.498 0.071test_eq(a1,b1)
test_eq(a2,b2)
test_eq(a3,b3)get_random_states 和 set_random_states 对于存储状态非常有用,以便您稍后可以返回到该状态。
def get_random_states():
"Gets states for `random`, `torch`, and `numpy` random number generators"
return {'random_state':random.getstate(),
'numpy_state':np.random.get_state(),
'torch_state':torch.get_rng_state(),
'torch_cuda_state':torch.cuda.get_rng_state_all(),
'torch_deterministic':torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic,
'torch_benchmark':torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark}def set_random_states(random_state,numpy_state,torch_state,torch_cuda_state,torch_deterministic,torch_benchmark):
"Set states for `random`, `torch`, and `numpy` random number generators"
random.setstate(random_state)
np.random.set_state(numpy_state)
torch.set_rng_state(torch_state)
torch.cuda.set_rng_state_all(torch_cuda_state)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic=torch_deterministic
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark=torch_benchmark注意到旧值和回退值是相同的,因为我们能够返回到先前的状态。
old_states = get_random_states()
olds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
news = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
set_random_states(**old_states)
rewinds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
print('olds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*olds))
print('news: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*news))
print('rewinds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*rewinds))olds: 0.435 0.134 0.023
news: 0.246 0.363 0.227
rewinds: 0.435 0.134 0.023test_ne(olds,news)
test_eq(olds,rewinds)在no_random中,我们结合了重置状态的思想与get_random_states和set_random_states,并具备set_seed的能力,创建了一个上下文管理器,可以让我们控制代码中某一部分的随机性。
注意:与torch.random.fork_rng类似,但也适用于numpy和random。
@contextmanager
def no_random(seed=42,reproducible=True):
"Stores and retrieves state of random number generators. Sets random seed for `random`, `torch`, and `numpy`."
states = get_random_states()
set_seed(seed,reproducible=reproducible)
try:
yield #我们正在管理全局变量
finally:
set_random_states(**states)以下是一些示例,说明我们如何使用 no_random 来控制代码块中的随机性。
states=get_random_states()
olds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
set_random_states(**states) #回溯上述随机调用
with no_random():
new1 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
with no_random():
new2 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
with no_random(seed=100):
seeded1 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
with no_random(seed=100):
seeded2 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
rewinds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
print('olds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*olds))
print('new1: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*new1))
print('new2: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*new2))
print('seeded1: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*seeded1))
print('seeded2: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*seeded2))
print('rewinds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*rewinds))olds: 0.246 0.363 0.227
new1: 0.639 0.375 0.882
new2: 0.639 0.375 0.882
seeded1: 0.146 0.543 0.112
seeded2: 0.146 0.543 0.112
rewinds: 0.246 0.363 0.227注意到旧值和重置值也是彼此相等的。从这一点来看,我们可以看到 with 块中的所有内容都没有更新块外的状态。在块内,任何特定种子的状态都会被重置,因此对于相同的种子,您应该得到相同的随机数生成器结果。
注意:重要的是要记住,像 Dataloader 这样的类具有内部随机数生成器,而 no_random 将对这些随机数生成器没有影响。
test_ne(olds,new1)
test_eq(new1,new2)
test_ne(new1,seeded1)
test_eq(seeded1,seeded2)
test_eq(olds,rewinds)def unsqueeze(x, dim=-1, n=1):
"Same as `torch.unsqueeze` but can add `n` dims"
for _ in range(n): x = x.unsqueeze(dim)
return xt = tensor([1])
t2 = unsqueeze(t, n=2)
test_eq(t2,t[:,None,None])def unsqueeze_(x, dim=-1, n=1):
"Same as `torch.unsqueeze_` but can add `n` dims"
for _ in range(n): x.unsqueeze_(dim)
return xt = tensor([1])
unsqueeze_(t, n=2)
test_eq(t, tensor([1]).view(1,1,1))def _fa_rebuild_tensor (cls, *args, **kwargs): return cls(torch._utils._rebuild_tensor_v2(*args, **kwargs))
def _fa_rebuild_qtensor(cls, *args, **kwargs): return cls(torch._utils._rebuild_qtensor (*args, **kwargs))def apply(func, x, *args, **kwargs):
"Apply `func` recursively to `x`, passing on args"
if is_listy(x): return type(x)([apply(func, o, *args, **kwargs) for o in x])
if isinstance(x,(dict,MutableMapping)): return {k: apply(func, v, *args, **kwargs) for k,v in x.items()}
res = func(x, *args, **kwargs)
return res if x is None else retain_type(res, x)def maybe_gather(x, axis=0):
"Gather copies of `x` on `axis` (if training is distributed)"
if num_distrib()<=1: return x
ndim = x.ndim
res = [x.new_zeros(*x.shape if ndim > 0 else (1,)) for _ in range(num_distrib())]
torch.distributed.all_gather(res, x.contiguous() if ndim > 0 else x[None])
return torch.cat(res, dim=axis) if ndim > 0 else torch.cat(res, dim=axis).mean()def to_detach(b, cpu=True, gather=True):
"Recursively detach lists of tensors in `b `; put them on the CPU if `cpu=True`."
def _inner(x, cpu=True, gather=True):
if not isinstance(x,Tensor): return x
x = x.detach()
if gather: x = maybe_gather(x)
return x.cpu() if cpu else x
return apply(_inner, b, cpu=cpu, gather=gather)gather 仅在分布式训练期间适用,结果张量将是通过进程收集的,如果 gather=True (因此,批量大小将乘以进程的数量)。
def to_half(b):
"Recursively map floating point tensors in `b ` to FP16."
return apply(lambda x: x.half() if torch.is_floating_point(x) else x, b)def to_float(b):
"Recursively map floating point tensors in `b ` to float."
return apply(lambda x: x.float() if torch.is_floating_point(x) else x, b)# None: 可用时为真;True: 不可用时报错;False: 使用CPU
defaults.use_cuda = Nonedef _has_mps():
if nested_attr(torch, 'backends.mps.is_available', noop)(): return True
return nested_attr(torch, 'backends.mps.is_built', False)()
def default_device(use=-1):
"Return or set default device; `use_cuda`: -1 - CUDA/mps if available; True - error if not available; False - CPU"
if use == -1: use = defaults.use_cuda
else: defaults.use_cuda=use
if use is None:
if torch.cuda.is_available() or _has_mps(): use = True
if use:
if torch.cuda.is_available(): return torch.device(torch.cuda.current_device())
if _has_mps(): return torch.device('mps')
return torch.device('cpu')::: {#cell-73 .cell 0=‘c’ 1=‘u’ 2=‘d’ 3=‘a’}
if torch.cuda.is_available():
_td = torch.device(torch.cuda.current_device())
test_eq(default_device(-1), _td)
test_eq(default_device(True), _td)
else:
test_eq(default_device(False), torch.device('cpu'))
default_device(-1);:::
def to_device(b, device=None, non_blocking=False):
"Recursively put `b` on `device`."
if defaults.use_cuda==False: device='cpu'
elif device is None: device=default_device()
def _inner(o):
# 待办事项:在发布后添加 TensorDict
if isinstance(o,Tensor): return o.to(device, non_blocking=non_blocking)
return o
return apply(_inner, b)t = to_device((3,(tensor(3),tensor(2))))
t1,(t2,t3) = t::: {#cell-76 .cell 0=‘c’ 1=‘u’ 2=‘d’ 3=‘a’}
if torch.cuda.is_available():
test_eq_type(t,(3,(tensor(3).cuda(),tensor(2).cuda())))
test_eq(t2.type(), "torch.cuda.LongTensor")
test_eq(t3.type(), "torch.cuda.LongTensor"):::
def to_cpu(b):
"Recursively map tensors in `b ` to the cpu."
return to_device(b,'cpu')t3 = to_cpu(t3)
test_eq(t3.type(), "torch.LongTensor")
test_eq(t3, 2)def to_np(x):
"Convert a tensor to a numpy array."
return apply(lambda o: o.data.cpu().numpy(), x)t3 = to_np(t3)
test_eq(type(t3), np.ndarray)
test_eq(t3, 2)def to_concat(xs, dim=0):
"Concat the element in `xs` (recursively if they are tuples/lists of tensors)"
if not xs: return xs
if is_listy(xs[0]): return type(xs[0])([to_concat([x[i] for x in xs], dim=dim) for i in range_of(xs[0])])
if isinstance(xs[0],dict): return {k: to_concat([x[k] for x in xs], dim=dim) for k in xs[0].keys()}
#我们可能会收到无法连接的xs(例如文本分类器的输入),
# 在这种情况下,我们返回一个大型列表。
try: return retain_type(torch.cat(xs, dim=dim), xs[0])
except: return sum([L(retain_type(o_.index_select(dim, tensor(i)).squeeze(dim), xs[0])
for i in range_of(o_)) for o_ in xs], L())test_eq(to_concat([tensor([1,2]), tensor([3,4])]), tensor([1,2,3,4]))
test_eq(to_concat([tensor([[1,2]]), tensor([[3,4]])], dim=1), tensor([[1,2,3,4]]))
test_eq_type(to_concat([(tensor([1,2]), tensor([3,4])), (tensor([3,4]), tensor([5,6]))]), (tensor([1,2,3,4]), tensor([3,4,5,6])))
test_eq_type(to_concat([[tensor([1,2]), tensor([3,4])], [tensor([3,4]), tensor([5,6])]]), [tensor([1,2,3,4]), tensor([3,4,5,6])])
test_eq_type(to_concat([(tensor([1,2]),), (tensor([3,4]),)]), (tensor([1,2,3,4]),))
test_eq(to_concat([tensor([[1,2]]), tensor([[3,4], [5,6]])], dim=1), [tensor([1]),tensor([3, 5]),tensor([4, 6])])test_eq(type(to_concat([dict(foo=tensor([1,2]), bar=tensor(3,4))])), dict)张量子类型
# 解析的PyTorch版本,用于更快的版本检查
_torch_version = parse(torch.__version__)
_torch_20 = parse('2.0')
_torch_113 = parse('1.13')
_torch_112 = parse('1.12')@patch
def set_meta(self:Tensor, x, as_copy=False):
"Set all metadata in `__dict__`"
if not hasattr(x,'__dict__'): return
# XXX:一旦PyTorch 1.7.1版本发布,请将其更改为`deepcopy`,并检查nb 23分割拟合是否正常工作。
self.__dict__ = copy(x.__dict__) if as_copy else x.__dict__if not hasattr(torch,'as_subclass'): torch.as_subclass = torch.Tensor.as_subclass@patch
def as_subclass(self:Tensor, typ):
"Cast to `typ` and include `__dict__` and meta"
return retain_meta(self, torch.as_subclass(self, typ))Tensor.set_meta 和 Tensor.as_subclass 一起工作,以在转换后保持 __dict__。
class _T(Tensor): pass
t = tensor(1.).requires_grad_()
t.img_size = 1
t2 = t.as_subclass(_T)
test_eq(t.img_size, t2.img_size)
test_eq(t2.img_size, 1)
assert(t2.requires_grad_)def _torch_handled(args, opt, func):
if func not in opt: return False
for oks in opt[func]:
if all(isinstance(arg,ok) for arg,ok in zip(args,oks) if ok): return True# 来自 https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/13c975684a220ec096216ec6468ccd0dc90ff50a/torch/_tensor.py#L34
def _rebuild_from_type(func, type, args, dict):
ret = func(*args).as_subclass(type)
ret.__dict__ = dict
return retdef _find_args(x):
x0 = x[0] if is_listy(x[0]) and x[0] else x
return [a for a in x0 if hasattr(a,'__dict__')]class TensorBase(Tensor):
"A `Tensor` which support subclass pickling, and maintains metadata when casting or after methods"
debug,_opt = False,defaultdict(list)
def __new__(cls, x, **kwargs):
res = cast(tensor(x), cls)
for k,v in kwargs.items(): setattr(res, k, v)
return res
@classmethod
def _before_cast(cls, x): return tensor(x)
def __repr__(self): return re.sub('tensor', self.__class__.__name__, super().__repr__())
def __reduce_ex__(self, proto):
if _torch_version >= _torch_20:
return super().__reduce_ex__(proto)
else:
torch.utils.hooks.warn_if_has_hooks(self)
args = (self.storage(), self.storage_offset(), tuple(self.size()), self.stride())
if self.is_quantized: args = args + (self.q_scale(), self.q_zero_point())
args = args + (self.requires_grad, OrderedDict())
f = torch._utils._rebuild_qtensor if self.is_quantized else torch._utils._rebuild_tensor_v2
return (_rebuild_from_type, (f, type(self), args, self.__dict__))
@classmethod
def register_func(cls, func, *oks): cls._opt[func].append(oks)
@classmethod
def __torch_function__(cls, func, types, args=(), kwargs=None):
if cls.debug and func.__name__ not in ('__str__','__repr__'): print(func, types, args, kwargs)
if _torch_handled(args, cls._opt, func): types = (torch.Tensor,)
res = super().__torch_function__(func, types, args, ifnone(kwargs, {}))
dict_objs = _find_args(args) if args else _find_args(list(kwargs.values()))
if issubclass(type(res),TensorBase) and dict_objs: res.set_meta(dict_objs[0],as_copy=True)
elif dict_objs and is_listy(res): [r.set_meta(dict_objs[0],as_copy=True) for r in res if issubclass(type(r),TensorBase)]
return res
def new_tensor(self, size, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False):
cls = type(self)
return self.as_subclass(Tensor).new_tensor(size, dtype=dtype, device=device, requires_grad=requires_grad).as_subclass(cls)
def new_ones(self, data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False):
cls = type(self)
return self.as_subclass(Tensor).new_ones(data, dtype=dtype, device=device, requires_grad=requires_grad).as_subclass(cls)
def new(self, x=None):
cls = type(self)
res = self.as_subclass(Tensor).new() if x is None else self.as_subclass(Tensor).new(x)
return res.as_subclass(cls)
def requires_grad_(self, requires_grad=True):
# 解决方法:https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50219
self.requires_grad = requires_grad
return self
def clone(self, *, memory_format=None):
cls = type(self)
return self.as_subclass(Tensor).clone(memory_format=memory_format).as_subclass(cls)
def new_empty(self, size, *, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, pin_memory=False, requires_grad=False):
cls = type(self)
if _torch_version < _torch_113 and layout is None:
layout = torch.strided
if _torch_version < _torch_112:
return super().new_empty(size, dtype=dtype, layout=layout, device=device, pin_memory=pin_memory, requires_grad=requires_grad)
return self.as_subclass(Tensor).new_empty(size, dtype=dtype, layout=layout, device=device, pin_memory=pin_memory, requires_grad=requires_grad).as_subclass(cls)
def new_empty(self, *size, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, pin_memory=False, requires_grad=False):
cls = type(self)
if _torch_version < _torch_113 and layout is None:
layout = torch.strided
if _torch_version < _torch_112:
return super().new_empty(*size, dtype=dtype, layout=layout, device=device, pin_memory=pin_memory, requires_grad=requires_grad)
return self.as_subclass(Tensor).new_empty(*size, dtype=dtype, layout=layout, device=device, pin_memory=pin_memory, requires_grad=requires_grad).as_subclass(cls)TensorBase 钩住 __torch_function__ 以确保元数据不会丢失。要查看所有被调用的函数,请设置 debug。
a = TensorBase(1)
TensorBase.debug=True
1/(a+1)TensorBase(0.5000)TensorBase及其子类还允许传递元数据大小作为img_size…
from torch.utils.data._utils.collate import default_collatea = TensorBase(1,img_size=(128,128))
test_eq(a.img_size,(128,128))
b = cast(a,TensorBase)
test_eq(b.img_size,(128,128))
test_eq(torch.stack([a,b],0).img_size,(128,128))
test_eq(default_collate([a,b]).img_size,(128,128))class _TImage(TensorBase): pass
class _TImage2(_TImage): pass
t1 = _TImage([1.])
t2 = _TImage2([1.])
t2+t1_TImage2([2.])class _T(TensorBase): pass
t = _T(range(5))
test_eq(t[0], 0)
test_eq_type(t+1, _T(range(1,6)))
test_eq(repr(t), '_T([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])')
test_eq_type(t[_T([False,False,True,True,True])], _T([2,3,4]))
test_eq_type(t[_T([2,3,4])], _T([2,3,4]))
test_eq(type(pickle.loads(pickle.dumps(t))), _T)
test_eq_type(t.new_ones(1), _T([1]))
test_eq_type(t.new_tensor([1,2]), _T([1,2]))t = tensor([1,2,3])
m = TensorBase([False,True,True])
test_eq(t[m], tensor([2,3]))
t = tensor([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]])
m = cast(tensor([[False,True,True],
[False,True,True]]), TensorBase)
test_eq(t[m], tensor([2,3,2,3]))t = tensor([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]])
t.img_size = 1
t2 = cast(t, TensorBase)
test_eq(t2.img_size, t.img_size)
x = retain_type(tensor([4,5,6]), t2)
test_eq(x.img_size, t.img_size)
t3 = TensorBase([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]], img_size=1)
test_eq(t3.img_size, t.img_size)
t4 = t2+1
t4.img_size = 2
test_eq(t2.img_size, 1)
test_eq(t4.img_size, 2)
# 这将导致`Tensor`失败,但使用`TensorBase`则可以正常工作。
test_eq(pickle.loads(pickle.dumps(t2)).img_size, t2.img_size)# 测试 https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47186
class _T(TensorBase): ...
t = _T([1.])
test_eq_type(t.new([1,2]), _T([1.,2.]))
test_eq_type(t.new(), _T([]))# 测试 https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50219
x = TensorBase(torch.rand(4,3,16,16))
with torch.no_grad():
y = x.requires_grad_()
assert y.requires_grad and x.requires_gradx = TensorBase(torch.rand(4,3,16,16))
x.test = 'test metadata'
y = deepcopy(x)
assert hasattr(y, 'test') and y.test == x.testclass TensorImageBase(TensorBase):
_show_args = ArrayImageBase._show_args
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
return show_image(self, ctx=ctx, **{**self._show_args, **kwargs})class TensorImage(TensorImageBase): passclass TensorImageBW(TensorImage): _show_args = ArrayImageBW._show_argsclass TensorMask(TensorImageBase):
_show_args = ArrayMask._show_args
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
codes = getattr(self, 'codes', None)
if codes is not None: kwargs = merge({'vmin': 0, 'vmax': len(codes)}, kwargs)
return super().show(ctx=ctx, **kwargs)for o in Tensor.__getitem__, Tensor.__ne__,Tensor.__eq__,Tensor.add,Tensor.sub,Tensor.mul,Tensor.div,Tensor.__rsub__,Tensor.__radd__,Tensor.matmul,Tensor.bmm:
TensorBase.register_func(o, TensorMask, TensorImageBase)
TensorBase.register_func(o, TensorImageBase, TensorMask)
TensorMask.register_func(torch.einsum, str, TensorImageBase, TensorMask)
TensorMask.register_func(torch.einsum, str, TensorMask, TensorImageBase)im = Image.open(TEST_IMAGE)
im_t = cast(array(im), TensorImage)
test_eq(type(im_t), TensorImage)im_t2 = cast(tensor(1), TensorMask)
test_eq(type(im_t2), TensorMask)
test_eq(im_t2, tensor(1))
ax = im_t.show(figsize=(2,2))
_ =(im_t == im_t2)
test_fig_exists(ax)TensorMask和TensorImageBase对象之间的操作返回TensorImageBase对象的类型:
a = TensorMask([1,2])
test_eq_type(TensorImage(1)+a, TensorImage([2,3]))
test_eq_type(1-a, TensorMask([0,-1]))::: {#cell-117 .cell 0=‘h’ 1=‘i’ 2=‘d’ 3=‘e’ 4=‘(’ 5=‘t’ 6=‘o’ 7=’_’ 8=‘c’ 9=‘o’ 10=‘n’ 11=‘c’ 12=‘a’ 13=‘t’ 14=’ ’ 15=‘的’ 16=‘最’ 17=‘后’ 18=‘一’ 19=‘次’ 20=‘测’ 21=‘试’ 22=‘)’}
test_eq_type(to_concat([TensorImage([1,2]), TensorImage([3,4])]), TensorImage([1,2,3,4])):::
class TensorFlowField(TensorBase): pass
TensorImage.register_func(F.grid_sample, TensorImageBase, TensorFlowField)t1 = TensorImage([1.]).view(1,1,1,1)
t2 = TensorFlowField([1.,1.]).view(1,1,1,2)
test_eq_type(F.grid_sample(t1, t2), TensorImage([[[[0.25]]]]))::: {#cell-120 .cell 0=‘e’ 1=‘x’ 2=‘p’ 3=‘o’ 4=‘r’ 5=‘t’}
class TensorCategory(TensorBase): pass
TensorBase.register_func(Tensor.__getitem__, TensorImageBase, TensorCategory):::
tc = TensorCategory([1,2,3])
mask_t = TensorMask([0,2,4,5])
im_t = TensorImage([0,2,4,5])
test_eq(mask_t[tc], tensor([2,4,5]))
test_eq(im_t[tc], tensor([2,4,5]))::: {#cell-122 .cell 0=‘e’ 1=‘x’ 2=‘p’ 3=‘o’ 4=‘r’ 5=‘t’}
class TensorMultiCategory(TensorCategory): pass:::
class TitledTensorScalar(TensorBase):
"A tensor containing a scalar that has a `show` method"
def show(self, **kwargs): show_title(self.item(), **kwargs)L -
@patch
def tensored(self:L):
"`mapped(tensor)`"
return self.map(tensor)
@patch
def stack(self:L, dim=0):
"Same as `torch.stack`"
return torch.stack(list(self.tensored()), dim=dim)
@patch
def cat (self:L, dim=0):
"Same as `torch.cat`"
return torch.cat (list(self.tensored()), dim=dim)show_doc(L.tensored)L.tensored
L.tensored ()
mapped(tensor)
如果你的 L 包含张量或可以转换的内容,torch.stack 和 torch.cat 有快捷方式。你可以手动使用 tensored 进行转换。
t = L(([1,2],[3,4]))
test_eq(t.tensored(), [tensor(1,2),tensor(3,4)])show_doc(L.stack)L.stack
L.stack (dim=0)
Same as torch.stack
test_eq(t.stack(), tensor([[1,2],[3,4]]))show_doc(L.cat)L.cat
L.cat (dim=0)
Same as torch.cat
test_eq(t.cat(), tensor([1,2,3,4]))块
def concat(*ls):
"Concatenate tensors, arrays, lists, or tuples"
if not len(ls): return []
it = ls[0]
if isinstance(it,torch.Tensor): res = torch.cat(ls)
elif isinstance(it,ndarray): res = np.concatenate(ls)
else:
res = itertools.chain.from_iterable(map(L,ls))
if isinstance(it,(tuple,list)): res = type(it)(res)
else: res = L(res)
return retain_type(res, it)a,b,c = [1],[1,2],[1,1,2]
test_eq(concat(a,b), c)
test_eq_type(concat(tuple (a),tuple (b)), tuple (c))
test_eq_type(concat(array (a),array (b)), array (c))
test_eq_type(concat(tensor(a),tensor(b)), tensor(c))
test_eq_type(concat(TensorBase(a),TensorBase(b)), TensorBase(c))
test_eq_type(concat([1,1],1), [1,1,1])
test_eq_type(concat(1,1,1), L(1,1,1))
test_eq_type(concat(L(1,2),1), L(1,2,1))class Chunks:
"Slice and int indexing into a list of lists"
def __init__(self, chunks, lens=None):
self.chunks = chunks
self.lens = L(map(len,self.chunks) if lens is None else lens)
self.cumlens = np.cumsum(0+self.lens)
self.totlen = self.cumlens[-1]
def __getitem__(self,i):
if isinstance(i,slice): return retain_type(self.getslice(i), old=self.chunks[0])
di,idx = self.doc_idx(i)
return retain_type(self.chunks[di][idx], old=self.chunks[0])
def getslice(self, i):
st_d,st_i = self.doc_idx(ifnone(i.start,0))
en_d,en_i = self.doc_idx(ifnone(i.stop,self.totlen+1))
res = [self.chunks[st_d][st_i:(en_i if st_d==en_d else sys.maxsize)]]
for b in range(st_d+1,en_d): res.append(self.chunks[b])
if st_d!=en_d and en_d<len(self.chunks): res.append(self.chunks[en_d][:en_i])
return concat(*res)
def doc_idx(self, i):
if i<0: i=self.totlen+i # 从末尾开始计数
docidx = np.searchsorted(self.cumlens, i+1)-1
cl = self.cumlens[docidx]
return docidx,i-cldocs = L(list(string.ascii_lowercase[a:b]) for a,b in ((0,3),(3,7),(7,8),(8,16),(16,24),(24,26)))
b = Chunks(docs)
test_eq([b[ o] for o in range(0,5)], ['a','b','c','d','e'])
test_eq([b[-o] for o in range(1,6)], ['z','y','x','w','v'])
test_eq(b[6:13], 'g,h,i,j,k,l,m'.split(','))
test_eq(b[20:77], 'u,v,w,x,y,z'.split(','))
test_eq(b[:5], 'a,b,c,d,e'.split(','))
test_eq(b[:2], 'a,b'.split(','))t = torch.arange(26)
docs = L(t[a:b] for a,b in ((0,3),(3,7),(7,8),(8,16),(16,24),(24,26)))
b = Chunks(docs)
test_eq([b[ o] for o in range(0,5)], range(0,5))
test_eq([b[-o] for o in range(1,6)], [25,24,23,22,21])
test_eq(b[6:13], torch.arange(6,13))
test_eq(b[20:77], torch.arange(20,26))
test_eq(b[:5], torch.arange(5))
test_eq(b[:2], torch.arange(2))docs = L(TensorBase(t[a:b]) for a,b in ((0,3),(3,7),(7,8),(8,16),(16,24),(24,26)))
b = Chunks(docs)
test_eq_type(b[:2], TensorBase(range(2)))
test_eq_type(b[:5], TensorBase(range(5)))
test_eq_type(b[9:13], TensorBase(range(9,13)))简单类型
def show_title(o, ax=None, ctx=None, label=None, color='black', **kwargs):
"Set title of `ax` to `o`, or print `o` if `ax` is `None`"
ax = ifnone(ax,ctx)
if ax is None: print(o)
elif hasattr(ax, 'set_title'):
t = ax.title.get_text()
if len(t) > 0: o = t+'\n'+str(o)
ax.set_title(o, color=color)
elif isinstance(ax, pd.Series):
while label in ax: label += '_'
ax = pd.concat([ax,pd.Series({label: o})])
return axtest_stdout(lambda: show_title("title"), "title")
# 确保在显示为 pandas 系列时列名是唯一的
assert show_title("title", ctx=pd.Series(dict(a=1)), label='a').equals(pd.Series(dict(a=1,a_='title')))class ShowTitle:
"Base class that adds a simple `show`"
_show_args = {'label': 'text'}
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
"Show self"
return show_title(str(self), ctx=ctx, **merge(self._show_args, kwargs))
class TitledInt(Int, ShowTitle):
_show_args = {'label': 'text'}
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
"Show self"
return show_title(str(self), ctx=ctx, **merge(self._show_args, kwargs))
class TitledFloat(Float, ShowTitle):
_show_args = {'label': 'text'}
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
"Show self"
return show_title(str(self), ctx=ctx, **merge(self._show_args, kwargs))
class TitledStr(Str, ShowTitle):
_show_args = {'label': 'text'}
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
"Show self"
return show_title(str(self), ctx=ctx, **merge(self._show_args, kwargs))
class TitledTuple(fastuple, ShowTitle):
_show_args = {'label': 'text'}
def show(self, ctx=None, **kwargs):
"Show self"
return show_title(str(self), ctx=ctx, **merge(self._show_args, kwargs))
add_docs(TitledInt, "An `int` with `show`"); add_docs(TitledStr, "An `str` with `show`");
add_docs(TitledFloat, "A `float` with `show`"); add_docs(TitledTuple, "A `fastuple` with `show`")show_doc(TitledInt, title_level=3)TitledInt
An int with show
show_doc(TitledStr, title_level=3)TitledStr
An str with show
show_doc(TitledFloat, title_level=3)TitledFloat
TitledFloat (x=0)
A float with show
test_stdout(lambda: TitledStr('s').show(), 's')
test_stdout(lambda: TitledInt(1).show(), '1')show_doc(TitledTuple, title_level=3)TitledTuple
TitledTuple (x=None, *rest)
A fastuple with show
df = pd.DataFrame(index = range(1))
row = df.iloc[0]
x = TitledFloat(2.56)
row = x.show(ctx=row, label='lbl')
test_eq(float(row.lbl), 2.56)@patch
def truncate(self:TitledStr, n):
"Truncate self to `n`"
words = self.split(' ')[:n]
return TitledStr(' '.join(words))其他函数
if not hasattr(pd.DataFrame,'_old_init'): pd.DataFrame._old_init = pd.DataFrame.__init__@patch
def __init__(self:pd.DataFrame, data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None, copy=None):
if data is not None and isinstance(data, Tensor): data = to_np(data)
self._old_init(data, index=index, columns=columns, dtype=dtype, copy=copy)def get_empty_df(n):
"Return `n` empty rows of a dataframe"
df = pd.DataFrame(index = range(n))
return [df.iloc[i] for i in range(n)]def display_df(df):
"Display `df` in a notebook or defaults to print"
try: from IPython.display import display, HTML
except: return print(df)
display(HTML(df.to_html()))def get_first(c):
"Get the first element of c, even if c is a dataframe"
return getattr(c, 'iloc', c)[0]def one_param(m):
"First parameter in `m`"
return first(m.parameters())def item_find(x, idx=0):
"Recursively takes the `idx`-th element of `x`"
if is_listy(x): return item_find(x[idx])
if isinstance(x,dict):
key = list(x.keys())[idx] if isinstance(idx, int) else idx
return item_find(x[key])
return xdef find_device(b):
"Recursively search the device of `b`."
return item_find(b).devicet2 = to_device(tensor(0))
dev = default_device()
test_eq(find_device(t2), dev)
test_eq(find_device([t2,t2]), dev)
test_eq(find_device({'a':t2,'b':t2}), dev)
test_eq(find_device({'a':[[t2],[t2]],'b':t2}), dev)def find_bs(b):
"Recursively search the batch size of `b`."
res = item_find(b)
if not hasattr(res, "shape"): return len(b)
return res.shape[0]x = torch.randn(4,5)
x1 = [1,2,3]
test_eq(find_bs(x1), 3)
test_eq(find_bs(x), 4)
test_eq(find_bs((x,x)), 4)
test_eq(find_bs([x, x]), 4)
test_eq(find_bs({'a':x,'b':x}), 4)
test_eq(find_bs({'a':[[x],[x]],'b':x}), 4)def np_func(f):
"Convert a function taking and returning numpy arrays to one taking and returning tensors"
def _inner(*args, **kwargs):
nargs = [to_np(arg) if isinstance(arg,Tensor) else arg for arg in args]
return tensor(f(*nargs, **kwargs))
functools.update_wrapper(_inner, f)
return _inner这个装饰器在将numpy函数用作fastai指标时特别有用,例如:
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score@np_func
def f1(inp,targ): return f1_score(targ, inp)
a1,a2 = array([0,1,1]),array([1,0,1])
t = f1(tensor(a1),tensor(a2))
test_eq(f1_score(a1,a2), t)
assert isinstance(t,Tensor)class Module(nn.Module, metaclass=PrePostInitMeta):
"Same as `nn.Module`, but no need for subclasses to call `super().__init__`"
def __pre_init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__()
def __init__(self): passshow_doc(Module, title_level=3)Module
Module ()
Same as nn.Module, but no need for subclasses to call super().__init__
class _T(Module):
def __init__(self): self.f = nn.Linear(1,1)
def forward(self,x): return self.f(x)
t = _T()
t(tensor([1.]))tensor([-0.0832], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParalleldef get_model(model):
"Return the model maybe wrapped inside `model`."
return model.module if isinstance(model, (DistributedDataParallel, nn.DataParallel)) else modeldef one_hot(x, c):
"One-hot encode `x` with `c` classes."
res = torch.zeros(c, dtype=torch.uint8)
if isinstance(x, Tensor) and x.numel()>0: res[x] = 1.
else: res[list(L(x, use_list=None))] = 1.
return restest_eq(one_hot([1,4], 5), tensor(0,1,0,0,1).byte())
test_eq(one_hot(torch.tensor([]), 5), tensor(0,0,0,0,0).byte())
test_eq(one_hot(2, 5), tensor(0,0,1,0,0).byte())def one_hot_decode(x, vocab=None):
return L(vocab[i] if vocab else i for i,x_ in enumerate(x) if x_==1)test_eq(one_hot_decode(tensor(0,1,0,0,1)), [1,4])
test_eq(one_hot_decode(tensor(0,0,0,0,0)), [ ])
test_eq(one_hot_decode(tensor(0,0,1,0,0)), [2 ])def params(m):
"Return all parameters of `m`"
return [p for p in m.parameters()]def trainable_params(m):
"Return all trainable parameters of `m`"
return [p for p in m.parameters() if p.requires_grad]m = nn.Linear(4,5)
test_eq(trainable_params(m), [m.weight, m.bias])
m.weight.requires_grad_(False)
test_eq(trainable_params(m), [m.bias])norm_types = (nn.BatchNorm1d, nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.BatchNorm3d, nn.InstanceNorm1d, nn.InstanceNorm2d, nn.InstanceNorm3d, nn.LayerNorm)def norm_bias_params(m, with_bias=True):
"Return all bias and BatchNorm parameters"
if isinstance(m, norm_types): return L(m.parameters())
res = L(m.children()).map(norm_bias_params, with_bias=with_bias).concat()
if with_bias and getattr(m, 'bias', None) is not None: res.append(m.bias)
return resfor norm_func in [nn.BatchNorm1d, partial(nn.InstanceNorm1d, affine=True)]:
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(10,20), norm_func(20), nn.Conv1d(3,4, 3))
test_eq(norm_bias_params(model), [model[0].bias, model[1].weight, model[1].bias, model[2].bias])
model = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(10,20, bias=False), nn.Sequential(norm_func(20), nn.Conv1d(3,4,3))])
test_eq(norm_bias_params(model), [model[1][0].weight, model[1][0].bias, model[1][1].bias])
model = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(10,20), nn.Sequential(norm_func(20), nn.Conv1d(3,4,3))])
test_eq(norm_bias_params(model, with_bias=False), [model[1][0].weight, model[1][0].bias])def batch_to_samples(b, max_n=10):
"'Transposes' a batch to (at most `max_n`) samples"
if isinstance(b, Tensor): return retain_types(list(b[:max_n]), [b])
else:
res = L(b).map(partial(batch_to_samples,max_n=max_n))
return retain_types(res.zip(), [b])t = tensor([1,2,3])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([t,t+1], max_n=2), ([1,2],[2,3]))
test_eq(batch_to_samples(tensor([1,2,3]), 10), [1, 2, 3])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), tensor([4,5,6])], 10), [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), tensor([4,5,6])], 2), [(1, 4), (2, 5)])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), [tensor([4,5,6]),tensor([7,8,9])]], 10),
[(1, (4, 7)), (2, (5, 8)), (3, (6, 9))])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), [tensor([4,5,6]),tensor([7,8,9])]], 2), [(1, (4, 7)), (2, (5, 8))])
t = fastuple(tensor([1,2,3]),TensorBase([2,3,4]))
test_eq_type(batch_to_samples(t)[0][1], TensorBase(2))
test_eq(batch_to_samples(t).map(type), [fastuple]*3)@patch
def interp_1d(x:Tensor, xp, fp):
"Same as `np.interp`"
slopes = (fp[1:]-fp[:-1])/(xp[1:]-xp[:-1])
incx = fp[:-1] - (slopes*xp[:-1])
locs = (x[:,None]>=xp[None,:]).long().sum(1)-1
locs = locs.clamp(0,len(slopes)-1)
return slopes[locs]*x + incx[locs]brks = tensor(0,1,2,4,8,64).float()
ys = tensor(range_of(brks)).float()
ys /= ys[-1].item()
pts = tensor(0.2,0.5,0.8,3,5,63)
preds = pts.interp_1d(brks, ys)
test_close(preds.numpy(), np.interp(pts.numpy(), brks.numpy(), ys.numpy()))
plt.scatter(brks,ys)
plt.scatter(pts,preds)
plt.legend(['breaks','preds']);
@patch
def pca(x:Tensor, k=2):
"Compute PCA of `x` with `k` dimensions."
x = x-torch.mean(x,0)
U,S,V = torch.svd(x.t())
return torch.mm(x,U[:,:k])def logit(x):
"Logit of `x`, clamped to avoid inf."
x = x.clamp(1e-7, 1-1e-7)
return -(1/x-1).log()def num_distrib():
"Return the number of processes in distributed training (if applicable)."
return int(os.environ.get('WORLD_SIZE', 0))def rank_distrib():
"Return the distributed rank of this process (if applicable)."
return int(os.environ.get('RANK', 0))def distrib_barrier():
"Place a synchronization barrier in distributed training"
if num_distrib() > 1 and torch.distributed.is_initialized(): torch.distributed.barrier()在调用此操作后,pytorch进程组中的所有子进程必须在继续之前到达此处。
# 保存数组需要 pytables - 可选依赖项
try: import tables
except: passdef _comp_filter(lib='lz4',lvl=3): return tables.Filters(complib=f'blosc:{lib}', complevel=lvl)@patch
def save_array(p:Path, o, complib='lz4', lvl=3):
"Save numpy array to a compressed `pytables` file, using compression level `lvl`"
if isinstance(o,Tensor): o = to_np(o)
with tables.open_file(p, mode='w', filters=_comp_filter(lib=complib,lvl=lvl)) as f: f.create_carray('/', 'data', obj=o)压缩库可以是以下任意一种:blosclz、lz4、lz4hc、snappy、zlib 或 zstd。
@patch
def load_array(p:Path):
"Save numpy array to a `pytables` file"
with tables.open_file(p, 'r') as f: return f.root.data.read()def base_doc(elt):
"Print a base documentation of `elt`"
name = getattr(elt, '__qualname__', getattr(elt, '__name__', ''))
print(f'{name}{inspect.signature(elt)}\n{inspect.getdoc(elt)}\n')
print('To get a prettier result with hyperlinks to source code and documentation, install nbdev: pip install nbdev')def doc(elt):
"Try to use doc form nbdev and fall back to `base_doc`"
try:
from nbdev.showdoc import doc
doc(elt)
except: base_doc(elt)def nested_reorder(t, idxs):
"Reorder all tensors in `t` using `idxs`"
if isinstance(t, (Tensor,L)): return t[idxs]
elif is_listy(t): return type(t)(nested_reorder(t_, idxs) for t_ in t)
if t is None: return t
raise TypeError(f"Expected tensor, tuple, list or L but got {type(t)}")x = tensor([0,1,2,3,4,5])
idxs = tensor([2,5,1,0,3,4])
test_eq_type(nested_reorder(([x], x), idxs), ([idxs], idxs))
y = L(0,1,2,3,4,5)
z = L(i.item() for i in idxs)
test_eq_type(nested_reorder((y, x), idxs), (z,idxs))def flatten_check(inp, targ):
"Check that `inp` and `targ` have the same number of elements and flatten them."
inp,targ = TensorBase(inp.contiguous()).view(-1),TensorBase(targ.contiguous()).view(-1)
test_eq(len(inp), len(targ))
return inp,targx1,x2 = torch.randn(5,4),torch.randn(20)
x1,x2 = flatten_check(x1,x2)
test_eq(x1.shape, [20])
test_eq(x2.shape, [20])
x1,x2 = torch.randn(5,4),torch.randn(21)
test_fail(lambda: flatten_check(x1,x2))图像助手
def make_cross_image(bw=True):
"Create a tensor containing a cross image, either `bw` (True) or color"
if bw:
im = torch.zeros(5,5)
im[2,:] = 1.
im[:,2] = 1.
else:
im = torch.zeros(3,5,5)
im[0,2,:] = 1.
im[1,:,2] = 1.
return implt.imshow(make_cross_image(), cmap="Greys");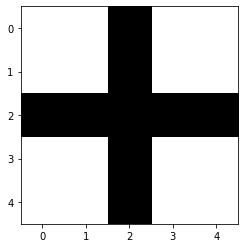
plt.imshow(make_cross_image(False).permute(1,2,0));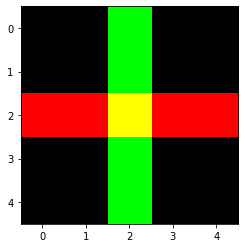
def show_image_batch(b, show=show_titled_image, items=9, cols=3, figsize=None, **kwargs):
"Display batch `b` in a grid of size `items` with `cols` width"
if items<cols: cols=items
rows = (items+cols-1) // cols
if figsize is None: figsize = (cols*3, rows*3)
fig,axs = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=figsize)
for *o,ax in zip(*to_cpu(b), axs.flatten()): show(o, ax=ax, **kwargs)show_image_batch(([Image.open(TEST_IMAGE_BW),Image.open(TEST_IMAGE)],['bw','color']), items=2)
模型初始化
def requires_grad(m):
"Check if the first parameter of `m` requires grad or not"
ps = list(m.parameters())
return ps[0].requires_grad if len(ps)>0 else Falsetst = nn.Linear(4,5)
assert requires_grad(tst)
for p in tst.parameters(): p.requires_grad_(False)
assert not requires_grad(tst)def init_default(m, func=nn.init.kaiming_normal_):
"Initialize `m` weights with `func` and set `bias` to 0."
if func:
if hasattr(m, 'weight'): func(m.weight)
if hasattr(m, 'bias') and hasattr(m.bias, 'data'): m.bias.data.fill_(0.)
return mtst = nn.Linear(4,5)
tst.weight.data.uniform_(-1,1)
tst.bias.data.uniform_(-1,1)
tst = init_default(tst, func = lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
test_eq(tst.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
test_eq(tst.bias, torch.zeros(5))def cond_init(m, func):
"Apply `init_default` to `m` unless it's a batchnorm module"
if (not isinstance(m, norm_types)) and requires_grad(m): init_default(m, func)tst = nn.Linear(4,5)
tst.weight.data.uniform_(-1,1)
tst.bias.data.uniform_(-1,1)
cond_init(tst, func = lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
test_eq(tst.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
test_eq(tst.bias, torch.zeros(5))
tst = nn.BatchNorm2d(5)
init = [tst.weight.clone(), tst.bias.clone()]
cond_init(tst, func = lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
test_eq(tst.weight, init[0])
test_eq(tst.bias, init[1])def apply_leaf(m, f):
"Apply `f` to children of `m`."
c = m.children()
if isinstance(m, nn.Module): f(m)
for l in c: apply_leaf(l,f)tst = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.Linear(4,5)))
apply_leaf(tst, partial(init_default, func=lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.)))
for l in [tst[0], *tst[1]]: test_eq(l.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
for l in [tst[0], *tst[1]]: test_eq(l.bias, torch.zeros(5))def apply_init(m, func=nn.init.kaiming_normal_):
"Initialize all non-batchnorm layers of `m` with `func`."
apply_leaf(m, partial(cond_init, func=func))tst = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.BatchNorm1d(5)))
init = [tst[1][1].weight.clone(), tst[1][1].bias.clone()]
apply_init(tst, func=lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
for l in [tst[0], tst[1][0]]: test_eq(l.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
for l in [tst[0], tst[1][0]]: test_eq(l.bias, torch.zeros(5))
test_eq(tst[1][1].weight, init[0])
test_eq(tst[1][1].bias, init[1])autograd jit 函数
def script_use_ctx(f):
"Decorator: create jit script and pass everything in `ctx.saved_variables to `f`, after `*args`"
sf = torch.jit.script(f)
def _f(ctx, *args, **kwargs): return sf(*args, *ctx.saved_variables, **kwargs)
return update_wrapper(_f,f)def script_save_ctx(static, *argidx):
"Decorator: create jit script and save args with indices `argidx` using `ctx.save_for_backward`"
def _dec(f):
sf = torch.jit.script(f)
def _f(ctx, *args, **kwargs):
if argidx:
save = [args[o] for o in argidx]
ctx.save_for_backward(*save)
if not argidx: args = [ctx]+args
return sf(*args, **kwargs)
if static: _f = staticmethod(_f)
return update_wrapper(_f,f)
return _decdef script_fwd(*argidx):
"Decorator: create static jit script and save args with indices `argidx` using `ctx.save_for_backward`"
return script_save_ctx(True, *argidx)def script_bwd(f):
"Decorator: create static jit script and pass everything in `ctx.saved_variables to `f`, after `*args`"
return staticmethod(script_use_ctx(f))def grad_module(cls):
"Decorator: convert `cls` into an autograd function"
class _c(nn.Module):
def forward(self, *args, **kwargs): return cls.apply(*args, **kwargs)
return _cTorch 版本检查 -
def ismin_torch(min_version):
"Check if `torch.__version__` >= `min_version` using packaging.version"
return _torch_version >= parse(min_version)def notmax_torch(max_version):
"Check if `torch.__version__` < `max_version` using packaging.version"
return _torch_version < parse(max_version)PyTorch 1.13 __format__ 解决方法 -
# PyTorch 1.13 引入了一个张量子类字符串格式化错误
# 来自待处理的PyTorch PR的解决方案:https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/82766
if ismin_torch('1.13') and notmax_torch('1.14'):
from torch.overrides import has_torch_function_unary, handle_torch_function
@patch
def __format__(self:Tensor, format_spec):
if has_torch_function_unary(self):
return handle_torch_function(Tensor.__format__, (self,), self, format_spec)
if self.dim() == 0 and not self.is_meta and issubclass(type(self), Tensor):
return self.item().__format__(format_spec)
return object.__format__(self, format_spec)导出 -
import nbdev; nbdev.nbdev_export()