! [ -e /content ] && pip install -Uqq fastai # 在Colab上升级fastai数据转换
from __future__ import annotations
from fastai.torch_basics import *
from fastai.data.core import *
from fastai.data.load import *
from fastai.data.external import *
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import posixpathfrom nbdev.showdoc import *获取、拆分和标记数据的函数,以及通用转换。
获取、拆分和标记
对于大多数数据源的创建,我们需要一些函数来获取项目列表,将其分割为训练集/验证集,并对其进行标记。 fastai 提供了函数,使每个步骤变得简单(尤其是结合使用 fastai.data.blocks 时)。
获取
首先,我们将查看一些获取项目列表的函数(通常是文件名)。
我们将使用 tiny MNIST(MNIST 的一个子集,仅包含两个类别,7 和 3)作为本页中示例/测试的基础。
path = untar_data(URLs.MNIST_TINY)
(path/'train').ls()(#2) [Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/3')]def _get_files(p, fs, extensions=None):
p = Path(p)
res = [p/f for f in fs if not f.startswith('.')
and ((not extensions) or f'.{f.split(".")[-1].lower()}' in extensions)]
return resdef get_files(path, extensions=None, recurse=True, folders=None, followlinks=True):
"Get all the files in `path` with optional `extensions`, optionally with `recurse`, only in `folders`, if specified."
path = Path(path)
folders=L(folders)
extensions = setify(extensions)
extensions = {e.lower() for e in extensions}
if recurse:
res = []
for i,(p,d,f) in enumerate(os.walk(path, followlinks=followlinks)): # 返回值(目录路径,目录名称,文件名称)
if len(folders) !=0 and i==0: d[:] = [o for o in d if o in folders]
else: d[:] = [o for o in d if not o.startswith('.')]
if len(folders) !=0 and i==0 and '.' not in folders: continue
res += _get_files(p, f, extensions)
else:
f = [o.name for o in os.scandir(path) if o.is_file()]
res = _get_files(path, f, extensions)
return L(res)这是从磁盘中获取一系列文件名的最通用方法。如果传递 extensions(包括 .),返回的文件名将根据该列表进行过滤。仅直接位于 path 中的文件会被包括,除非你传递 recurse,此时所有子文件夹也会被递归搜索。folders 是一个可选的目录列表,用于限制搜索范围。
t3 = get_files(path/'train'/'3', extensions='.png', recurse=False)
t7 = get_files(path/'train'/'7', extensions='.png', recurse=False)
t = get_files(path/'train', extensions='.png', recurse=True)
test_eq(len(t), len(t3)+len(t7))
test_eq(len(get_files(path/'train'/'3', extensions='.jpg', recurse=False)),0)
test_eq(len(t), len(get_files(path, extensions='.png', recurse=True, folders='train')))
t(#709) [Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/9243.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/9519.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/7534.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/9082.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/8377.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/994.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/8559.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/8217.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/8571.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/8954.png')...]test_eq(len(get_files(path/'train'/'3', recurse=False)),346)
test_eq(len(get_files(path, extensions='.png', recurse=True, folders=['train', 'test'])),729)
test_eq(len(get_files(path, extensions='.png', recurse=True, folders='train')),709)
test_eq(len(get_files(path, extensions='.png', recurse=True, folders='training')),0)能够创建具有自定义行为的函数通常很有用。 fastai.data 通常使用以 er 结尾的 CamelCase 动词命名的函数来创建这些函数。 FileGetter 就是这样的一个简单函数创建器的例子。
def FileGetter(suf='', extensions=None, recurse=True, folders=None):
"Create `get_files` partial function that searches path suffix `suf`, only in `folders`, if specified, and passes along args"
def _inner(o, extensions=extensions, recurse=recurse, folders=folders):
return get_files(o/suf, extensions, recurse, folders)
return _innerfpng = FileGetter(extensions='.png', recurse=False)
test_eq(len(t7), len(fpng(path/'train'/'7')))
test_eq(len(t), len(fpng(path/'train', recurse=True)))
fpng_r = FileGetter(extensions='.png', recurse=True)
test_eq(len(t), len(fpng_r(path/'train')))image_extensions = set(k for k,v in mimetypes.types_map.items() if v.startswith('image/'))def get_image_files(path, recurse=True, folders=None):
"Get image files in `path` recursively, only in `folders`, if specified."
return get_files(path, extensions=image_extensions, recurse=recurse, folders=folders)这只是用标准图像扩展名列表调用的 get_files。
test_eq(len(t), len(get_image_files(path, recurse=True, folders='train')))def ImageGetter(suf='', recurse=True, folders=None):
"Create `get_image_files` partial that searches suffix `suf` and passes along `kwargs`, only in `folders`, if specified"
def _inner(o, recurse=recurse, folders=folders): return get_image_files(o/suf, recurse, folders)
return _inner与FileGetter相同,但适用于图像扩展名。
test_eq(len(get_files(path/'train', extensions='.png', recurse=True, folders='3')),
len(ImageGetter( 'train', recurse=True, folders='3')(path)))def get_text_files(path, recurse=True, folders=None):
"Get text files in `path` recursively, only in `folders`, if specified."
return get_files(path, extensions=['.txt'], recurse=recurse, folders=folders)class ItemGetter(ItemTransform):
"Creates a proper transform that applies `itemgetter(i)` (even on a tuple)"
_retain = False
def __init__(self, i): self.i = i
def encodes(self, x): return x[self.i]test_eq(ItemGetter(1)((1,2,3)), 2)
test_eq(ItemGetter(1)(L(1,2,3)), 2)
test_eq(ItemGetter(1)([1,2,3]), 2)
test_eq(ItemGetter(1)(np.array([1,2,3])), 2)class AttrGetter(ItemTransform):
"Creates a proper transform that applies `attrgetter(nm)` (even on a tuple)"
_retain = False
def __init__(self, nm, default=None): store_attr()
def encodes(self, x): return getattr(x, self.nm, self.default)test_eq(AttrGetter('shape')(torch.randn([4,5])), [4,5])
test_eq(AttrGetter('shape', [0])([4,5]), [0])拆分
下一组函数用于拆分数据为训练集和验证集。这些函数返回两个列表 - 一个是训练集的索引或掩码列表,另一个是验证集的索引或掩码列表。
def RandomSplitter(valid_pct=0.2, seed=None):
"Create function that splits `items` between train/val with `valid_pct` randomly."
def _inner(o):
if seed is not None: torch.manual_seed(seed)
rand_idx = L(list(torch.randperm(len(o)).numpy()))
cut = int(valid_pct * len(o))
return rand_idx[cut:],rand_idx[:cut]
return _innerdef _test_splitter(f, items=None):
"A basic set of condition a splitter must pass"
items = ifnone(items, range_of(30))
trn,val = f(items)
assert 0<len(trn)<len(items)
assert all(o not in val for o in trn)
test_eq(len(trn), len(items)-len(val))
# 测试随机种子一致性
test_eq(f(items)[0], trn)
return trn, val_test_splitter(RandomSplitter(seed=42))((#24) [10,18,16,23,28,26,20,7,21,22...], (#6) [12,0,6,25,8,15])使用scikit-learn的train_test_split。这允许以分层的方式(根据“标签”分布均匀地)对项目进行拆分。
def TrainTestSplitter(test_size=0.2, random_state=None, stratify=None, train_size=None, shuffle=True):
"Split `items` into random train and test subsets using sklearn train_test_split utility."
def _inner(o, **kwargs):
train,valid = train_test_split(range_of(o), test_size=test_size, random_state=random_state,
stratify=stratify, train_size=train_size, shuffle=shuffle)
return L(train), L(valid)
return _innersrc = list(range(30))
labels = [0] * 20 + [1] * 10
test_size = 0.2
f = TrainTestSplitter(test_size=test_size, random_state=42, stratify=labels)
trn,val = _test_splitter(f, items=src)
# 测试标签分布一致性
# 验证集中应分别有 test_size% 的零和一。
test_eq(len([t for t in val if t < 20]) / 20, test_size)
test_eq(len([t for t in val if t > 20]) / 10, test_size)def IndexSplitter(valid_idx):
"Split `items` so that `val_idx` are in the validation set and the others in the training set"
def _inner(o):
train_idx = np.setdiff1d(np.array(range_of(o)), np.array(valid_idx))
return L(train_idx, use_list=True), L(valid_idx, use_list=True)
return _inneritems = 'a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j'.split(',') #以明确区分索引与元素。
splitter = IndexSplitter([3,7,9])
_test_splitter(splitter, items)
test_eq(splitter(items),[[0,1,2,4,5,6,8],[3,7,9]])def EndSplitter(valid_pct=0.2, valid_last=True):
"Create function that splits `items` between train/val with `valid_pct` at the end if `valid_last` else at the start. Useful for ordered data."
assert 0<valid_pct<1, "valid_pct must be in (0,1)"
def _inner(o):
idxs = range_of(o)
cut = int(valid_pct * len(o))
return (idxs[:-cut], idxs[-cut:]) if valid_last else (idxs[cut:],idxs[:cut])
return _inneritems = range_of(10)
splitter_last = EndSplitter(valid_last=True)
_test_splitter(splitter_last)
test_eq(splitter_last(items), ([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7], [8,9]))
splitter_start = EndSplitter(valid_last=False)
_test_splitter(splitter_start)
test_eq(splitter_start(items), ([2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9], [0,1]))def _grandparent_idxs(items, name):
def _inner(items, name): return mask2idxs(Path(o).parent.parent.name == name for o in items)
return [i for n in L(name) for i in _inner(items,n)]def GrandparentSplitter(train_name='train', valid_name='valid'):
"Split `items` from the grand parent folder names (`train_name` and `valid_name`)."
def _inner(o):
return _grandparent_idxs(o, train_name),_grandparent_idxs(o, valid_name)
return _innerfnames = [path/'train/3/9932.png', path/'valid/7/7189.png',
path/'valid/7/7320.png', path/'train/7/9833.png',
path/'train/3/7666.png', path/'valid/3/925.png',
path/'train/7/724.png', path/'valid/3/93055.png']
splitter = GrandparentSplitter()_test_splitter(splitter, items=fnames)
test_eq(splitter(fnames),[[0,3,4,6],[1,2,5,7]])fnames2 = fnames + [path/'test/3/4256.png', path/'test/7/2345.png', path/'valid/7/6467.png']
splitter = GrandparentSplitter(train_name=('train', 'valid'), valid_name='test')
_test_splitter(splitter, items=fnames2)
test_eq(splitter(fnames2),[[0,3,4,6,1,2,5,7,10],[8,9]])def FuncSplitter(func):
"Split `items` by result of `func` (`True` for validation, `False` for training set)."
def _inner(o):
val_idx = mask2idxs(func(o_) for o_ in o)
return IndexSplitter(val_idx)(o)
return _innersplitter = FuncSplitter(lambda o: Path(o).parent.parent.name == 'valid')
_test_splitter(splitter, fnames)
test_eq(splitter(fnames),[[0,3,4,6],[1,2,5,7]])def MaskSplitter(mask):
"Split `items` depending on the value of `mask`."
def _inner(o): return IndexSplitter(mask2idxs(mask))(o)
return _inneritems = list(range(6))
splitter = MaskSplitter([True,False,False,True,False,True])
_test_splitter(splitter, items)
test_eq(splitter(items),[[1,2,4],[0,3,5]])def FileSplitter(fname):
"Split `items` by providing file `fname` (contains names of valid items separated by newline)."
valid = Path(fname).read_text().split('\n')
def _func(x): return x.name in valid
def _inner(o): return FuncSplitter(_func)(o)
return _innerwith tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as d:
fname = Path(d)/'valid.txt'
fname.write_text('\n'.join([Path(fnames[i]).name for i in [1,3,4]]))
splitter = FileSplitter(fname)
_test_splitter(splitter, fnames)
test_eq(splitter(fnames),[[0,2,5,6,7],[1,3,4]])def ColSplitter(col='is_valid', on=None):
"Split `items` (supposed to be a dataframe) by value in `col`"
def _inner(o):
assert isinstance(o, pd.DataFrame), "ColSplitter only works when your items are a pandas DataFrame"
c = o.iloc[:,col] if isinstance(col, int) else o[col]
if on is None: valid_idx = c.values.astype('bool')
elif is_listy(on): valid_idx = c.isin(on)
else: valid_idx = c == on
return IndexSplitter(mask2idxs(valid_idx))(o)
return _innerdf = pd.DataFrame({'a': [0,1,2,3,4], 'b': [True,False,True,True,False]})
splits = ColSplitter('b')(df)
test_eq(splits, [[1,4], [0,2,3]])
# 适用于字符串或索引
splits = ColSplitter(1)(df)
test_eq(splits, [[1,4], [0,2,3]])
# does not get confused if the type of 'is_valid' is integer, but it meant to be a yes/no
df = pd.DataFrame({'a': [0,1,2,3,4], 'is_valid': [1,0,1,1,0]})
splits_by_int = ColSplitter('is_valid')(df)
test_eq(splits_by_int, [[1,4], [0,2,3]])
# 可选择传递一个特定值作为分割依据
df = pd.DataFrame({'a': [0,1,2,3,4,5], 'b': [1,2,3,1,2,3]})
splits_on_val = ColSplitter('b', 3)(df)
test_eq(splits_on_val, [[0,1,3,4], [2,5]])
# 或多个值
splits_on_val = ColSplitter('b', [2,3])(df)
test_eq(splits_on_val, [[0,3], [1,2,4,5]])def RandomSubsetSplitter(train_sz, valid_sz, seed=None):
"Take randoms subsets of `splits` with `train_sz` and `valid_sz`"
assert 0 < train_sz < 1
assert 0 < valid_sz < 1
assert train_sz + valid_sz <= 1.
def _inner(o):
if seed is not None: torch.manual_seed(seed)
train_len,valid_len = int(len(o)*train_sz),int(len(o)*valid_sz)
idxs = L(list(torch.randperm(len(o)).numpy()))
return idxs[:train_len],idxs[train_len:train_len+valid_len]
return _inneritems = list(range(100))
valid_idx = list(np.arange(70,100))
splitter = RandomSubsetSplitter(0.3, 0.1)
splits = RandomSubsetSplitter(0.3, 0.1)(items)
test_eq(len(splits[0]), 30)
test_eq(len(splits[1]), 10)标签
最终一组函数用于标记单个数据项。
def parent_label(o):
"Label `item` with the parent folder name."
return Path(o).parent.name请注意,parent_label 并没有任何自定义内容,因此它不会返回一个函数 - 您可以直接使用它。
test_eq(parent_label(fnames[0]), '3')
test_eq(parent_label("fastai_dev/dev/data/mnist_tiny/train/3/9932.png"), '3')
[parent_label(o) for o in fnames]['3', '7', '7', '7', '3', '3', '7', '3']#test for MS Windows when os.path.sep is '\\' instead of '/'
test_eq(parent_label(os.path.join("fastai_dev","dev","data","mnist_tiny","train", "3", "9932.png") ), '3')class RegexLabeller():
"Label `item` with regex `pat`."
def __init__(self, pat, match=False):
self.pat = re.compile(pat)
self.matcher = self.pat.match if match else self.pat.search
def __call__(self, o):
o = str(o).replace(os.sep, posixpath.sep)
res = self.matcher(o)
assert res,f'Failed to find "{self.pat}" in "{o}"'
return res.group(1)RegexLabeller 是一个非常灵活的函数,因为它处理字符串化项的任何正则表达式搜索。传递 match=True 使用 re.match(即仅检查字符串开头),否则使用 re.search(默认)。
例如,下面的示例复制了之前的 parent_label 结果。
f = RegexLabeller(fr'{posixpath.sep}(\d){posixpath.sep}')
test_eq(f(fnames[0]), '3')
[f(o) for o in fnames]['3', '7', '7', '7', '3', '3', '7', '3']f = RegexLabeller(fr'{posixpath.sep}(\d){posixpath.sep}')
a1 = Path(fnames[0]).as_posix()
test_eq(f(a1), '3')
[f(o) for o in fnames]['3', '7', '7', '7', '3', '3', '7', '3']f = RegexLabeller(r'(\d*)', match=True)
test_eq(f(fnames[0].name), '9932')class ColReader(DisplayedTransform):
"Read `cols` in `row` with potential `pref` and `suff`"
def __init__(self, cols, pref='', suff='', label_delim=None):
store_attr()
self.pref = str(pref) + os.path.sep if isinstance(pref, Path) else pref
self.cols = L(cols)
def _do_one(self, r, c):
o = r[c] if isinstance(c, int) or not c in getattr(r, '_fields', []) else getattr(r, c)
if len(self.pref)==0 and len(self.suff)==0 and self.label_delim is None: return o
if self.label_delim is None: return f'{self.pref}{o}{self.suff}'
else: return o.split(self.label_delim) if len(o)>0 else []
def __call__(self, o, **kwargs):
if len(self.cols) == 1: return self._do_one(o, self.cols[0])
return L(self._do_one(o, c) for c in self.cols)cols 可以是列名的列表或索引的列表(或者两者的混合)。如果传递了 label_delim,结果将通过它进行拆分。
df = pd.DataFrame({'a': 'a b c d'.split(), 'b': ['1 2', '0', '', '1 2 3']})
f = ColReader('a', pref='0', suff='1')
test_eq([f(o) for o in df.itertuples()], '0a1 0b1 0c1 0d1'.split())
f = ColReader('b', label_delim=' ')
test_eq([f(o) for o in df.itertuples()], [['1', '2'], ['0'], [], ['1', '2', '3']])
df['a1'] = df['a']
f = ColReader(['a', 'a1'], pref='0', suff='1')
test_eq([f(o) for o in df.itertuples()], [L('0a1', '0a1'), L('0b1', '0b1'), L('0c1', '0c1'), L('0d1', '0d1')])
df = pd.DataFrame({'a': [L(0,1), L(2,3,4), L(5,6,7)]})
f = ColReader('a')
test_eq([f(o) for o in df.itertuples()], [L(0,1), L(2,3,4), L(5,6,7)])
df['name'] = df['a']
f = ColReader('name')
test_eq([f(df.iloc[0,:])], [L(0,1)])
df['mask'] = df['a']
f = ColReader('mask')
test_eq([f(o) for o in df.itertuples()], [L(0,1), L(2,3,4), L(5,6,7)])
test_eq([f(df.iloc[0,:])], [L(0,1)])分类 -
class CategoryMap(CollBase):
"Collection of categories with the reverse mapping in `o2i`"
def __init__(self, col, sort=True, add_na=False, strict=False):
if hasattr(col, 'dtype') and isinstance(col.dtype, CategoricalDtype):
items = L(col.cat.categories, use_list=True)
#移除未使用的类别,同时保持顺序
if strict: items = L(o for o in items if o in col.unique())
else:
if not hasattr(col,'unique'): col = L(col, use_list=True)
# `o==o` 是 Pandas 中用于定义非 NaN 的广义定义
items = L(o for o in col.unique() if o==o)
if sort: items = items.sorted()
self.items = '#na#' + items if add_na else items
self.o2i = defaultdict(int, self.items.val2idx()) if add_na else dict(self.items.val2idx())
def map_objs(self,objs):
"Map `objs` to IDs"
return L(self.o2i[o] for o in objs)
def map_ids(self,ids):
"Map `ids` to objects in vocab"
return L(self.items[o] for o in ids)
def __eq__(self,b): return all_equal(b,self)t = CategoryMap([4,2,3,4])
test_eq(t, [2,3,4])
test_eq(t.o2i, {2:0,3:1,4:2})
test_eq(t.map_objs([2,3]), [0,1])
test_eq(t.map_ids([0,1]), [2,3])
test_fail(lambda: t.o2i['unseen label'])t = CategoryMap([4,2,3,4], add_na=True)
test_eq(t, ['#na#',2,3,4])
test_eq(t.o2i, {'#na#':0,2:1,3:2,4:3})t = CategoryMap(pd.Series([4,2,3,4]), sort=False)
test_eq(t, [4,2,3])
test_eq(t.o2i, {4:0,2:1,3:2})col = pd.Series(pd.Categorical(['M','H','L','M'], categories=['H','M','L'], ordered=True))
t = CategoryMap(col)
test_eq(t, ['H','M','L'])
test_eq(t.o2i, {'H':0,'M':1,'L':2})col = pd.Series(pd.Categorical(['M','H','M'], categories=['H','M','L'], ordered=True))
t = CategoryMap(col, strict=True)
test_eq(t, ['H','M'])
test_eq(t.o2i, {'H':0,'M':1})class Categorize(DisplayedTransform):
"Reversible transform of category string to `vocab` id"
loss_func,order=CrossEntropyLossFlat(),1
def __init__(self, vocab=None, sort=True, add_na=False):
if vocab is not None: vocab = CategoryMap(vocab, sort=sort, add_na=add_na)
store_attr()
def setups(self, dsets):
if self.vocab is None and dsets is not None: self.vocab = CategoryMap(dsets, sort=self.sort, add_na=self.add_na)
self.c = len(self.vocab)
def encodes(self, o):
try:
return TensorCategory(self.vocab.o2i[o])
except KeyError as e:
raise KeyError(f"Label '{o}' was not included in the training dataset") from e
def decodes(self, o): return Category (self.vocab [o])class Category(str, ShowTitle): _show_args = {'label': 'category'}cat = Categorize()
tds = Datasets(['cat', 'dog', 'cat'], tfms=[cat])
test_eq(cat.vocab, ['cat', 'dog'])
test_eq(cat('cat'), 0)
test_eq(cat.decode(1), 'dog')
test_stdout(lambda: show_at(tds,2), 'cat')
test_fail(lambda: cat('bird'))cat = Categorize(add_na=True)
tds = Datasets(['cat', 'dog', 'cat'], tfms=[cat])
test_eq(cat.vocab, ['#na#', 'cat', 'dog'])
test_eq(cat('cat'), 1)
test_eq(cat.decode(2), 'dog')
test_stdout(lambda: show_at(tds,2), 'cat')cat = Categorize(vocab=['dog', 'cat'], sort=False, add_na=True)
tds = Datasets(['cat', 'dog', 'cat'], tfms=[cat])
test_eq(cat.vocab, ['#na#', 'dog', 'cat'])
test_eq(cat('dog'), 1)
test_eq(cat.decode(2), 'cat')
test_stdout(lambda: show_at(tds,2), 'cat')多分类 -
class MultiCategorize(Categorize):
"Reversible transform of multi-category strings to `vocab` id"
loss_func,order=BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(),1
def __init__(self, vocab=None, add_na=False): super().__init__(vocab=vocab,add_na=add_na,sort=vocab==None)
def setups(self, dsets):
if not dsets: return
if self.vocab is None:
vals = set()
for b in dsets: vals = vals.union(set(b))
self.vocab = CategoryMap(list(vals), add_na=self.add_na)
def encodes(self, o):
if not all(elem in self.vocab.o2i.keys() for elem in o):
diff = [elem for elem in o if elem not in self.vocab.o2i.keys()]
diff_str = "', '".join(diff)
raise KeyError(f"Labels '{diff_str}' were not included in the training dataset")
return TensorMultiCategory([self.vocab.o2i[o_] for o_ in o])
def decodes(self, o): return MultiCategory ([self.vocab [o_] for o_ in o])class MultiCategory(L):
def show(self, ctx=None, sep=';', color='black', **kwargs):
return show_title(sep.join(self.map(str)), ctx=ctx, color=color, **kwargs)cat = MultiCategorize()
tds = Datasets([['b', 'c'], ['a'], ['a', 'c'], []], tfms=[cat])
test_eq(tds[3][0], TensorMultiCategory([]))
test_eq(cat.vocab, ['a', 'b', 'c'])
test_eq(cat(['a', 'c']), tensor([0,2]))
test_eq(cat([]), tensor([]))
test_eq(cat.decode([1]), ['b'])
test_eq(cat.decode([0,2]), ['a', 'c'])
test_stdout(lambda: show_at(tds,2), 'a;c')
# if vocab supplied, ensure it maintains its order (i.e., it doesn't sort)
cat = MultiCategorize(vocab=['z', 'y', 'x'])
test_eq(cat.vocab, ['z','y','x'])
test_fail(lambda: cat('bird'))class OneHotEncode(DisplayedTransform):
"One-hot encodes targets"
order=2
def __init__(self, c=None): store_attr()
def setups(self, dsets):
if self.c is None: self.c = len(L(getattr(dsets, 'vocab', None)))
if not self.c: warn("Couldn't infer the number of classes, please pass a value for `c` at init")
def encodes(self, o): return TensorMultiCategory(one_hot(o, self.c).float())
def decodes(self, o): return one_hot_decode(o, None)与 MultiCategorize 一起工作,或在您具有独热编码目标时单独使用(在这种情况下,传递 vocab 进行解码,并将 do_encode=False)。
_tfm = OneHotEncode(c=3)
test_eq(_tfm([0,2]), tensor([1.,0,1]))
test_eq(_tfm.decode(tensor([0,1,1])), [1,2])tds = Datasets([['b', 'c'], ['a'], ['a', 'c'], []], [[MultiCategorize(), OneHotEncode()]])
test_eq(tds[1], [tensor([1.,0,0])])
test_eq(tds[3], [tensor([0.,0,0])])
test_eq(tds.decode([tensor([False, True, True])]), [['b','c']])
test_eq(type(tds[1][0]), TensorMultiCategory)
test_stdout(lambda: show_at(tds,2), 'a;c')#通过词汇测试
tds = Datasets([['b', 'c'], ['a'], ['a', 'c'], []], [[MultiCategorize(vocab=['a', 'b', 'c']), OneHotEncode()]])
test_eq(tds[1], [tensor([1.,0,0])])
test_eq(tds[3], [tensor([0.,0,0])])
test_eq(tds.decode([tensor([False, True, True])]), [['b','c']])
test_eq(type(tds[1][0]), TensorMultiCategory)
test_stdout(lambda: show_at(tds,2), 'a;c')class EncodedMultiCategorize(Categorize):
"Transform of one-hot encoded multi-category that decodes with `vocab`"
loss_func,order=BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(),1
def __init__(self, vocab):
super().__init__(vocab, sort=vocab==None)
self.c = len(vocab)
def encodes(self, o): return TensorMultiCategory(tensor(o).float())
def decodes(self, o): return MultiCategory (one_hot_decode(o, self.vocab))_tfm = EncodedMultiCategorize(vocab=['a', 'b', 'c'])
test_eq(_tfm([1,0,1]), tensor([1., 0., 1.]))
test_eq(type(_tfm([1,0,1])), TensorMultiCategory)
test_eq(_tfm.decode(tensor([False, True, True])), ['b','c'])
_tfm2 = EncodedMultiCategorize(vocab=['c', 'b', 'a'])
test_eq(_tfm2.vocab, ['c', 'b', 'a'])class RegressionSetup(DisplayedTransform):
"Transform that floatifies targets"
loss_func=MSELossFlat()
def __init__(self, c=None): store_attr()
def encodes(self, o): return tensor(o).float()
def decodes(self, o): return TitledFloat(o) if o.ndim==0 else TitledTuple(o_.item() for o_ in o)
def setups(self, dsets):
if self.c is not None: return
try: self.c = len(dsets[0]) if hasattr(dsets[0], '__len__') else 1
except: self.c = 0_tfm = RegressionSetup()
dsets = Datasets([0, 1, 2], RegressionSetup)
test_eq(dsets.c, 1)
test_eq_type(dsets[0], (tensor(0.),))
dsets = Datasets([[0, 1, 2], [3,4,5]], RegressionSetup)
test_eq(dsets.c, 3)
test_eq_type(dsets[0], (tensor([0.,1.,2.]),))def get_c(dls):
if getattr(dls, 'c', False): return dls.c
if nested_attr(dls, 'train.after_item.c', False): return dls.train.after_item.c
if nested_attr(dls, 'train.after_batch.c', False): return dls.train.after_batch.c
vocab = getattr(dls, 'vocab', [])
if len(vocab) > 0 and is_listy(vocab[-1]): vocab = vocab[-1]
return len(vocab)MNIST 数据集的端到端示例
让我们展示如何使用这些函数来获取 Datasets 中的 mnist 数据集。首先,我们抓取所有的图像。
path = untar_data(URLs.MNIST_TINY)
items = get_image_files(path)然后我们根据文件夹进行训练集和验证集的拆分。
splitter = GrandparentSplitter()
splits = splitter(items)
train,valid = (items[i] for i in splits)
train[:3],valid[:3]((#3) [Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/9243.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/9519.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/train/7/7534.png')],
(#3) [Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/valid/7/9294.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/valid/7/9257.png'),Path('/Users/jhoward/.fastai/data/mnist_tiny/valid/7/8175.png')])我们的输入是我们打开并转换为张量的图像,目标是根据父目录进行标记的类别。
from PIL import Imagedef open_img(fn:Path): return Image.open(fn).copy()
def img2tensor(im:Image.Image): return TensorImage(array(im)[None])
tfms = [[open_img, img2tensor],
[parent_label, Categorize()]]
train_ds = Datasets(train, tfms)x,y = train_ds[3]
xd,yd = decode_at(train_ds,3)
test_eq(parent_label(train[3]),yd)
test_eq(array(Image.open(train[3])),xd[0].numpy())ax = show_at(train_ds, 3, cmap="Greys", figsize=(1,1))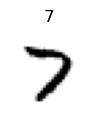
assert ax.title.get_text() in ('3','7')
test_fig_exists(ax)ToTensor -
class ToTensor(Transform):
"Convert item to appropriate tensor class"
order = 5IntToFloatTensor -
class IntToFloatTensor(DisplayedTransform):
"Transform image to float tensor, optionally dividing by 255 (e.g. for images)."
order = 10 #需要在GPU上运行PIL变换后执行
def __init__(self, div=255., div_mask=1): store_attr()
def encodes(self, o:TensorImage): return o.float().div_(self.div)
def encodes(self, o:TensorMask ): return (o.long() / self.div_mask).long()
def decodes(self, o:TensorImage): return ((o.clamp(0., 1.) * self.div).long()) if self.div else ot = (TensorImage(tensor(1)),tensor(2).long(),TensorMask(tensor(3)))
tfm = IntToFloatTensor()
ft = tfm(t)
test_eq(ft, [1./255, 2, 3])
test_eq(type(ft[0]), TensorImage)
test_eq(type(ft[2]), TensorMask)
test_eq(ft[0].type(),'torch.FloatTensor')
test_eq(ft[1].type(),'torch.LongTensor')
test_eq(ft[2].type(),'torch.LongTensor')归一化 -
def broadcast_vec(dim, ndim, *t, cuda=True):
"Make a vector broadcastable over `dim` (out of `ndim` total) by prepending and appending unit axes"
v = [1]*ndim
v[dim] = -1
f = to_device if cuda else noop
return [f(tensor(o).view(*v)) for o in t]@docs
class Normalize(DisplayedTransform):
"Normalize/denorm batch of `TensorImage`"
parameters,order = L('mean', 'std'),99
def __init__(self, mean=None, std=None, axes=(0,2,3)): store_attr()
@classmethod
def from_stats(cls, mean, std, dim=1, ndim=4, cuda=True): return cls(*broadcast_vec(dim, ndim, mean, std, cuda=cuda))
def setups(self, dl:DataLoader):
if self.mean is None or self.std is None:
x,*_ = dl.one_batch()
self.mean,self.std = x.mean(self.axes, keepdim=True),x.std(self.axes, keepdim=True)+1e-7
def encodes(self, x:TensorImage): return (x-self.mean) / self.std
def decodes(self, x:TensorImage):
f = to_cpu if x.device.type=='cpu' else noop
return (x*f(self.std) + f(self.mean))
_docs=dict(encodes="Normalize batch", decodes="Denormalize batch")mean,std = [0.5]*3,[0.5]*3
mean,std = broadcast_vec(1, 4, mean, std)
batch_tfms = [IntToFloatTensor(), Normalize.from_stats(mean,std)]
tdl = TfmdDL(train_ds, after_batch=batch_tfms, bs=4, device=default_device())x,y = tdl.one_batch()
xd,yd = tdl.decode((x,y))
assert x.type().endswith('.FloatTensor')
test_eq(xd.type(), 'torch.LongTensor')
test_eq(type(x), TensorImage)
test_eq(type(y), TensorCategory)
assert x.mean()<0.0
assert x.std()>0.3
assert 0<xd.float().mean()/255.<1
assert 0<xd.float().std()/255.<0.7nrm = Normalize()
batch_tfms = [IntToFloatTensor(), nrm]
tdl = TfmdDL(train_ds, after_batch=batch_tfms, bs=4)
x,y = tdl.one_batch()
test_close(x.mean(), 0.0, 1e-4)
assert x.std()>0.9, x.std()#仅供视觉效果
from fastai.vision.core import *tdl.show_batch((x,y))



x,y = cast(x,Tensor),cast(y,Tensor) #张量丢失类型(用于模拟预测)
test_ne(type(x), TensorImage)
tdl.show_batch((x,y), figsize=(1,1)) #检查类型是否已由dl放回。



导出 -
from nbdev import nbdev_export
nbdev_export()