语言服务器扩展指南
正如你在编程语言特性主题中所见,可以直接使用languages.* API来实现语言特性。然而,语言服务器扩展提供了另一种实现此类语言支持的方式。
本主题:
- 解释了语言服务器扩展的好处。
- 引导您使用
Microsoft/vscode-languageserver-node库构建语言服务器。您也可以直接跳转到lsp-sample中的代码。
为什么需要语言服务器?
语言服务器是一种特殊类型的Visual Studio Code扩展,它为许多编程语言提供了强大的编辑体验。通过语言服务器,您可以实现自动完成、错误检查(诊断)、跳转到定义以及VS Code中支持的许多其他语言功能。
然而,在VS Code中实现语言功能支持时,我们发现了三个常见问题:
首先,语言服务器通常是用它们的原生编程语言实现的,这在与具有Node.js运行时的VS Code集成时提出了挑战。
此外,语言功能可能会占用大量资源。例如,为了正确验证文件,语言服务器需要解析大量文件,为它们构建抽象语法树并执行静态程序分析。这些操作可能会导致显著的CPU和内存使用,我们需要确保VS Code的性能不受影响。
最后,将多种语言工具与多种代码编辑器集成可能需要大量的努力。从语言工具的角度来看,它们需要适应具有不同API的代码编辑器。从代码编辑器的角度来看,它们不能期望语言工具提供任何统一的API。这使得为M种语言在N种代码编辑器中实现语言支持成为M * N的工作。
为了解决这些问题,微软指定了语言服务器协议,该协议标准化了语言工具和代码编辑器之间的通信。这样,语言服务器可以用任何语言实现,并在自己的进程中运行,以避免性能开销,因为它们通过语言服务器协议与代码编辑器通信。此外,任何符合LSP的语言工具都可以与多个符合LSP的代码编辑器集成,任何符合LSP的代码编辑器都可以轻松地选择多个符合LSP的语言工具。LSP对语言工具提供商和代码编辑器供应商来说都是双赢的!

在本指南中,我们将:
- 解释如何使用提供的Node SDK在VS Code中构建语言服务器扩展。
- 解释如何运行、调试、记录和测试Language Server扩展。
- 向您介绍一些关于语言服务器的高级主题。
实现语言服务器
概述
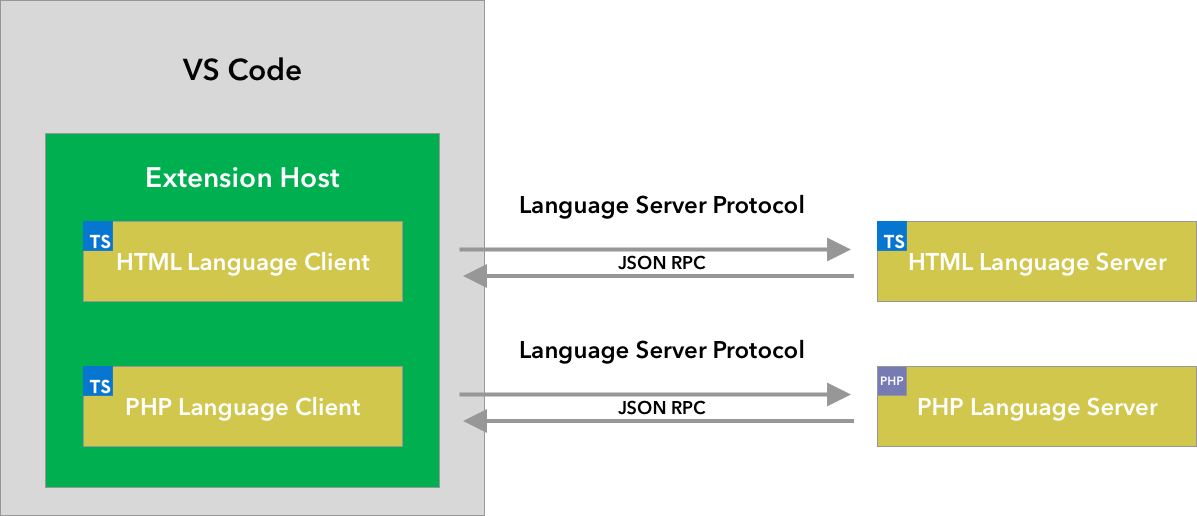
在 VS Code 中,语言服务器有两个部分:
- 语言客户端:一个用JavaScript / TypeScript编写的普通VS Code扩展。此扩展可以访问所有VS Code命名空间API。
- 语言服务器:一种在独立进程中运行的语言分析工具。
如上所述,在单独进程中运行语言服务器有两个好处:
- 分析工具可以用任何语言实现,只要它能遵循语言服务器协议与语言客户端通信。
- 由于语言分析工具通常对CPU和内存使用率较高,将它们运行在单独的进程中可以避免性能成本。
这里展示了VS Code运行两个语言服务器扩展的示例。HTML语言客户端和PHP语言客户端是用TypeScript编写的普通VS Code扩展。它们各自实例化一个相应的语言服务器,并通过LSP与它们通信。尽管PHP语言服务器是用PHP编写的,但它仍然可以通过LSP与PHP语言客户端通信。
本指南将教你如何使用我们的Node SDK构建语言客户端/服务器。本文档假设你已经熟悉VS Code的扩展API。
LSP 示例 - 一个简单的纯文本文件语言服务器
让我们构建一个简单的语言服务器扩展,该扩展为纯文本文件实现自动完成和诊断。我们还将涵盖客户端/服务器之间配置的同步。
如果您更喜欢直接跳转到代码:
- lsp-sample: 本指南的详细源代码。
- lsp-multi-server-sample: 一个详细记录的、高级版本的 lsp-sample,它为每个工作区文件夹启动不同的服务器实例,以支持 VS Code 中的 多根工作区 功能。
克隆仓库 Microsoft/vscode-extension-samples 并打开示例:
> git clone https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples.git
> cd vscode-extension-samples/lsp-sample
> npm install
> npm run compile
> code .
上述操作安装了所有依赖项,并打开了包含客户端和服务器代码的lsp-sample工作区。以下是lsp-sample结构的大致概述:
.
├── client // Language Client
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── test // End to End tests for Language Client / Server
│ │ └── extension.ts // Language Client entry point
├── package.json // The extension manifest
└── server // Language Server
└── src
└── server.ts // Language Server entry point
解释 'Language Client'
首先让我们看一下/package.json,它描述了语言客户端的功能。有两个有趣的部分:
首先,查看configuration部分:
"configuration": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Example configuration",
"properties": {
"languageServerExample.maxNumberOfProblems": {
"scope": "resource",
"type": "number",
"default": 100,
"description": "Controls the maximum number of problems produced by the server."
}
}
}
本节为VS Code提供了configuration设置。示例将解释这些设置在启动时以及每次设置更改时如何发送到语言服务器。
注意: 如果你的扩展兼容VS Code 1.74.0之前的版本,你必须在
activationEvents字段中声明onLanguage:plaintext,以告诉VS Code在打开纯文本文件(例如扩展名为.txt的文件)时立即激活扩展:"activationEvents": []
实际的Language Client源代码和相应的package.json位于/client文件夹中。/client/package.json文件中有趣的部分是它通过engines字段引用了vscode扩展主机API,并添加了对vscode-languageclient库的依赖:
"engines": {
"vscode": "^1.52.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"vscode-languageclient": "^7.0.0"
}
如前所述,客户端是作为普通的VS Code扩展实现的,并且可以访问所有VS Code命名空间API。
下面是对应的extension.ts文件的内容,这是lsp-sample扩展的入口:
import * as path from 'path';
import { workspace, ExtensionContext } from 'vscode';
import {
LanguageClient,
LanguageClientOptions,
ServerOptions,
TransportKind
} from 'vscode-languageclient/node';
let client: LanguageClient;
export function activate(context: ExtensionContext) {
// The server is implemented in node
let serverModule = context.asAbsolutePath(path.join('server', 'out', 'server.js'));
// The debug options for the server
// --inspect=6009: runs the server in Node's Inspector mode so VS Code can attach to the server for debugging
let debugOptions = { execArgv: ['--nolazy', '--inspect=6009'] };
// If the extension is launched in debug mode then the debug server options are used
// Otherwise the run options are used
let serverOptions: ServerOptions = {
run: { module: serverModule, transport: TransportKind.ipc },
debug: {
module: serverModule,
transport: TransportKind.ipc,
options: debugOptions
}
};
// Options to control the language client
let clientOptions: LanguageClientOptions = {
// Register the server for plain text documents
documentSelector: [{ scheme: 'file', language: 'plaintext' }],
synchronize: {
// Notify the server about file changes to '.clientrc files contained in the workspace
fileEvents: workspace.createFileSystemWatcher('**/.clientrc')
}
};
// Create the language client and start the client.
client = new LanguageClient(
'languageServerExample',
'Language Server Example',
serverOptions,
clientOptions
);
// Start the client. This will also launch the server
client.start();
}
export function deactivate(): Thenable<void> | undefined {
if (!client) {
return undefined;
}
return client.stop();
}
解释 '语言服务器'
注意: 从GitHub仓库克隆的'Server'实现包含了最终的演练实现。要跟随演练,你可以创建一个新的
server.ts或修改克隆版本的内容。
在示例中,服务器也是用TypeScript实现的,并使用Node.js执行。由于VS Code已经自带了一个Node.js运行时,除非你对运行时环境有特定要求,否则不需要提供自己的运行时。
语言服务器的源代码位于 /server。服务器 package.json 文件中的有趣部分是:
"dependencies": {
"vscode-languageserver": "^7.0.0",
"vscode-languageserver-textdocument": "^1.0.1"
}
这引入了vscode-languageserver库。
下面是一个服务器实现,它使用提供的文本文档管理器,通过始终从VS Code向服务器发送增量差异来同步文本文档。
import {
createConnection,
TextDocuments,
Diagnostic,
DiagnosticSeverity,
ProposedFeatures,
InitializeParams,
DidChangeConfigurationNotification,
CompletionItem,
CompletionItemKind,
TextDocumentPositionParams,
TextDocumentSyncKind,
InitializeResult
} from 'vscode-languageserver/node';
import { TextDocument } from 'vscode-languageserver-textdocument';
// Create a connection for the server, using Node's IPC as a transport.
// Also include all preview / proposed LSP features.
let connection = createConnection(ProposedFeatures.all);
// Create a simple text document manager.
let documents: TextDocuments<TextDocument> = new TextDocuments(TextDocument);
let hasConfigurationCapability: boolean = false;
let hasWorkspaceFolderCapability: boolean = false;
let hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability: boolean = false;
connection.onInitialize((params: InitializeParams) => {
let capabilities = params.capabilities;
// Does the client support the `workspace/configuration` request?
// If not, we fall back using global settings.
hasConfigurationCapability = !!(
capabilities.workspace && !!capabilities.workspace.configuration
);
hasWorkspaceFolderCapability = !!(
capabilities.workspace && !!capabilities.workspace.workspaceFolders
);
hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability = !!(
capabilities.textDocument &&
capabilities.textDocument.publishDiagnostics &&
capabilities.textDocument.publishDiagnostics.relatedInformation
);
const result: InitializeResult = {
capabilities: {
textDocumentSync: TextDocumentSyncKind.Incremental,
// Tell the client that this server supports code completion.
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
result.capabilities.workspace = {
workspaceFolders: {
supported: true
}
};
}
return result;
});
connection.onInitialized(() => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Register for all configuration changes.
connection.client.register(DidChangeConfigurationNotification.type, undefined);
}
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
connection.workspace.onDidChangeWorkspaceFolders(_event => {
connection.console.log('Workspace folder change event received.');
});
}
});
// The example settings
interface ExampleSettings {
maxNumberOfProblems: number;
}
// The global settings, used when the `workspace/configuration` request is not supported by the client.
// Please note that this is not the case when using this server with the client provided in this example
// but could happen with other clients.
const defaultSettings: ExampleSettings = { maxNumberOfProblems: 1000 };
let globalSettings: ExampleSettings = defaultSettings;
// Cache the settings of all open documents
let documentSettings: Map<string, Thenable<ExampleSettings>> = new Map();
connection.onDidChangeConfiguration(change => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Reset all cached document settings
documentSettings.clear();
} else {
globalSettings = <ExampleSettings>(
(change.settings.languageServerExample || defaultSettings)
);
}
// Revalidate all open text documents
documents.all().forEach(validateTextDocument);
});
function getDocumentSettings(resource: string): Thenable<ExampleSettings> {
if (!hasConfigurationCapability) {
return Promise.resolve(globalSettings);
}
let result = documentSettings.get(resource);
if (!result) {
result = connection.workspace.getConfiguration({
scopeUri: resource,
section: 'languageServerExample'
});
documentSettings.set(resource, result);
}
return result;
}
// Only keep settings for open documents
documents.onDidClose(e => {
documentSettings.delete(e.document.uri);
});
// The content of a text document has changed. This event is emitted
// when the text document first opened or when its content has changed.
documents.onDidChangeContent(change => {
validateTextDocument(change.document);
});
async function validateTextDocument(textDocument: TextDocument): Promise<void> {
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
}
connection.onDidChangeWatchedFiles(_change => {
// Monitored files have change in VS Code
connection.console.log('We received a file change event');
});
// This handler provides the initial list of the completion items.
connection.onCompletion(
(_textDocumentPosition: TextDocumentPositionParams): CompletionItem[] => {
// The pass parameter contains the position of the text document in
// which code complete got requested. For the example we ignore this
// info and always provide the same completion items.
return [
{
label: 'TypeScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 1
},
{
label: 'JavaScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 2
}
];
}
);
// This handler resolves additional information for the item selected in
// the completion list.
connection.onCompletionResolve(
(item: CompletionItem): CompletionItem => {
if (item.data === 1) {
item.detail = 'TypeScript details';
item.documentation = 'TypeScript documentation';
} else if (item.data === 2) {
item.detail = 'JavaScript details';
item.documentation = 'JavaScript documentation';
}
return item;
}
);
// Make the text document manager listen on the connection
// for open, change and close text document events
documents.listen(connection);
// Listen on the connection
connection.listen();
添加简单验证
为了向服务器添加文档验证,我们向文本文档管理器添加了一个监听器,每当文本文档的内容发生变化时,该监听器就会被调用。然后由服务器决定何时是验证文档的最佳时间。在示例实现中,服务器验证纯文本文档并标记所有使用全大写的单词。相应的代码片段如下所示:
// The content of a text document has changed. This event is emitted
// when the text document first opened or when its content has changed.
documents.onDidChangeContent(async change => {
let textDocument = change.document;
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
});
诊断技巧与窍门
- 如果起始位置和结束位置相同,VS Code 将在该位置的单词下用波浪线标记。
- 如果你想用波浪线一直下划线到行尾,那么将结束位置的字符设置为Number.MAX_VALUE。
要运行语言服务器,请执行以下步骤:
- 按下 ⇧⌘B (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+B) 以启动构建任务。该任务将编译客户端和服务器。
- 打开运行视图,选择启动客户端启动配置,然后按下开始调试按钮,以启动一个额外的扩展开发主机实例的VS Code,该实例执行扩展代码。
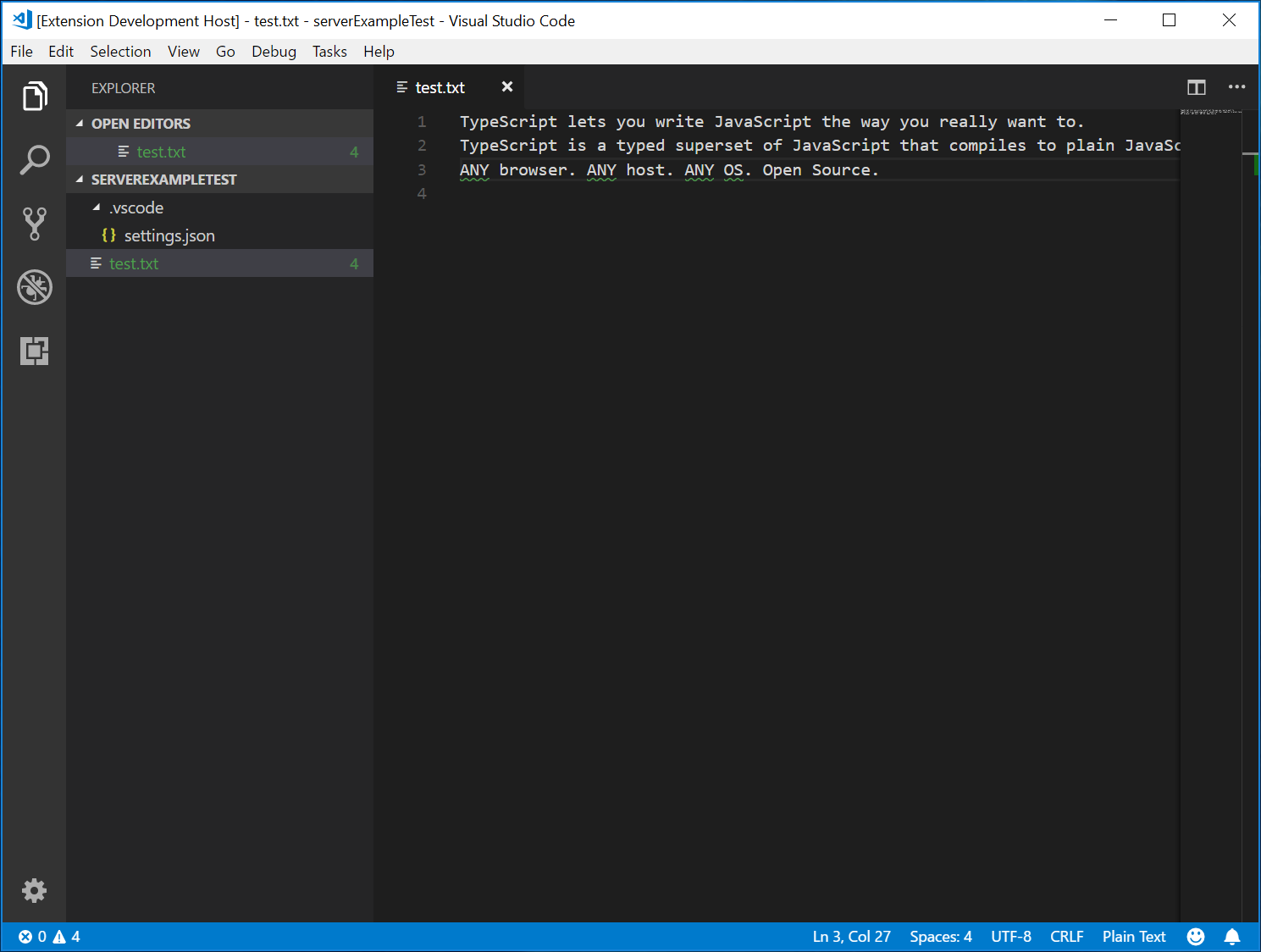
- 在根文件夹中创建一个
test.txt文件并粘贴以下内容:
TypeScript lets you write JavaScript the way you really want to.
TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript.
ANY browser. ANY host. ANY OS. Open Source.
扩展开发主机实例将如下所示:
调试客户端和服务器
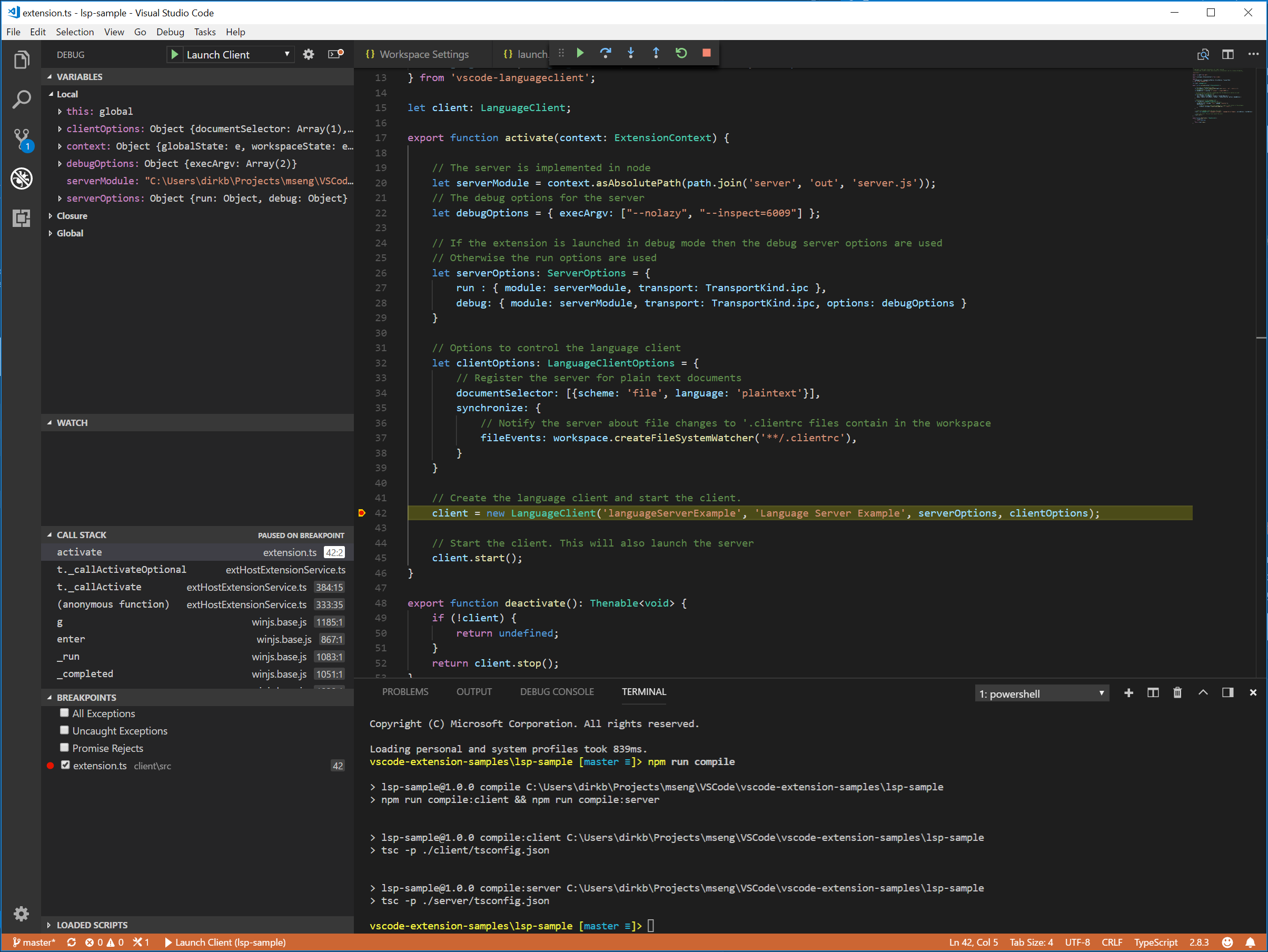
调试客户端代码就像调试普通扩展一样简单。在客户端代码中设置断点,然后通过按下 F5 来调试扩展。
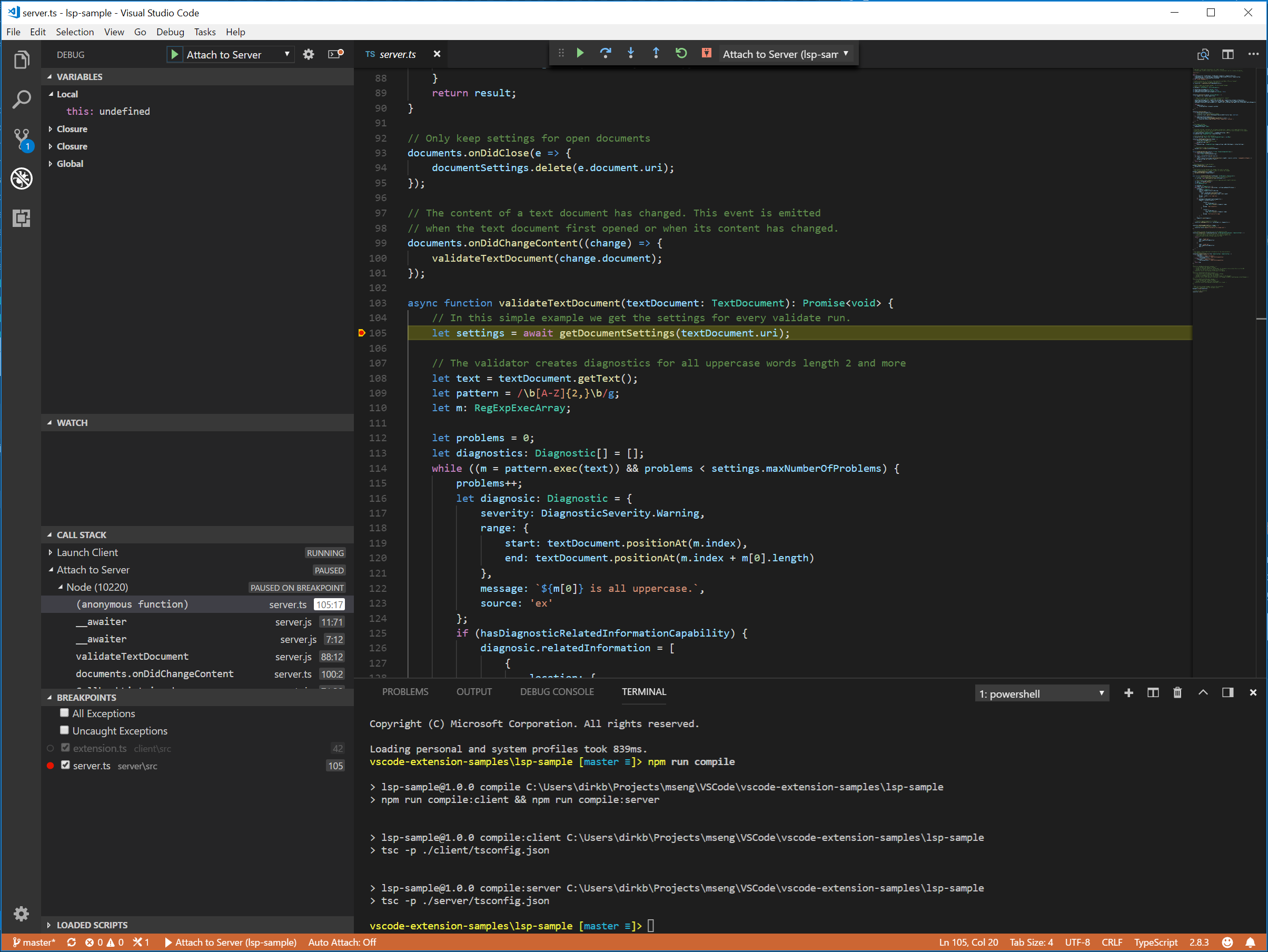
由于服务器是由扩展(客户端)中运行的LanguageClient启动的,我们需要将调试器附加到正在运行的服务器上。为此,切换到运行和调试视图,选择启动配置附加到服务器,然后按下F5。这将把调试器附加到服务器上。
语言服务器的日志支持
如果您正在使用vscode-languageclient来实现客户端,您可以指定一个设置[langId].trace.server,该设置指示客户端将语言客户端/服务器之间的通信记录到语言客户端的name通道中。
对于lsp-sample,您可以设置此设置:"languageServerExample.trace.server": "verbose"。现在转到“Language Server Example”频道。您应该会看到日志:
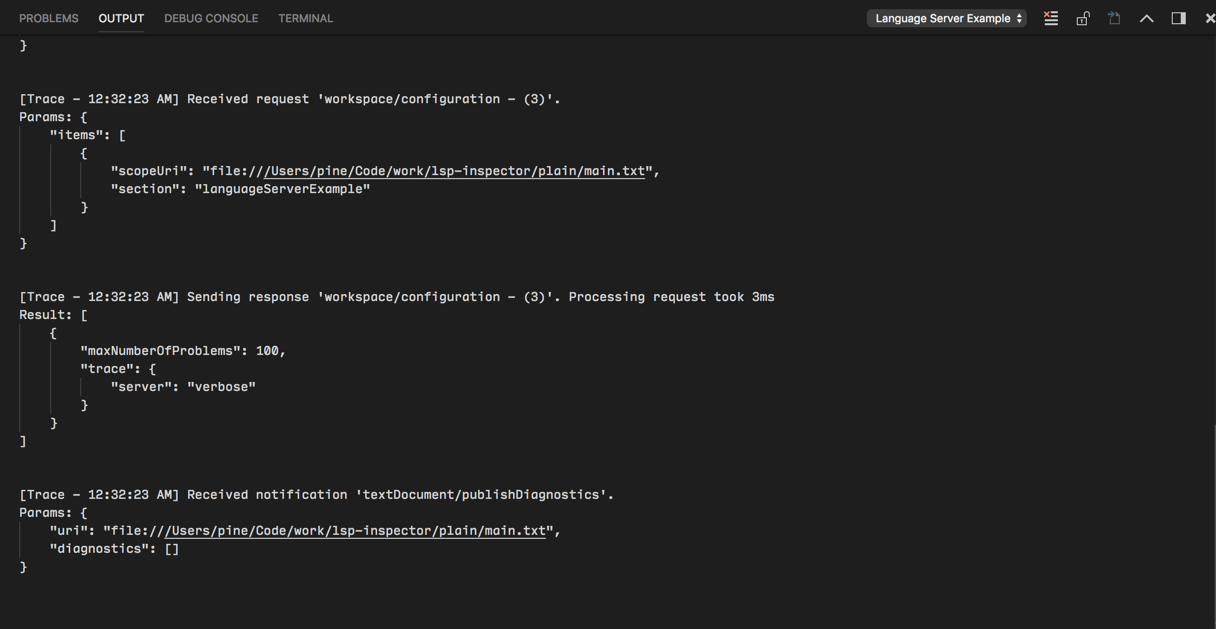
在服务器中使用配置设置
在编写扩展的客户端部分时,我们已经定义了一个设置来控制报告的最大问题数量。我们还在服务器端编写了代码来从客户端读取这些设置:
function getDocumentSettings(resource: string): Thenable<ExampleSettings> {
if (!hasConfigurationCapability) {
return Promise.resolve(globalSettings);
}
let result = documentSettings.get(resource);
if (!result) {
result = connection.workspace.getConfiguration({
scopeUri: resource,
section: 'languageServerExample'
});
documentSettings.set(resource, result);
}
return result;
}
我们现在唯一需要做的就是监听服务器端的配置更改,如果设置发生变化,重新验证打开的文本文档。为了能够重用文档更改事件处理的验证逻辑,我们将代码提取到一个validateTextDocument函数中,并修改代码以尊重maxNumberOfProblems变量:
async function validateTextDocument(textDocument: TextDocument): Promise<void> {
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
}
配置更改的处理是通过为连接添加配置更改的通知处理程序来完成的。相应的代码如下所示:
connection.onDidChangeConfiguration(change => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Reset all cached document settings
documentSettings.clear();
} else {
globalSettings = <ExampleSettings>(
(change.settings.languageServerExample || defaultSettings)
);
}
// Revalidate all open text documents
documents.all().forEach(validateTextDocument);
});
再次启动客户端并将设置更改为最大报告1问题会导致以下验证:
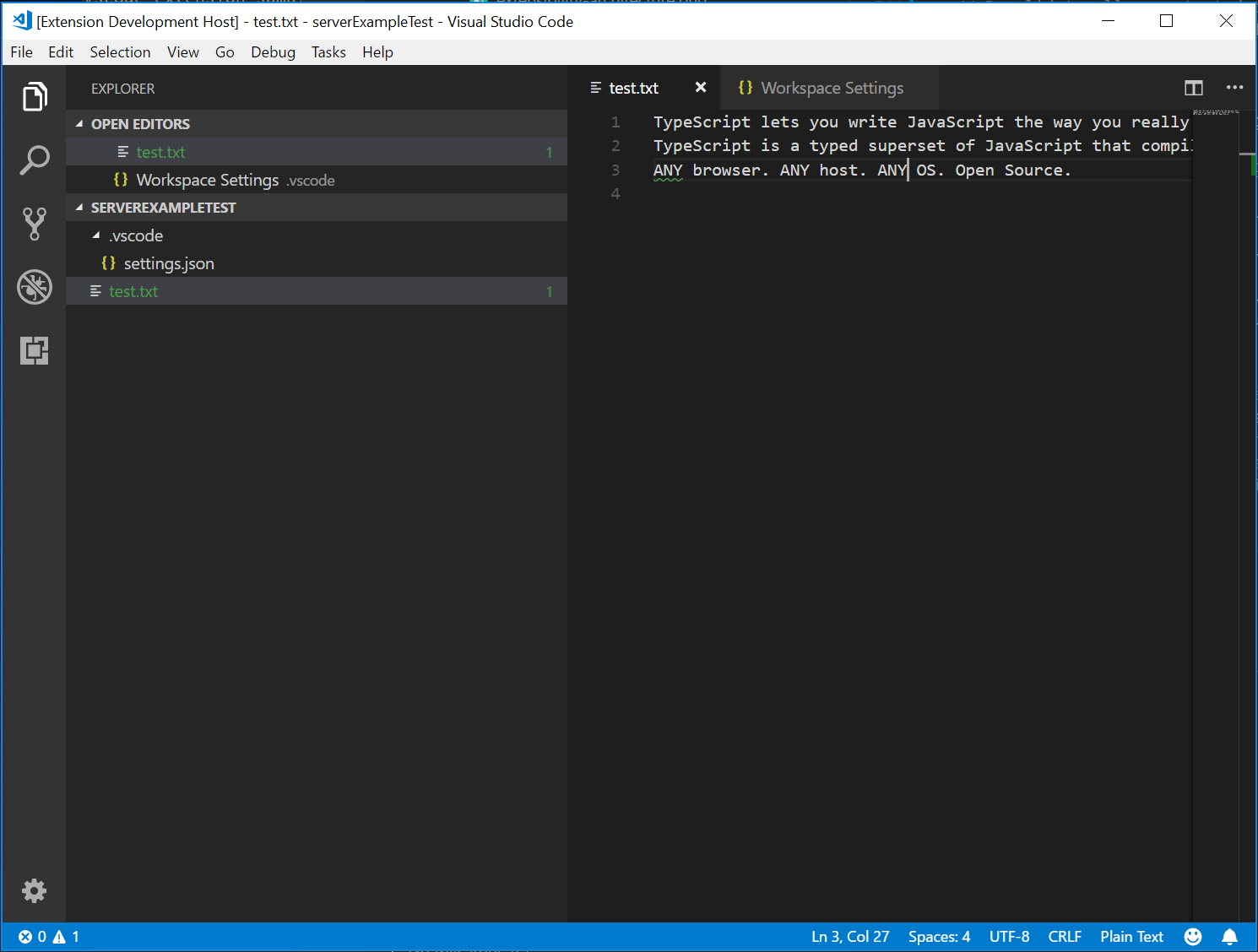
添加额外的语言功能
语言服务器通常实现的第一个有趣功能是文档的验证。从这个意义上说,甚至一个linter也可以算作一个语言服务器,在VS Code中,linter通常作为语言服务器实现(参见eslint和jshint作为例子)。但语言服务器还有更多功能。它们可以提供代码补全、查找所有引用或转到定义。下面的示例代码为服务器添加了代码补全功能。它建议了两个词'TypeScript'和'JavaScript'。
// This handler provides the initial list of the completion items.
connection.onCompletion(
(_textDocumentPosition: TextDocumentPositionParams): CompletionItem[] => {
// The pass parameter contains the position of the text document in
// which code complete got requested. For the example we ignore this
// info and always provide the same completion items.
return [
{
label: 'TypeScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 1
},
{
label: 'JavaScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 2
}
];
}
);
// This handler resolves additional information for the item selected in
// the completion list.
connection.onCompletionResolve(
(item: CompletionItem): CompletionItem => {
if (item.data === 1) {
item.detail = 'TypeScript details';
item.documentation = 'TypeScript documentation';
} else if (item.data === 2) {
item.detail = 'JavaScript details';
item.documentation = 'JavaScript documentation';
}
return item;
}
);
data 字段用于在解析处理程序中唯一标识一个完成项。数据属性对协议是透明的。由于底层消息传递协议是基于 JSON 的,因此数据字段应仅包含可序列化为 JSON 和从 JSON 反序列化的数据。
唯一缺少的是告诉VS Code服务器支持代码完成请求。为此,在初始化处理程序中标记相应的能力:
connection.onInitialize((params): InitializeResult => {
...
return {
capabilities: {
...
// Tell the client that the server supports code completion
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
});
下面的截图显示了在纯文本文件上运行的完整代码:
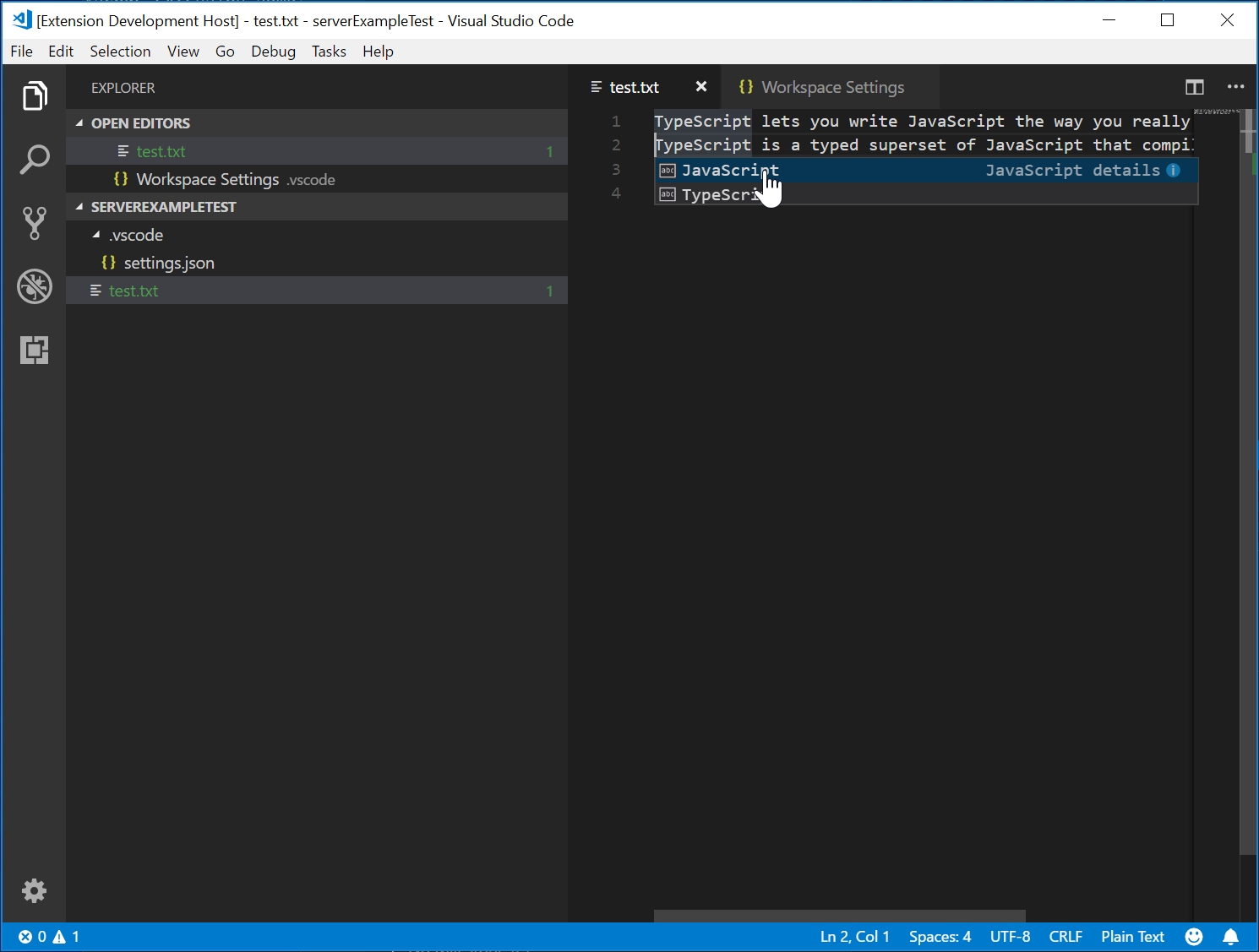
测试语言服务器
要创建一个高质量的语言服务器,我们需要构建一个涵盖其功能的良好测试套件。测试语言服务器有两种常见的方法:
- 单元测试:如果你想通过模拟所有发送到语言服务器的信息来测试特定功能,这非常有用。VS Code的HTML / CSS / JSON 语言服务器采用这种方法进行测试。LSP npm模块也使用这种方法。参见这里查看一些使用npm协议模块编写的单元测试。
- 端到端测试:这与VS Code 扩展测试类似。这种方法的优点是它通过实例化一个带有工作区的 VS Code 实例、打开文件、激活语言客户端/服务器并运行VS Code 命令来运行测试。如果您有难以或无法模拟的文件、设置或依赖项(例如
node_modules),这种方法更为优越。流行的Python扩展采用这种方法进行测试。
可以在您选择的任何测试框架中进行单元测试。这里我们描述了如何对语言服务器扩展进行端到端测试。
打开 .vscode/launch.json,你可以找到一个 E2E 测试目标:
{
"name": "Language Server E2E Test",
"type": "extensionHost",
"request": "launch",
"runtimeExecutable": "${execPath}",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceRoot}",
"--extensionTestsPath=${workspaceRoot}/client/out/test/index",
"${workspaceRoot}/client/testFixture"
],
"outFiles": ["${workspaceRoot}/client/out/test/**/*.js"]
}
如果你运行这个调试目标,它将启动一个VS Code实例,并将client/testFixture作为活动工作区。然后,VS Code将继续执行client/src/test中的所有测试。作为调试提示,你可以在client/src/test中的TypeScript文件中设置断点,它们将会被触发。
让我们看一下completion.test.ts文件:
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
import * as assert from 'assert';
import { getDocUri, activate } from './helper';
suite('Should do completion', () => {
const docUri = getDocUri('completion.txt');
test('Completes JS/TS in txt file', async () => {
await testCompletion(docUri, new vscode.Position(0, 0), {
items: [
{ label: 'JavaScript', kind: vscode.CompletionItemKind.Text },
{ label: 'TypeScript', kind: vscode.CompletionItemKind.Text }
]
});
});
});
async function testCompletion(
docUri: vscode.Uri,
position: vscode.Position,
expectedCompletionList: vscode.CompletionList
) {
await activate(docUri);
// Executing the command `vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider` to simulate triggering completion
const actualCompletionList = (await vscode.commands.executeCommand(
'vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider',
docUri,
position
)) as vscode.CompletionList;
assert.ok(actualCompletionList.items.length >= 2);
expectedCompletionList.items.forEach((expectedItem, i) => {
const actualItem = actualCompletionList.items[i];
assert.equal(actualItem.label, expectedItem.label);
assert.equal(actualItem.kind, expectedItem.kind);
});
}
在这个测试中,我们:
- 激活扩展。
- 运行命令
vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider并使用 URI 和位置来模拟完成触发。 - 将返回的完成项与我们的预期完成项进行断言。
让我们更深入地了解一下activate(docURI)函数。它定义在client/src/test/helper.ts中:
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
import * as path from 'path';
export let doc: vscode.TextDocument;
export let editor: vscode.TextEditor;
export let documentEol: string;
export let platformEol: string;
/**
* Activates the vscode.lsp-sample extension
*/
export async function activate(docUri: vscode.Uri) {
// The extensionId is `publisher.name` from package.json
const ext = vscode.extensions.getExtension('vscode-samples.lsp-sample')!;
await ext.activate();
try {
doc = await vscode.workspace.openTextDocument(docUri);
editor = await vscode.window.showTextDocument(doc);
await sleep(2000); // Wait for server activation
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
async function sleep(ms: number) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
在激活部分,我们:
- 使用
{publisher.name}.{extensionId}获取扩展,如package.json中所定义。 - 打开指定的文档,并在活动的文本编辑器中显示它。
- 睡眠2秒,以确保语言服务器已实例化。
准备完成后,我们可以运行与每个语言功能对应的VS Code 命令,并对返回的结果进行断言。
还有一个测试覆盖了我们刚刚实现的诊断功能。请在client/src/test/diagnostics.test.ts查看。
高级主题
到目前为止,本指南涵盖了:
- 语言服务器和语言服务器协议的简要概述。
- VS Code 中语言服务器扩展的架构
- lsp-sample 扩展,以及如何开发/调试/检查/测试它。
本指南中未涵盖一些更高级的主题。我们将提供这些资源的链接,以便进一步学习语言服务器开发。
额外的语言服务器功能
以下语言特性目前在语言服务器中支持,同时支持代码补全:
- 文档高亮: 在文本文档中高亮所有'等于'符号。
- 悬停: 为在文本文档中选择的符号提供悬停信息。
- 签名帮助: 为在文本文档中选择的符号提供签名帮助。
- 转到定义:为在文本文档中选择的符号提供转到定义支持。
- 转到类型定义:为在文本文档中选择的符号提供转到类型/接口定义的支持。
- 转到实现: 为在文本文档中选择的符号提供转到实现定义的支持。
- 查找引用:查找在文本文档中选择的符号的所有项目范围内的引用。
- 列出文档符号: 列出文本文档中定义的所有符号。
- 列出工作区符号: 列出所有项目范围内的符号。
- 代码操作:计算要运行的命令(通常是美化/重构)以用于给定的文本文档和范围。
- CodeLens: 计算给定文本文档的CodeLens统计信息。
- 文档格式化: 这包括整个文档的格式化、文档范围的格式化以及输入时的格式化。
- 重命名: 项目范围内对符号的重命名。
- 文档链接: 计算并解析文档内的链接。
- 文档颜色:计算并解析文档中的颜色,以在编辑器中提供颜色选择器。
编程语言特性主题描述了上述每种语言特性,并提供了如何通过语言服务器协议或直接从扩展中使用可扩展性API实现它们的指导。
增量文本文档同步
该示例使用由vscode-languageserver模块提供的简单文本文档管理器来同步VS Code和语言服务器之间的文档。
这有两个缺点:
- 由于文本文档的整个内容被重复发送到服务器,因此传输了大量数据。
- 如果使用现有的语言库,这些库通常支持增量文档更新,以避免不必要的解析和抽象语法树创建。
因此,该协议也支持增量文档同步。
要使用增量文档同步,服务器需要安装三个通知处理程序:
- onDidOpenTextDocument: 当在VS Code中打开一个文本文档时调用。
- onDidChangeTextDocument: 当VS Code中的文本文档内容发生变化时调用。
- onDidCloseTextDocument: 当在VS Code中关闭文本文档时调用。
以下是一个代码片段,展示了如何在连接上挂载这些通知处理程序以及如何在初始化时返回正确的功能:
connection.onInitialize((params): InitializeResult => {
...
return {
capabilities: {
// Enable incremental document sync
textDocumentSync: TextDocumentSyncKind.Incremental,
...
}
};
});
connection.onDidOpenTextDocument((params) => {
// A text document was opened in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document. For documents stored on disk, this is a file URI.
// params.text the initial full content of the document.
});
connection.onDidChangeTextDocument((params) => {
// The content of a text document has change in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document.
// params.contentChanges describe the content changes to the document.
});
connection.onDidCloseTextDocument((params) => {
// A text document was closed in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document.
});
/*
Make the text document manager listen on the connection
for open, change and close text document events.
Comment out this line to allow `connection.onDidOpenTextDocument`,
`connection.onDidChangeTextDocument`, and `connection.onDidCloseTextDocument` to handle the events
*/
// documents.listen(connection);
直接使用VS Code API实现语言功能
虽然语言服务器有许多优点,但它们并不是扩展VS Code编辑功能的唯一选择。在您想为某种文档类型添加一些简单语言功能的情况下,可以考虑使用vscode.languages.register[LANGUAGE_FEATURE]Provider作为选项。
这里有一个completions-sample,使用vscode.languages.registerCompletionItemProvider来添加一些代码片段作为纯文本文件的补全。
更多展示VS Code API用法的示例可以在https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples找到。
语言服务器的容错解析器
大多数时候,编辑器中的代码是不完整且语法不正确的,但开发者仍然期望自动补全和其他语言功能能够正常工作。因此,语言服务器需要一个容错解析器:解析器从部分完整的代码中生成有意义抽象语法树(AST),语言服务器基于AST提供语言功能。
当我们在VS Code中改进PHP支持时,我们意识到官方的PHP解析器不具备容错性,无法直接在语言服务器中重用。因此,我们致力于Microsoft/tolerant-php-parser,并留下了详细的笔记,这些笔记可能对需要实现容错解析器的语言服务器作者有所帮助。
常见问题
当我尝试连接到服务器时,我收到“无法连接到运行时进程(5000毫秒后超时)”?
如果您在尝试附加调试器时服务器未运行,您将看到此超时错误。客户端启动语言服务器,因此请确保您已启动客户端以便拥有一个正在运行的服务器。如果客户端断点干扰了服务器的启动,您可能还需要禁用它们。
我已经阅读了本指南和LSP规范,但我仍然有一些未解决的问题。我可以在哪里获得帮助?
请在https://github.com/microsoft/language-server-protocol上打开一个问题。