OWL-ViT
概述
OWL-ViT(全称为Vision Transformer for Open-World Localization)由Matthias Minderer、Alexey Gritsenko、Austin Stone、Maxim Neumann、Dirk Weissenborn、Alexey Dosovitskiy、Aravindh Mahendran、Anurag Arnab、Mostafa Dehghani、Zhuoran Shen、Xiao Wang、Xiaohua Zhai、Thomas Kipf和Neil Houlsby在Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers中提出。OWL-ViT是一个开放词汇对象检测网络,训练于多种(图像,文本)对。它可以用于通过一个或多个文本查询来查询图像,以搜索和检测文本中描述的目标对象。
论文的摘要如下:
将简单的架构与大规模预训练相结合,已经在图像分类领域带来了巨大的改进。对于目标检测,预训练和扩展方法尚未完全确立,尤其是在长尾和开放词汇设置中,训练数据相对稀缺。在本文中,我们提出了一种将图像-文本模型迁移到开放词汇目标检测的强大方法。我们使用标准的Vision Transformer架构,仅进行最小限度的修改,结合对比图像-文本预训练和端到端的检测微调。我们对这种设置的扩展特性分析表明,增加图像级预训练和模型规模在下游检测任务中带来了一致的改进。我们提供了适应策略和正则化方法,以在零样本文本条件和单样本图像条件的目标检测中实现非常强的性能。代码和模型可在GitHub上获取。
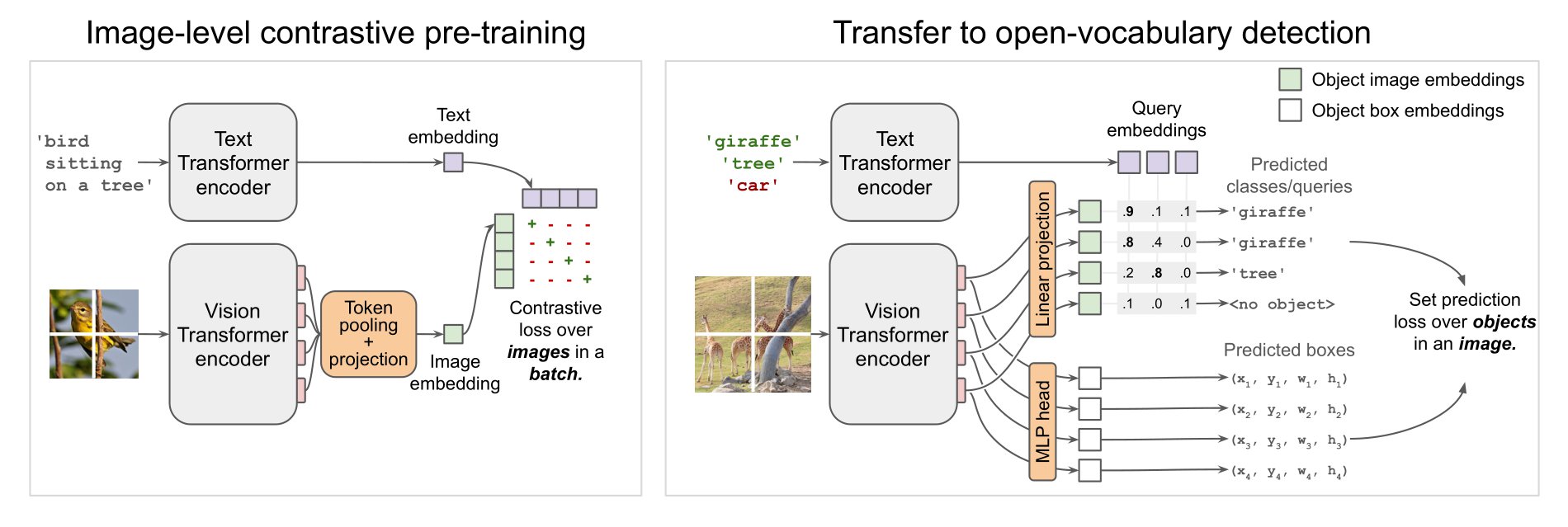 OWL-ViT architecture. Taken from the original paper.
OWL-ViT architecture. Taken from the original paper. 使用提示
OWL-ViT 是一个零样本文本条件目标检测模型。OWL-ViT 使用 CLIP 作为其多模态骨干网络,使用类似 ViT 的 Transformer 获取视觉特征,并使用因果语言模型获取文本特征。为了将 CLIP 用于检测,OWL-ViT 移除了视觉模型的最终令牌池化层,并在每个 Transformer 输出令牌上附加了一个轻量级的分类和边界框头。通过用从文本模型获得的类名嵌入替换固定的分类层权重,实现了开放词汇分类。作者首先从头训练 CLIP,并使用二分匹配损失在标准检测数据集上对分类和边界框头进行端到端微调。每张图像可以使用一个或多个文本查询来执行零样本文本条件目标检测。
OwlViTImageProcessor 可以用于调整(或重新缩放)和归一化模型的图像,而 CLIPTokenizer 用于编码文本。OwlViTProcessor 将 OwlViTImageProcessor 和 CLIPTokenizer 封装到一个实例中,以便同时编码文本和准备图像。以下示例展示了如何使用 OwlViTProcessor 和 OwlViTForObjectDetection 执行对象检测。
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import OwlViTProcessor, OwlViTForObjectDetection
>>> processor = OwlViTProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> model = OwlViTForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> texts = [["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]]
>>> inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # Target image sizes (height, width) to rescale box predictions [batch_size, 2]
>>> target_sizes = torch.Tensor([image.size[::-1]])
>>> # Convert outputs (bounding boxes and class logits) to Pascal VOC format (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
>>> results = processor.post_process_object_detection(outputs=outputs, target_sizes=target_sizes, threshold=0.1)
>>> i = 0 # Retrieve predictions for the first image for the corresponding text queries
>>> text = texts[i]
>>> boxes, scores, labels = results[i]["boxes"], results[i]["scores"], results[i]["labels"]
>>> for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels):
... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()]
... print(f"Detected {text[label]} with confidence {round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}")
Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.707 at location [324.97, 20.44, 640.58, 373.29]
Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.717 at location [1.46, 55.26, 315.55, 472.17]资源
一个关于使用OWL-ViT进行零样本和单样本(图像引导)目标检测的演示笔记本可以在这里找到。
OwlViTConfig
类 transformers.OwlViTConfig
< source >( text_config = None vision_config = None projection_dim = 512 logit_scale_init_value = 2.6592 return_dict = True **kwargs )
参数
- text_config (
dict, optional) — 用于初始化 OwlViTTextConfig 的配置选项字典。 - vision_config (
dict, optional) — 用于初始化 OwlViTVisionConfig 的配置选项字典。 - projection_dim (
int, optional, 默认为 512) — 文本和视觉投影层的维度。 - logit_scale_init_value (
float, optional, 默认为 2.6592) — logit_scale 参数的初始值。默认值按照原始 OWL-ViT 实现使用。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 模型是否应返回字典。如果False,则返回一个元组。 - kwargs (可选) — 关键字参数字典。
OwlViTConfig 是用于存储 OwlViTModel 配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化一个 OWL-ViT 模型,定义文本模型和视觉模型的配置。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与 OWL-ViT google/owlvit-base-patch32 架构相似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
from_text_vision_configs
< source >( text_config: typing.Dict vision_config: typing.Dict **kwargs ) → OwlViTConfig
从owlvit文本模型配置和owlvit视觉模型配置实例化一个OwlViTConfig(或派生类)。
OwlViTTextConfig
类 transformers.OwlViTTextConfig
< source >( vocab_size = 49408 hidden_size = 512 intermediate_size = 2048 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 8 max_position_embeddings = 16 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 pad_token_id = 0 bos_token_id = 49406 eos_token_id = 49407 **kwargs )
参数
- vocab_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 49408) — OWL-ViT 文本模型的词汇表大小。定义了调用 OwlViTTextModel 时传递的inputs_ids可以表示的不同标记的数量。 - hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 512) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 2048) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, 可选, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, 默认为 16) — 此模型可能使用的最大序列长度。通常将其设置为较大的值以防万一(例如,512 或 1024 或 2048)。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"quick_gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu","relu","selu"和"gelu_new""quick_gelu". - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - attention_dropout (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比例。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认值为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - initializer_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为 1.0) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的因子(应保持为1,内部用于初始化测试)。 - pad_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 0) — 输入序列中填充标记的id. - bos_token_id (
int, optional, 默认为 49406) — 输入序列中开始序列标记的id. - eos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 49407) — 输入序列中结束序列标记的id。
这是用于存储OwlViTTextModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化一个OwlViT文本编码器,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与OwlViT google/owlvit-base-patch32架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import OwlViTTextConfig, OwlViTTextModel
>>> # Initializing a OwlViTTextModel with google/owlvit-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> configuration = OwlViTTextConfig()
>>> # Initializing a OwlViTTextConfig from the google/owlvit-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> model = OwlViTTextModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configOwlViTVisionConfig
类 transformers.OwlViTVisionConfig
< source >( hidden_size = 768 intermediate_size = 3072 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 num_channels = 3 image_size = 768 patch_size = 32 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 **kwargs )
参数
- hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 3072) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — 输入图像中的通道数。 - image_size (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 每张图像的尺寸(分辨率)。 - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — 每个补丁的大小(分辨率)。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"quick_gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"selu"和"gelu_new""quick_gelu"。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比率。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认值为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - initializer_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为 1.0) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的因子(应保持为1,内部用于初始化测试)。
这是用于存储OwlViTVisionModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化一个OWL-ViT图像编码器,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与OWL-ViT google/owlvit-base-patch32架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import OwlViTVisionConfig, OwlViTVisionModel
>>> # Initializing a OwlViTVisionModel with google/owlvit-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> configuration = OwlViTVisionConfig()
>>> # Initializing a OwlViTVisionModel model from the google/owlvit-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> model = OwlViTVisionModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configOwlViTImageProcessor
类 transformers.OwlViTImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize = True size = None resample =
参数
- do_resize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否将输入的较短边调整为某个size. - size (
Dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为 {“height” — 768, “width”: 768}): 用于调整图像大小的尺寸。仅在do_resize设置为True时有效。如果size是一个像 (h, w) 这样的序列,输出大小将与此匹配。如果size是一个整数,则图像将被调整为 (size, size)。 - resample (
int, 可选, 默认为Resampling.BICUBIC) — 一个可选的重采样过滤器。这可以是PIL.Image.Resampling.NEAREST,PIL.Image.Resampling.BOX,PIL.Image.Resampling.BILINEAR,PIL.Image.Resampling.HAMMING,PIL.Image.Resampling.BICUBIC或PIL.Image.Resampling.LANCZOS。只有在do_resize设置为True时才会生效。 - do_center_crop (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 是否在中心裁剪输入。如果输入尺寸在任何一边小于crop_size,图像将用0填充,然后进行中心裁剪。 - crop_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 {“height” — 768, “width”: 768}): 用于中心裁剪图像的尺寸。仅在do_center_crop设置为True时有效。 - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — 是否通过某个因子重新缩放输入。 - rescale_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为1/255) — 用于重新缩放图像的因子。仅在do_rescale设置为True时有效。 - do_normalize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否使用image_mean和image_std对输入进行归一化。应用中心裁剪时所需的输出大小。仅在do_center_crop设置为True时有效。 - image_mean (
List[int], 可选, 默认为[0.48145466, 0.4578275, 0.40821073]) — 每个通道的均值序列,用于图像归一化时使用。 - image_std (
List[int], 可选, 默认为[0.26862954, 0.26130258, 0.27577711]) — 每个通道的标准差序列,用于在归一化图像时使用。
构建一个OWL-ViT图像处理器。
此图像处理器继承自ImageProcessingMixin,其中包含了大部分主要方法。用户应参考此超类以获取有关这些方法的更多信息。
预处理
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]] do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: typing.Optional[bool] = None crop_size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] =
参数
- 图片 (
ImageInput) — 要准备的图片或图片批次。期望输入单个或批次的图片,像素值范围为0到255。如果传入的图片像素值在0到1之间,请设置do_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — 是否调整输入的大小。如果为True,将调整输入到size指定的大小。 - size (
Dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为self.size) — 调整输入的大小。仅在do_resize设置为True时有效。 - resample (
PILImageResampling, 可选, 默认为self.resample) — 调整输入大小时使用的重采样过滤器。仅在do_resize设置为True时有效。 - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_center_crop) — 是否对输入进行中心裁剪。如果为True,将输入中心裁剪到crop_size指定的大小。 - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为self.crop_size) — 输入的中心裁剪大小。仅在do_center_crop设置为True时有效。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选, 默认为self.do_rescale) — 是否对输入进行重新缩放。如果为True,将通过将输入除以rescale_factor来重新缩放输入。 - rescale_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为self.rescale_factor) — 用于重新缩放输入的因子。仅在do_rescale设置为True时有效。 - do_normalize (
bool, 可选, 默认为self.do_normalize) — 是否对输入进行归一化。如果为True,将通过减去image_mean并除以image_std来归一化输入。 - image_mean (
Union[float, List[float]], 可选, 默认为self.image_mean) — 在归一化时从输入中减去的均值。仅在do_normalize设置为True时有效。 - image_std (
Union[float, List[float]], 可选, 默认为self.image_std) — 在归一化时用于除以输入的标准差。仅在do_normalize设置为True时有效。 - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选) — 返回的张量类型。可以是以下之一:- 未设置:返回一个
np.ndarray列表。 TensorType.TENSORFLOW或'tf':返回一个类型为tf.Tensor的批次。TensorType.PYTORCH或'pt':返回一个类型为torch.Tensor的批次。TensorType.NUMPY或'np':返回一个类型为np.ndarray的批次。TensorType.JAX或'jax':返回一个类型为jax.numpy.ndarray的批次。
- 未设置:返回一个
- data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选, 默认为ChannelDimension.FIRST) — 输出图像的通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。- 未设置:默认为输入图像的通道维度格式。
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:"channels_first"或ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。"channels_last"或ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。"none"或ChannelDimension.NONE: 图像格式为 (height, width)。
为模型准备一张或一批图像。
post_process_object_detection
< source >( outputs threshold: float = 0.1 target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = None ) → List[Dict]
将OwlViTForObjectDetection的原始输出转换为最终边界框,格式为(左上角x,左上角y,右下角x,右下角y)。
post_process_image_guided_detection
< source >( outputs threshold = 0.0 nms_threshold = 0.3 target_sizes = None ) → List[Dict]
参数
- 输出 (
OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput) — 模型的原始输出。 - threshold (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 用于过滤预测框的最小置信度阈值。 - nms_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.3) — 用于非最大抑制重叠框的IoU阈值。 - target_sizes (
torch.Tensor, 可选) — 形状为 (batch_size, 2) 的张量,其中每个条目是批次中相应图像的 (高度, 宽度)。如果设置,预测的归一化边界框将重新缩放到目标大小。如果留空为 None,预测将不会进行反归一化。
返回
List[Dict]
一个字典列表,每个字典包含模型预测的批次中图像的分数、标签和框。所有标签都设置为None,因为OwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection执行一次性目标检测。
将OwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection()的输出转换为COCO API所期望的格式。
OwlViTFeatureExtractor
预处理一张图像或一批图像。
后处理
< source >( outputs target_sizes ) → List[Dict]
将OwlViTForObjectDetection的原始输出转换为最终边界框,格式为(左上角x,左上角y,右下角x,右下角y)。
post_process_image_guided_detection
< source >( outputs threshold = 0.0 nms_threshold = 0.3 target_sizes = None ) → List[Dict]
参数
- 输出 (
OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput) — 模型的原始输出。 - threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 用于过滤预测框的最小置信度阈值。 - nms_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.3) — 用于非最大抑制重叠框的IoU阈值。 - target_sizes (
torch.Tensor, 可选) — 形状为 (batch_size, 2) 的张量,其中每个条目是批次中相应图像的 (高度, 宽度)。如果设置,预测的归一化边界框将重新缩放到目标大小。如果留空为 None,预测将不会进行反归一化。
返回
List[Dict]
一个字典列表,每个字典包含模型预测的批次中图像的分数、标签和框。所有标签都设置为None,因为OwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection执行一次性目标检测。
将OwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection()的输出转换为COCO API所期望的格式。
OwlViTProcessor
类 transformers.OwlViTProcessor
< source >( image_processor = 无 tokenizer = 无 **kwargs )
参数
- image_processor (OwlViTImageProcessor, optional) — 图像处理器是一个必需的输入。
- tokenizer ([
CLIPTokenizer,CLIPTokenizerFast], optional) — tokenizer 是一个必需的输入。
构建一个OWL-ViT处理器,它将OwlViTImageProcessor和CLIPTokenizer/CLIPTokenizerFast封装成一个单一的处理器,继承了图像处理器和分词器的功能。更多信息请参见__call__()和decode()。
此方法将其所有参数转发给CLIPTokenizerFast的batch_decode()。请参考该方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
此方法将其所有参数转发给CLIPTokenizerFast的decode()。请参考该方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
此方法将其所有参数转发给OwlViTImageProcessor.post_process()。请参阅该方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
此方法将其所有参数转发给OwlViTImageProcessor.post_process_one_shot_object_detection。
请参阅此方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
此方法将其所有参数转发给OwlViTImageProcessor.post_process_object_detection()。请参考该方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
OwlViTModel
类 transformers.OwlViTModel
< source >( 配置: OwlViTConfig )
参数
- config (OwlViTConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_loss: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_base_image_embeds: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — 词汇表中输入序列标记的索引。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见 PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() 和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。什么是输入ID? - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — 用于避免在填充标记索引上执行注意力的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示 未掩码 的标记,
- 0 表示 掩码 的标记。 什么是注意力掩码?
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值. - return_loss (
bool, optional) — 是否返回对比损失。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTOutput 或一个由 torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种元素,具体取决于配置(
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当return_loss为True时返回) — 图像-文本相似度的对比损失。 - logits_per_image (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(image_batch_size, text_batch_size)) —image_embeds和text_embeds之间的缩放点积分数。这表示图像-文本相似度分数。 - logits_per_text (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(text_batch_size, image_batch_size)) —text_embeds和image_embeds之间的缩放点积分数。这表示文本-图像相似度分数。 - text_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, output_dim) — 通过将投影层应用于 OwlViTTextModel 的池化输出获得的文本嵌入。 - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, output_dim) — 通过将投影层应用于 OwlViTVisionModel 的池化输出获得的图像嵌入。 - text_model_output (Tuple
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — OwlViTTextModel 的输出。 - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — OwlViTVisionModel 的输出。
OwlViTModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTModel
>>> model = OwlViTModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(text=[["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]], images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits_per_image = outputs.logits_per_image # this is the image-text similarity score
>>> probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1) # we can take the softmax to get the label probabilitiesget_text_features
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → 文本特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, sequence_length)) — 词汇表中输入序列标记的索引。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见 PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() 和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。什么是输入ID? - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — 用于避免在填充标记索引上执行注意力的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示 未掩码 的标记,
- 0 表示 掩码 的标记。 什么是注意力掩码?
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
文本特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
通过将投影层应用于OwlViTTextModel的池化输出获得的文本嵌入。
OwlViTModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTModel
>>> model = OwlViTModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = processor(
... text=[["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], ["photo of a astranaut"]], return_tensors="pt"
... )
>>> text_features = model.get_text_features(**inputs)get_image_features
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → 图像特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
图像特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
通过将投影层应用于OwlViTVisionModel的池化输出获得的图像嵌入。
OwlViTModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTModel
>>> model = OwlViTModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> image_features = model.get_image_features(**inputs)OwlViTTextModel
前进
< source >( input_ids: Tensor attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, sequence_length)) — 词汇表中输入序列标记的索引。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见 PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() 和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。什么是输入ID? - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — 用于避免在填充标记索引上执行注意力的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示 未掩码 的标记,
- 0 表示 掩码 的标记。 什么是注意力掩码?
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, hidden_size)) — 序列的第一个标记(分类标记)在经过用于辅助预训练任务的层进一步处理后的最后一层隐藏状态。例如,对于BERT系列模型,这返回经过线性层和tanh激活函数处理后的分类标记。线性层的权重是在预训练期间通过下一个句子预测(分类)目标训练的。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力softmax后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
OwlViTTextModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTTextModel
>>> model = OwlViTTextModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = processor(
... text=[["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], ["photo of a astranaut"]], return_tensors="pt"
... )
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled (EOS token) statesOwlViTVisionModel
前进
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, hidden_size)) — 序列的第一个标记(分类标记)在经过用于辅助预训练任务的层进一步处理后的最后一层隐藏状态。例如,对于BERT系列模型,这返回经过线性层和tanh激活函数处理后的分类标记。线性层的权重是在预训练期间通过下一个句子预测(分类)目标训练的。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力softmax后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
OwlViTVisionModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTVisionModel
>>> model = OwlViTVisionModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled CLS statesOwlViTForObjectDetection
前进
< source >( input_ids: Tensor pixel_values: FloatTensor attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值. - input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — 词汇表中输入序列标记的索引。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见 PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() 和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。 什么是输入ID?. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — 用于避免在填充标记索引上执行注意力的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示 未掩码 的标记,
- 0 表示 掩码 的标记。 什么是注意力掩码?
- output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回最后的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参阅返回的张量中的text_model_last_hidden_state和vision_model_last_hidden_state。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput 或一个由 torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种元素,具体取决于配置(
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 总损失,作为类别预测的负对数似然(交叉熵)和边界框损失的线性组合。后者定义为 L1 损失和广义尺度不变 IoU 损失的线性组合。 - loss_dict (
Dict,可选) — 包含各个损失的字典。用于记录日志。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, num_queries)) — 所有查询的分类 logits(包括无对象)。 - pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, 4)) — 所有查询的归一化框坐标,表示为 (center_x, center_y, width, height)。这些值在 [0, 1] 范围内归一化,相对于批次中每个单独图像的大小(忽略可能的填充)。您可以使用 post_process_object_detection() 来检索未归一化的边界框。 - text_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, output_dim) — 通过将投影层应用于 OwlViTTextModel 的池化输出获得的文本嵌入。 - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, patch_size, patch_size, output_dim) — OwlViTVisionModel 的池化输出。OWL-ViT 将图像表示为一组图像块,并计算每个块的图像嵌入。 - class_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, hidden_size)) — 所有图像块的类别嵌入。OWL-ViT 将图像表示为一组图像块,其中总块数为 (image_size / patch_size)**2。 - text_model_output (Tuple
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — OwlViTTextModel 的输出。 - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — OwlViTVisionModel 的输出。
OwlViTForObjectDetection 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTForObjectDetection
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> model = OwlViTForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> texts = [["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]]
>>> inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # Target image sizes (height, width) to rescale box predictions [batch_size, 2]
>>> target_sizes = torch.Tensor([image.size[::-1]])
>>> # Convert outputs (bounding boxes and class logits) to final bounding boxes and scores
>>> results = processor.post_process_object_detection(
... outputs=outputs, threshold=0.1, target_sizes=target_sizes
... )
>>> i = 0 # Retrieve predictions for the first image for the corresponding text queries
>>> text = texts[i]
>>> boxes, scores, labels = results[i]["boxes"], results[i]["scores"], results[i]["labels"]
>>> for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels):
... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()]
... print(f"Detected {text[label]} with confidence {round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}")
Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.707 at location [324.97, 20.44, 640.58, 373.29]
Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.717 at location [1.46, 55.26, 315.55, 472.17]image_guided_detection
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor query_pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值. - query_pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 要检测的查询图像的像素值。每个目标图像传入一个查询图像。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput 或一个由 torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含根据配置(
- logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, num_queries)) — 所有查询的分类 logits(包括无对象)。 - target_pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, 4)) — 所有查询的归一化框坐标,表示为 (center_x, center_y, width, height)。这些值在 [0, 1] 范围内归一化,相对于批次中每个目标图像的大小(忽略可能的填充)。您可以使用 post_process_object_detection() 来检索未归一化的边界框。 - query_pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, 4)) — 所有查询的归一化框坐标,表示为 (center_x, center_y, width, height)。这些值在 [0, 1] 范围内归一化,相对于批次中每个查询图像的大小(忽略可能的填充)。您可以使用 post_process_object_detection() 来检索未归一化的边界框。 - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, patch_size, patch_size, output_dim) — OwlViTVisionModel 的池化输出。OWL-ViT 将图像表示为一组图像块,并计算每个块的图像嵌入。 - query_image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, patch_size, patch_size, output_dim) — OwlViTVisionModel 的池化输出。OWL-ViT 将图像表示为一组图像块,并计算每个块的图像嵌入。 - class_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_patches, hidden_size)) — 所有图像块的类别嵌入。OWL-ViT 将图像表示为一组图像块,其中总块数为 (image_size / patch_size)**2。 - text_model_output (Tuple
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — OwlViTTextModel 的输出。 - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — OwlViTVisionModel 的输出。
OwlViTForObjectDetection 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTForObjectDetection
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch16")
>>> model = OwlViTForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch16")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> query_url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000001675.jpg"
>>> query_image = Image.open(requests.get(query_url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, query_images=query_image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model.image_guided_detection(**inputs)
>>> # Target image sizes (height, width) to rescale box predictions [batch_size, 2]
>>> target_sizes = torch.Tensor([image.size[::-1]])
>>> # Convert outputs (bounding boxes and class logits) to Pascal VOC format (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
>>> results = processor.post_process_image_guided_detection(
... outputs=outputs, threshold=0.6, nms_threshold=0.3, target_sizes=target_sizes
... )
>>> i = 0 # Retrieve predictions for the first image
>>> boxes, scores = results[i]["boxes"], results[i]["scores"]
>>> for box, score in zip(boxes, scores):
... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()]
... print(f"Detected similar object with confidence {round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}")
Detected similar object with confidence 0.856 at location [10.94, 50.4, 315.8, 471.39]
Detected similar object with confidence 1.0 at location [334.84, 25.33, 636.16, 374.71]