YOLOS
概述
YOLOS模型由Yuxin Fang、Bencheng Liao、Xinggang Wang、Jiemin Fang、Jiyang Qi、Rui Wu、Jianwei Niu、Wenyu Liu在《You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection》中提出。 YOLOS提出仅利用普通的Vision Transformer (ViT)进行目标检测,灵感来源于DETR。结果表明,仅使用基础大小的编码器Transformer也可以在COCO上达到42 AP,与DETR和更复杂的框架如Faster R-CNN相当。
论文的摘要如下:
Transformer 能否从纯序列到序列的角度,以最少的关于二维空间结构的知识,执行二维对象和区域级别的识别?为了回答这个问题,我们提出了 You Only Look at One Sequence (YOLOS),这是一系列基于原始 Vision Transformer 的对象检测模型,具有最少的修改、区域先验以及目标任务的归纳偏差。我们发现,仅在中型 ImageNet-1k 数据集上预训练的 YOLOS 已经在具有挑战性的 COCO 对象检测基准上取得了相当有竞争力的性能,例如,直接从 BERT-Base 架构采用的 YOLOS-Base 可以在 COCO val 上获得 42.0 的 box AP。我们还通过 YOLOS 讨论了当前预训练方案和模型扩展策略对视觉中 Transformer 的影响和局限性。
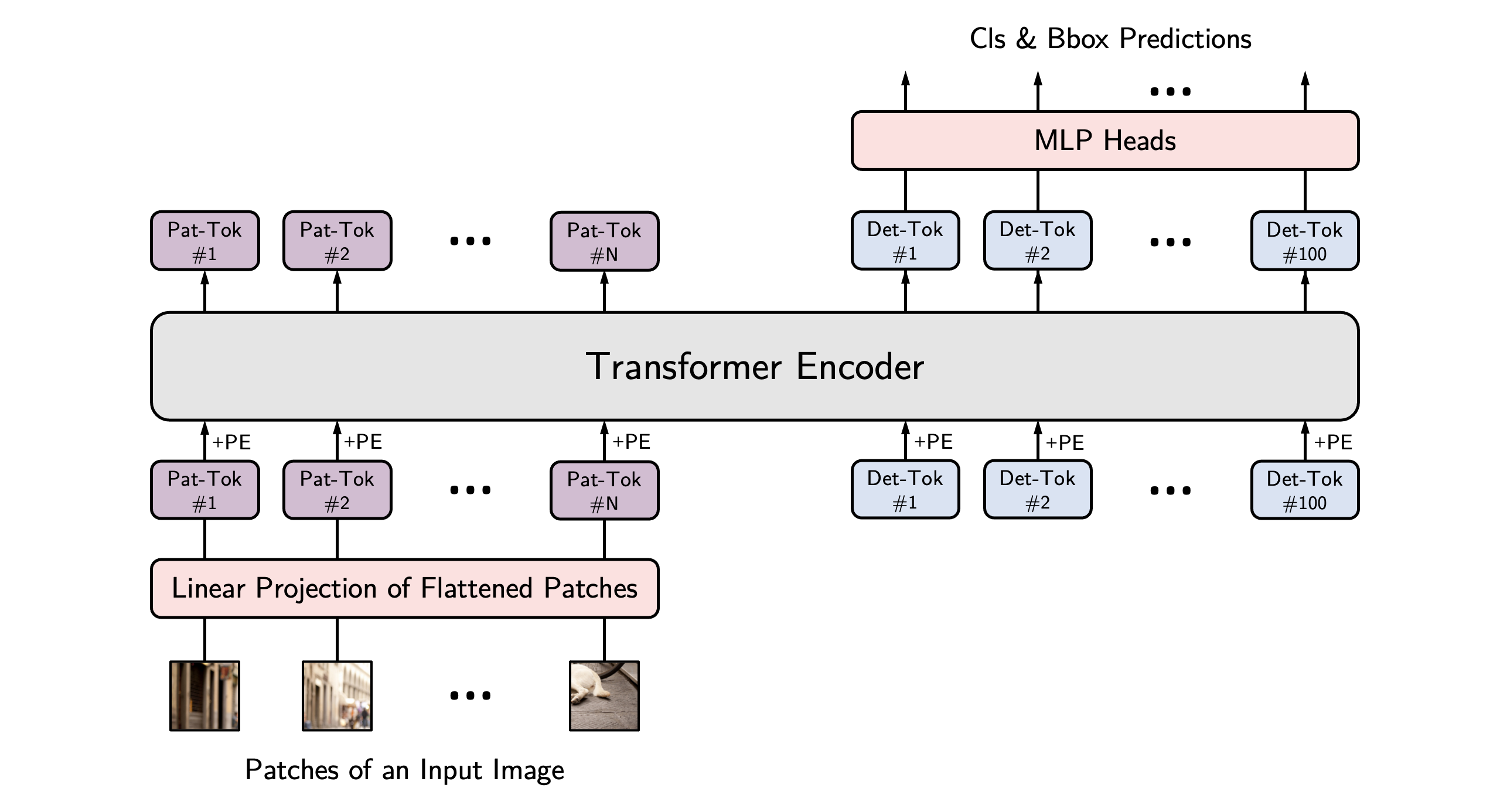 YOLOS architecture. Taken from the original paper.
YOLOS architecture. Taken from the original paper. 使用缩放点积注意力 (SDPA)
PyTorch 包含一个原生的缩放点积注意力(SDPA)操作符,作为 torch.nn.functional 的一部分。这个函数
包含了几种实现,可以根据输入和使用的硬件进行应用。更多信息请参阅
官方文档
或 GPU 推理
页面。
默认情况下,当有可用实现时,SDPA 用于 torch>=2.1.1,但你也可以在 from_pretrained() 中设置 attn_implementation="sdpa" 来明确请求使用 SDPA。
from transformers import AutoModelForObjectDetection
model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-base", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
...为了获得最佳加速效果,我们建议以半精度加载模型(例如 torch.float16 或 torch.bfloat16)。
在本地基准测试(A100-40GB,PyTorch 2.3.0,操作系统 Ubuntu 22.04)中,使用float32和hustvl/yolos-base模型,我们在推理过程中看到了以下加速效果。
| 批量大小 | 平均推理时间(毫秒),eager模式 | 平均推理时间(毫秒),sdpa模型 | 加速比,Sdpa / Eager(倍) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 106 | 76 | 1.39 |
| 2 | 154 | 90 | 1.71 |
| 4 | 222 | 116 | 1.91 |
| 8 | 368 | 168 | 2.19 |
资源
一份官方的 Hugging Face 和社区(由🌎表示)资源列表,帮助您开始使用 YOLOS。
- 所有展示推理 + 微调的示例笔记本 YolosForObjectDetection 在自定义数据集上的内容可以在 这里 找到。
- 用于微调YolosForObjectDetection的脚本,使用Trainer或Accelerate,可以在这里找到。
- 另请参阅:Object detection task guide
如果您有兴趣提交资源以包含在此处,请随时打开一个 Pull Request,我们将进行审核!理想情况下,资源应展示一些新内容,而不是重复现有资源。
使用 YolosImageProcessor 来为模型准备图像(以及可选的目标)。与 DETR 不同,YOLOS 不需要创建 pixel_mask。
YolosConfig
类 transformers.YolosConfig
< source >( hidden_size = 768 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 intermediate_size = 3072 hidden_act = 'gelu' hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 image_size = [512, 864] patch_size = 16 num_channels = 3 qkv_bias = True num_detection_tokens = 100 use_mid_position_embeddings = True auxiliary_loss = False class_cost = 1 bbox_cost = 5 giou_cost = 2 bbox_loss_coefficient = 5 giou_loss_coefficient = 2 eos_coefficient = 0.1 **kwargs )
参数
- hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, 可选, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 3072) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"selu"和"gelu_new"。 - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 嵌入层、编码器和池化器中所有全连接层的 dropout 概率。 - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比率。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, 可选, 默认为 1e-12) — 层归一化层使用的 epsilon 值。 - image_size (
List[int], 可选, 默认为[512, 864]) — 每张图像的尺寸(分辨率)。 - patch_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 16) — 每个补丁的大小(分辨率)。 - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — 输入通道的数量。 - qkv_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — 是否向查询、键和值添加偏置。 - num_detection_tokens (
int, optional, 默认为 100) — 检测令牌的数量。 - use_mid_position_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — 是否使用中间层位置编码. - auxiliary_loss (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 是否使用辅助解码损失(每个解码器层的损失)。 - class_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — 匈牙利匹配成本中分类错误的相对权重。 - bbox_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 5) — 匈牙利匹配成本中边界框坐标的L1误差的相对权重。 - giou_cost (
float, optional, 默认为 2) — 在匈牙利匹配成本中,边界框的广义 IoU 损失的相对权重。 - bbox_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 5) — 在目标检测损失中,L1边界框损失的相对权重。 - giou_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 2) — 在目标检测损失中,广义IoU损失的相对权重。 - eos_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — 在目标检测损失中,‘无对象’类的相对分类权重。
这是用于存储YolosModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化YOLOS模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生类似于YOLOS hustvl/yolos-base架构的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import YolosConfig, YolosModel
>>> # Initializing a YOLOS hustvl/yolos-base style configuration
>>> configuration = YolosConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the hustvl/yolos-base style configuration
>>> model = YolosModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configYolosImageProcessor
类 transformers.YolosImageProcessor
< source >( format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.AnnotationFormat] =
参数
- format (
str, optional, defaults to"coco_detection") — 注释的数据格式。可选值为“coco_detection”或“coco_panoptic”。 - do_resize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 控制是否将图像的(高度,宽度)尺寸调整为指定的size。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_resize参数进行覆盖。 - size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"shortest_edge" -- 800, "longest_edge": 1333}): Size of the image’s(height, width)dimensions after resizing. Can be overridden by thesizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. Available options are:{"height": int, "width": int}: The image will be resized to the exact size(height, width). Do NOT keep the aspect ratio.{"shortest_edge": int, "longest_edge": int}: The image will be resized to a maximum size respecting the aspect ratio and keeping the shortest edge less or equal toshortest_edgeand the longest edge less or equal tolongest_edge.{"max_height": int, "max_width": int}: The image will be resized to the maximum size respecting the aspect ratio and keeping the height less or equal tomax_heightand the width less or equal tomax_width.
- resample (
PILImageResampling, 可选, 默认为PILImageResampling.BILINEAR) — 如果调整图像大小,则使用的重采样过滤器。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 控制是否通过指定的比例rescale_factor重新缩放图像。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_rescale参数覆盖此设置。 - rescale_factor (
int或float, 可选, 默认为1/255) — 如果重新缩放图像,则使用的缩放因子。可以在preprocess方法中通过rescale_factor参数覆盖此值。 - do_normalize —
控制是否对图像进行归一化。可以在
preprocess方法中通过do_normalize参数进行覆盖。 - image_mean (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN) — 在标准化图像时使用的均值。可以是单个值或一个值列表,每个通道一个值。可以在preprocess方法中通过image_mean参数覆盖。 - image_std (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD) — 用于图像归一化的标准差值。可以是单个值或一个值列表,每个通道一个值。可以通过preprocess方法中的image_std参数进行覆盖。 - do_pad (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 控制是否对图像进行填充。可以通过preprocess方法中的do_pad参数进行覆盖。如果为True,图像将在底部和右侧用零进行填充。 如果提供了pad_size,图像将被填充到指定的尺寸。 否则,图像将被填充到批次中的最大高度和宽度。 - pad_size (
Dict[str, int], optional) — 图像填充的大小{"height": int, "width" int}。必须大于任何预处理提供的图像大小。 如果未提供pad_size,图像将被填充到批次中最大的高度和宽度。
构建一个Detr图像处理器。
预处理
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]] annotations: typing.Union[typing.Dict[str, typing.Union[int, str, typing.List[typing.Dict]]], typing.List[typing.Dict[str, typing.Union[int, str, typing.List[typing.Dict]]]], NoneType] = None return_segmentation_masks: bool = None masks_path: typing.Union[str, pathlib.Path, NoneType] = None do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None resample = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float, NoneType] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None do_convert_annotations: typing.Optional[bool] = None do_pad: typing.Optional[bool] = None format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.AnnotationFormat, NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] =
参数
- images (
ImageInput) — 要预处理的图像或图像批次。期望输入单个或批次的图像,像素值范围从0到255。如果传入的图像的像素值在0到1之间,请设置do_rescale=False. - annotations (
AnnotationTypeorList[AnnotationType], optional) — List of annotations associated with the image or batch of images. If annotation is for object detection, the annotations should be a dictionary with the following keys:- “image_id” (
int): The image id. - “annotations” (
List[Dict]): List of annotations for an image. Each annotation should be a dictionary. An image can have no annotations, in which case the list should be empty. If annotation is for segmentation, the annotations should be a dictionary with the following keys: - “image_id” (
int): The image id. - “segments_info” (
List[Dict]): List of segments for an image. Each segment should be a dictionary. An image can have no segments, in which case the list should be empty. - “file_name” (
str): The file name of the image.
- “image_id” (
- return_segmentation_masks (
bool, optional, defaults to self.return_segmentation_masks) — 是否返回分割掩码。 - masks_path (
str或pathlib.Path, 可选) — 包含分割掩码的目录路径。 - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_resize) — 是否调整图像大小. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to self.size) — Size of the image’s(height, width)dimensions after resizing. Available options are:{"height": int, "width": int}: The image will be resized to the exact size(height, width). Do NOT keep the aspect ratio.{"shortest_edge": int, "longest_edge": int}: The image will be resized to a maximum size respecting the aspect ratio and keeping the shortest edge less or equal toshortest_edgeand the longest edge less or equal tolongest_edge.{"max_height": int, "max_width": int}: The image will be resized to the maximum size respecting the aspect ratio and keeping the height less or equal tomax_heightand the width less or equal tomax_width.
- resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults to self.resample) — 调整图像大小时使用的重采样过滤器。 - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_rescale) — 是否对图像进行重新缩放. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults to self.rescale_factor) — 在重新缩放图像时使用的重新缩放因子。 - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_normalize) — 是否对图像进行归一化处理。 - image_mean (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为 self.image_mean) — 在标准化图像时使用的均值. - image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults to self.image_std) — 用于标准化图像时的标准差。 - do_convert_annotations (
bool, 可选, 默认为 self.do_convert_annotations) — 是否将注释转换为模型期望的格式。将边界框从格式(top_left_x, top_left_y, width, height)转换为(center_x, center_y, width, height)并转换为相对坐标。 - do_pad (
bool, 可选, 默认为 self.do_pad) — 是否对图像进行填充。如果为True,将在图像的底部和右侧用零进行填充。如果提供了pad_size,图像将被填充到指定的尺寸。否则,图像将被填充到批次中的最大高度和宽度。 - format (
str或AnnotationFormat, 可选, 默认为 self.format) — 注释的格式。 - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选, 默认为 self.return_tensors) — 返回的张量类型。如果为None,将返回图像列表。 - data_format (
str或ChannelDimension, 可选, 默认为 self.data_format) — 图像的通道维度格式。如果未提供,将与输入图像相同。 - input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:"channels_first"或ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。"channels_last"或ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。"none"或ChannelDimension.NONE: 图像格式为 (height, width)。
- pad_size (
Dict[str, int], 可选) — 图像填充的大小{"height": int, "width" int}。必须大于任何预处理提供的图像大小。 如果未提供pad_size,图像将被填充到批次中最大的高度和宽度。
预处理一张图像或一批图像,以便模型可以使用。
pad
< source >( images: typing.List[numpy.ndarray] annotations: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Dict[str, typing.Any]]] = None constant_values: typing.Union[float, typing.Iterable[float]] = 0 return_pixel_mask: bool = False return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Optional[transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = None input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None update_bboxes: bool = True pad_size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None )
参数
- image (
np.ndarray) — 要填充的图像。 - annotations (
List[Dict[str, any]], optional) — 与图像一起填充的注释。如果提供,边界框将更新以匹配填充后的图像。 - constant_values (
float或Iterable[float], 可选) — 如果mode是"constant",则用于填充的值。 - return_pixel_mask (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — 是否返回像素掩码。 - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选) — 返回的张量类型。可以是以下之一:- 未设置:返回一个
np.ndarray列表。 TensorType.TENSORFLOW或'tf':返回一个类型为tf.Tensor的批次。TensorType.PYTORCH或'pt':返回一个类型为torch.Tensor的批次。TensorType.NUMPY或'np':返回一个类型为np.ndarray的批次。TensorType.JAX或'jax':返回一个类型为jax.numpy.ndarray的批次。
- 未设置:返回一个
- data_format (
str或ChannelDimension, 可选) — 图像的通道维度格式。如果未提供,将与输入图像相同。 - input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未提供,将会自动推断。 - update_bboxes (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否更新注释中的边界框以匹配填充后的图像。如果边界框尚未转换为相对坐标和(centre_x, centre_y, width, height)格式,则边界框将不会更新。 - pad_size (
Dict[str, int], 可选) — 图像填充的大小{"height": int, "width" int}。必须大于预处理中提供的任何图像大小。 如果未提供pad_size,图像将被填充到批次中最大的高度和宽度。
将一批图像用零填充到图像的底部和右侧,使其达到批次中最大高度和宽度的尺寸,并可选择返回其相应的像素掩码。
post_process_object_detection
< source >( outputs threshold: float = 0.5 target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = None ) → List[Dict]
将YolosForObjectDetection的原始输出转换为最终边界框,格式为(左上角x,左上角y,右下角x,右下角y)。仅支持PyTorch。
YolosFeatureExtractor
预处理一张图像或一批图像。
pad
< source >( images: typing.List[numpy.ndarray] annotations: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Dict[str, typing.Any]]] = None constant_values: typing.Union[float, typing.Iterable[float]] = 0 return_pixel_mask: bool = False return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Optional[transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = None input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None update_bboxes: bool = True pad_size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None )
参数
- image (
np.ndarray) — 要填充的图像. - annotations (
List[Dict[str, any]], optional) — 与图像一起填充的注释。如果提供,边界框将更新以匹配填充后的图像。 - constant_values (
float或Iterable[float], 可选) — 如果mode是"constant",则用于填充的值。 - return_pixel_mask (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — 是否返回像素掩码。 - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选) — 返回的张量类型。可以是以下之一:- 未设置:返回一个
np.ndarray列表。 TensorType.TENSORFLOW或'tf':返回一个类型为tf.Tensor的批次。TensorType.PYTORCH或'pt':返回一个类型为torch.Tensor的批次。TensorType.NUMPY或'np':返回一个类型为np.ndarray的批次。TensorType.JAX或'jax':返回一个类型为jax.numpy.ndarray的批次。
- 未设置:返回一个
- data_format (
str或ChannelDimension, 可选) — 图像的通道维度格式。如果未提供,将与输入图像相同。 - input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未提供,将自动推断。 - update_bboxes (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否更新注释中的边界框以匹配填充后的图像。如果 边界框尚未转换为相对坐标和(centre_x, centre_y, width, height)格式,边界框将不会被更新。 - pad_size (
Dict[str, int], 可选) — 图像填充的大小{"height": int, "width" int}。必须大于预处理中提供的任何图像大小。 如果未提供pad_size,图像将被填充到批次中最大的高度和宽度。
将一批图像用零填充到图像的底部和右侧,使其达到批次中最大高度和宽度的尺寸,并可选择返回其相应的像素掩码。
post_process_object_detection
< source >( outputs threshold: float = 0.5 target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = None ) → List[Dict]
将YolosForObjectDetection的原始输出转换为最终边界框,格式为(左上角x,左上角y,右下角x,右下角y)。仅支持PyTorch。
YolosModel
类 transformers.YolosModel
< source >( config: YolosConfig add_pooling_layer: bool = True )
参数
- config (YolosConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
裸的YOLOS模型变压器输出原始隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。 这个模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其用作常规的PyTorch模块,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有事项。
前进
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 YolosImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(YolosConfig)和输入。
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, hidden_size)) — 序列的第一个标记(分类标记)在经过用于辅助预训练任务的层进一步处理后的最后一层隐藏状态。例如,对于BERT系列模型,这返回经过线性层和tanh激活函数处理后的分类标记。线性层的权重是在预训练期间通过下一个句子预测(分类)目标训练的。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力softmax后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
YolosModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, YolosModel
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-small")
>>> model = YolosModel.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-small")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 3401, 384]YolosForObjectDetection
类 transformers.YolosForObjectDetection
< source >( config: YolosConfig )
参数
- config (YolosConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
YOLOS模型(由ViT编码器组成)在顶部带有目标检测头,用于诸如COCO检测等任务。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其用作常规的PyTorch模块,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor labels: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Dict]] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.yolos.modeling_yolos.YolosObjectDetectionOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 YolosImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
List[Dict]长度为(batch_size,), 可选) — 用于计算二分匹配损失的标签。字典列表,每个字典至少包含以下2个键:'class_labels'和'boxes'(分别是批次中图像的类别标签和边界框)。类别标签本身应为长度为(图像中边界框的数量,)的torch.LongTensor,而边界框应为形状为(图像中边界框的数量, 4)的torch.FloatTensor。
返回
transformers.models.yolos.modeling_yolos.YolosObjectDetectionOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.yolos.modeling_yolos.YolosObjectDetectionOutput 或一个由 torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含根据配置(YolosConfig)和输入的各种元素。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 总损失,作为类别预测的负对数似然(交叉熵)和边界框损失的线性组合。后者定义为 L1 损失和广义尺度不变 IoU 损失的线性组合。 - loss_dict (
Dict,可选) — 包含各个损失的字典。用于记录日志。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_queries, num_classes + 1)) — 所有查询的分类 logits(包括无对象)。 - pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_queries, 4)) — 所有查询的归一化框坐标,表示为 (center_x, center_y, width, height)。这些值在 [0, 1] 范围内归一化,相对于批次中每个单独图像的大小(忽略可能的填充)。您可以使用post_process()来检索未归一化的边界框。 - auxiliary_outputs (
list[Dict],可选) — 可选,仅在激活辅助损失时返回(即config.auxiliary_loss设置为True)并且提供了标签。它是一个字典列表,包含每个解码器层的上述两个键(logits和pred_boxes)。 - last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size),可选) — 模型解码器最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型每层输出的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
YolosForObjectDetection 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, AutoModelForObjectDetection
>>> import torch
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-tiny")
>>> model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-tiny")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # convert outputs (bounding boxes and class logits) to Pascal VOC format (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
>>> target_sizes = torch.tensor([image.size[::-1]])
>>> results = image_processor.post_process_object_detection(outputs, threshold=0.9, target_sizes=target_sizes)[
... 0
... ]
>>> for score, label, box in zip(results["scores"], results["labels"], results["boxes"]):
... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()]
... print(
... f"Detected {model.config.id2label[label.item()]} with confidence "
... f"{round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}"
... )
Detected remote with confidence 0.991 at location [46.48, 72.78, 178.98, 119.3]
Detected remote with confidence 0.908 at location [336.48, 79.27, 368.23, 192.36]
Detected cat with confidence 0.934 at location [337.18, 18.06, 638.14, 373.09]
Detected cat with confidence 0.979 at location [10.93, 53.74, 313.41, 470.67]
Detected remote with confidence 0.974 at location [41.63, 72.23, 178.09, 119.99]