- Installation
- Guides
- Overview
- SQL Features
- Data Import & Export
- CSV Import
- CSV Export
- Parquet Import
- Parquet Export
- Query Parquet
- HTTP Parquet Import
- S3 Parquet Import
- S3 Parquet Export
- JSON Import
- JSON Export
- Excel Import
- Excel Export
- SQLite Import
- Postgres Import
- Meta Queries
- Python
- Install
- Execute SQL
- Jupyter Notebooks
- SQL on Pandas
- Import From Pandas
- Export To Pandas
- SQL on Arrow
- Import From Arrow
- Export To Arrow
- Relational API on Pandas
- Multiple Python Threads
- DuckDB with Ibis
- DuckDB with Fugue
- DuckDB with Polars
- DuckDB with Vaex
- DuckDB with DataFusion
- DuckDB with fsspec filesystems
- SQL Editors
- Data Viewers
- Documentation
- Connect
- Data Import
- Overview
- CSV Files
- JSON Files
- Multiple Files
- Parquet Files
- Partitioning
- Appender
- Insert Statements
- Client APIs
- Overview
- C
- Overview
- Startup
- Configure
- Query
- Data Chunks
- Values
- Types
- Prepared Statements
- Appender
- Table Functions
- Replacement Scans
- API Reference
- C++
- CLI
- Java
- Julia
- Node.js
- ODBC
- Python
- Overview
- Data Ingestion
- Result Conversion
- DB API
- Relational API
- Function API
- Types API
- API Reference
- R
- Rust
- Scala
- Swift
- Wasm
- SQL
- Introduction
- Statements
- Overview
- Alter Table
- Attach/Detach
- Call
- Checkpoint
- Copy
- Create Macro
- Create Schema
- Create Sequence
- Create Table
- Create View
- Delete
- Drop
- Export
- Insert
- Pivot
- Select
- Set/Reset
- Unpivot
- Update
- Use
- Vacuum
- Query Syntax
- SELECT
- FROM & JOIN
- WHERE
- GROUP BY
- GROUPING SETS
- HAVING
- ORDER BY
- LIMIT
- SAMPLE
- UNNEST
- WITH
- WINDOW
- QUALIFY
- VALUES
- FILTER
- Set Operations
- Data Types
- Overview
- Bitstring
- Blob
- Boolean
- Date
- Enum
- Interval
- List
- Map
- NULL Values
- Numeric
- Struct
- Text
- Timestamp
- Union
- Expressions
- Functions
- Overview
- Bitstring Functions
- Blob Functions
- Date Format Functions
- Date Functions
- Date Part Functions
- Enum Functions
- Interval Functions
- Nested Functions
- Numeric Functions
- Pattern Matching
- Text Functions
- Time Functions
- Timestamp Functions
- Timestamp With Time Zone Functions
- Utility Functions
- Aggregates
- Configuration
- Constraints
- Indexes
- Information Schema
- Metadata Functions
- Pragmas
- Samples
- Window Functions
- Extensions
- Sitemap
- Why DuckDB
- Media
- FAQ
- Code of Conduct
- Live Demo
Harlequin is an open-source, terminal-based SQL IDE for DuckDB. You can install it using pip and run it anywhere you can run the DuckDB CLI.
Installing Harlequin
After installing Python 3.8 or above, install Harlequin using pip or pipx with:
pip install harlequin
Using Harlequin
From any shell, to open a DuckDB database file:
harlequin "path/to/duck.db"
To open an in-memory DuckDB session, run Harlequin with no arguments:
harlequin
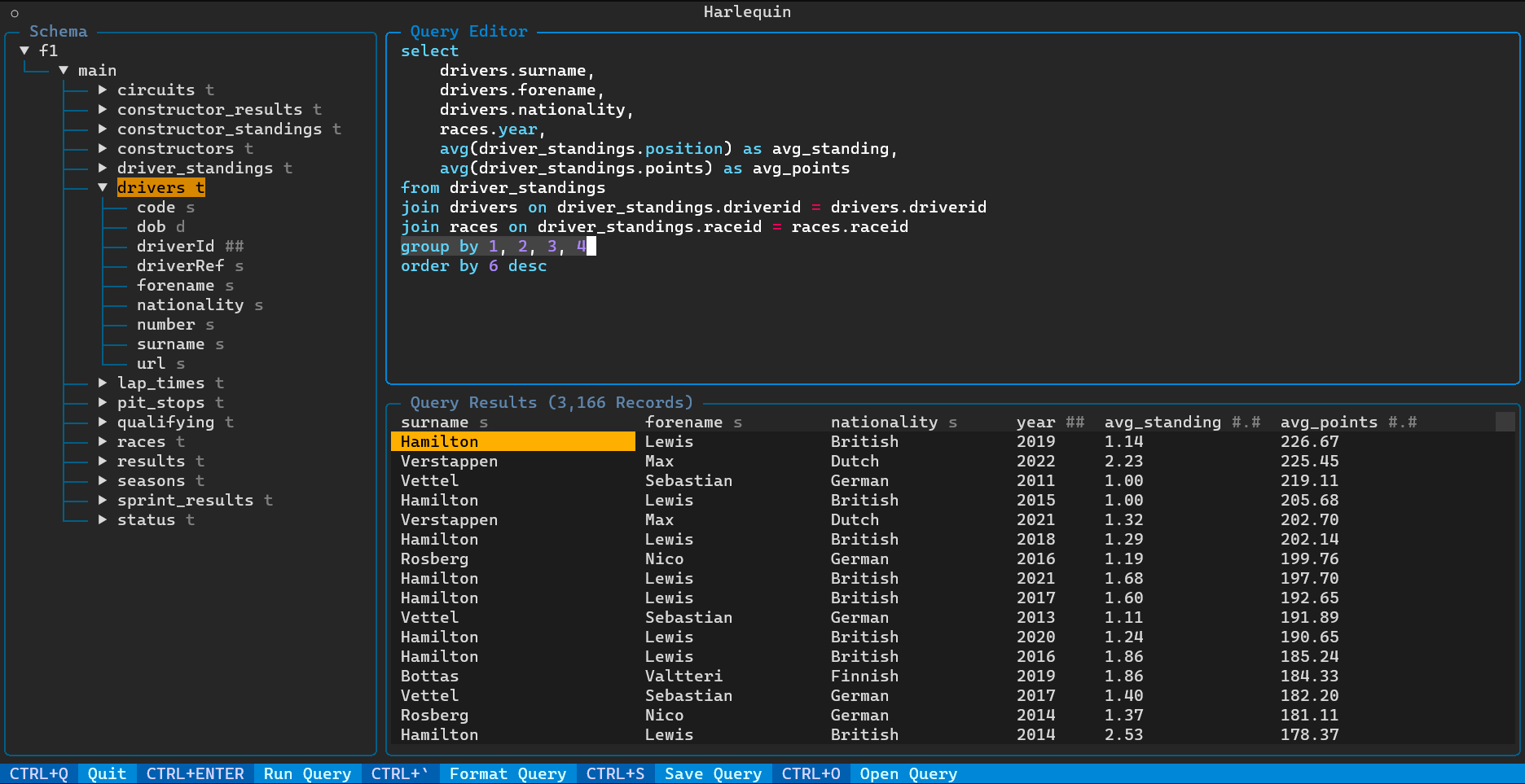
Viewing the Schema of your Database
When Harlequin is open, you can view the schema of your DuckDB database in the left sidebar. You can use your mouse or the arrow keys + enter to navigate the tree. The tree shows schemas, tables/views and their types, and columns and their types.
Editing a Query
The main query editor is a full-featured text editor, with features including syntax highlighting, auto-formatting with ctrl + `, text selection, copy/paste, and more.
You can save the query currently in the editor with ctrl + s. You can open a query in any text or .sql file with ctrl + o.
Running a Query and Viewing Results
To run a query, press ctrl + enter. Up to 50k records will be loaded into the results pane below the query editor. When the focus is on the data pane, you can use your arrow keys or mouse to select different cells.
Exiting Harlequin
Press ctrl + q to quit and return to your shell.
