感知器
概述
Perceiver IO模型由Andrew Jaegle、Sebastian Borgeaud、Jean-Baptiste Alayrac、Carl Doersch、Catalin Ionescu、David Ding、Skanda Koppula、Daniel Zoran、Andrew Brock、Evan Shelhamer、Olivier Hénaff、Matthew M. Botvinick、Andrew Zisserman、Oriol Vinyals和João Carreira在Perceiver IO: A General Architecture for Structured Inputs & Outputs中提出。
Perceiver IO 是 Perceiver 的泛化版本,除了处理任意输入外,还能处理任意输出。原始的 Perceiver 只能生成单一的分类标签。除了分类标签外,Perceiver IO 还可以生成(例如)语言、光流和带有音频的多模态视频。这是通过使用与原始 Perceiver 相同的构建块来实现的。Perceiver IO 的计算复杂度在输入和输出大小上是线性的,并且大部分处理发生在潜在空间中,这使得我们能够处理比标准 Transformer 所能处理的更大规模的输入和输出。这意味着,例如,Perceiver IO 可以直接使用字节而不是分词输入来进行 BERT 风格的掩码语言建模。
论文的摘要如下:
最近提出的Perceiver模型在多个领域(图像、音频、多模态、点云)上取得了良好的结果,同时在计算和内存方面与输入大小呈线性扩展。虽然Perceiver支持多种输入,但它只能产生非常简单的输出,例如类别分数。Perceiver IO通过学习灵活查询模型的潜在空间以产生任意大小和语义的输出,克服了这一限制,同时不牺牲原始模型的吸引力特性。Perceiver IO仍然将模型深度与数据大小解耦,并且仍然与数据大小呈线性扩展,但现在同时考虑了输入和输出大小。完整的Perceiver IO模型在具有高度结构化输出空间的任务上取得了强劲的结果,例如自然语言和视觉理解、星际争霸II以及多任务和多模态领域。作为亮点,Perceiver IO在GLUE语言基准测试中与基于Transformer的BERT基线相匹配,而无需输入标记化,并在Sintel光流估计上实现了最先进的性能。
以下是Perceiver工作原理的简要说明:
Transformer的自注意力机制的主要问题是时间和内存需求随着序列长度的增加呈二次方增长。因此,像BERT和RoBERTa这样的模型被限制在最大512个标记的序列长度。Perceiver旨在通过不在输入上执行自注意力,而是在一组潜在变量上执行自注意力,并仅使用输入进行交叉注意力来解决这个问题。通过这种方式,时间和内存需求不再依赖于输入的长度,因为使用的是固定数量的潜在变量,如256或512。这些变量是随机初始化的,然后通过反向传播进行端到端的训练。
在内部,PerceiverModel 会创建潜在变量,这是一个形状为 (batch_size, num_latents, d_latents) 的张量。必须向模型提供 inputs(可以是文本、图像、音频等),模型将使用这些输入与潜在变量进行交叉注意力操作。Perceiver 编码器的输出是一个相同形状的张量。然后,可以像 BERT 一样,通过对序列维度进行平均,将潜在变量的最后隐藏状态转换为分类 logits,并在其上放置一个线性层,将 d_latents 投影到 num_labels。
这是原始Perceiver论文的想法。然而,它只能输出分类的logits。在后续的工作PerceiverIO中,他们将其推广,使模型也能产生任意大小的输出。你可能会问,这是如何实现的?这个想法实际上相对简单:定义任意大小的输出,然后使用输出作为查询,潜在变量的最后隐藏状态作为键和值,应用交叉注意力。
假设有人想要使用Perceiver进行掩码语言建模(BERT风格)。由于Perceiver的输入长度不会影响自注意力层的计算时间,因此可以提供原始字节,向模型提供长度为2048的inputs。如果现在掩码掉这2048个标记中的某些部分,可以将outputs定义为形状为(batch_size, 2048, 768)的张量。接下来,使用潜在变量的最终隐藏状态进行交叉注意力,以更新outputs张量。在交叉注意力之后,仍然会得到一个形状为(batch_size, 2048, 768)的张量。然后可以在顶部放置一个常规的语言建模头,将最后一个维度投影到模型的词汇表大小,即创建形状为(batch_size, 2048, 262)的logits(因为Perceiver使用262个字节ID的词汇表大小)。
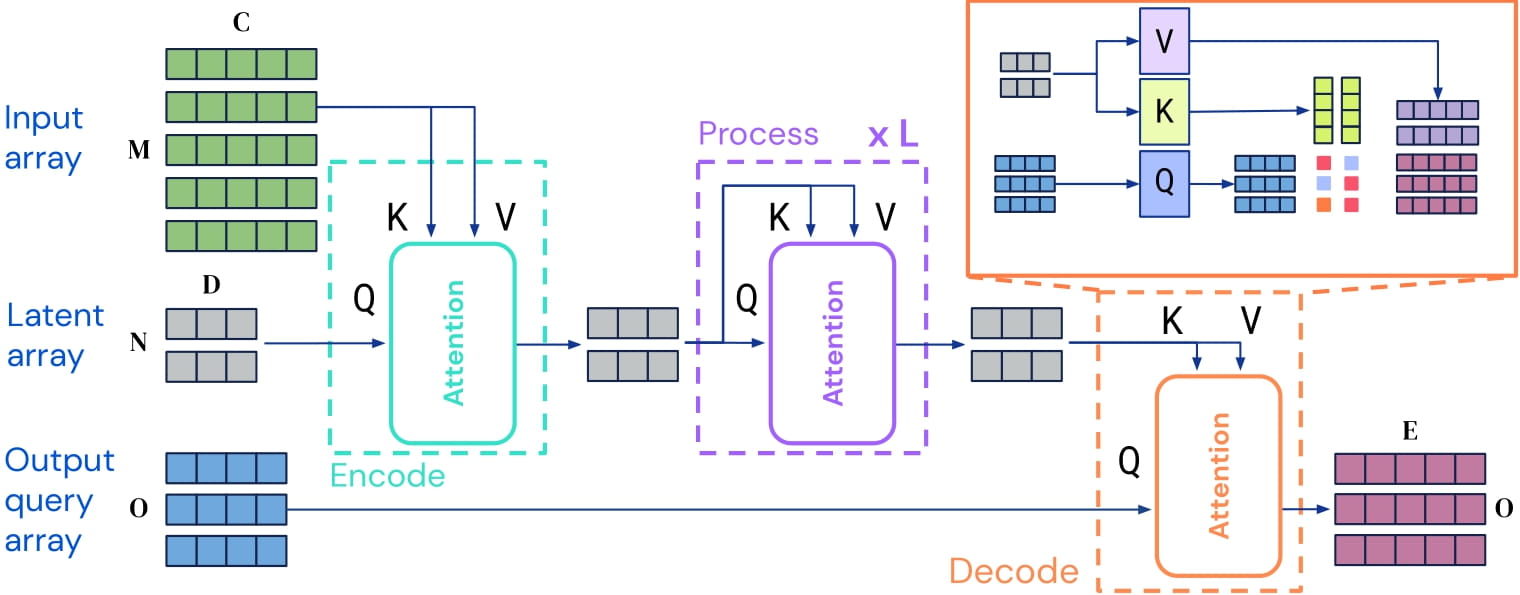 Perceiver IO architecture. Taken from the original paper
Perceiver IO architecture. Taken from the original paper Perceiver 不 与 torch.nn.DataParallel 一起工作,因为 PyTorch 中存在一个错误,请参阅 issue #36035
资源
- 开始使用Perceiver的最快方法是查看教程笔记本。
- 如果您想完全理解模型的工作原理及其在库中的实现,请参考博客文章。请注意,库中提供的模型仅展示了您可以使用Perceiver完成的一些示例。还有许多其他用例,包括问答、命名实体识别、对象检测、音频分类、视频分类等。
- 文本分类任务指南
- Masked language modeling task guide
- 图像分类任务指南
Perceiver 特定输出
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverModelOutput
< source >( logits: FloatTensor = None last_hidden_state: FloatTensor = None hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None cross_attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
参数
- logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每一层的输出)的形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。 - 注意力 (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
Perceiver基础模型输出的基类,可能包含隐藏状态、注意力和交叉注意力。
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverDecoderOutput
< source >( logits: FloatTensor = None cross_attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
参数
- logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_labels)) — 基础解码器的输出。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
Perceiver解码器输出的基类,可能包含交叉注意力。
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMaskedLMOutput
< source >( loss: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None logits: FloatTensor = None hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None cross_attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
参数
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,), 可选, 当提供labels时返回) — 掩码语言建模(MLM)损失. - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax之前每个词汇标记的分数)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每一层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。 - 注意力 (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, num_latents, num_latents)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当output_attentions=True传递或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
Perceiver 的掩码语言模型输出的基类。
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput
< source >( loss: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None logits: FloatTensor = None hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None cross_attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
参数
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, 当提供labels时返回) — 分类(如果 config.num_labels==1 则为回归)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(如果 config.num_labels==1 则为回归)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每一层的输出)的形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。 - 注意力 (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)的torch.FloatTensor元组(每层一个)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
Perceiver 的序列/图像分类模型、光流和多模态自动编码输出的基类。
PerceiverConfig
类 transformers.PerceiverConfig
< source >( num_latents = 256 d_latents = 1280 d_model = 768 num_blocks = 1 num_self_attends_per_block = 26 num_self_attention_heads = 8 num_cross_attention_heads = 8 qk_channels = None v_channels = None cross_attention_shape_for_attention = 'kv' self_attention_widening_factor = 1 cross_attention_widening_factor = 1 hidden_act = 'gelu' attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.1 initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 use_query_residual = True vocab_size = 262 max_position_embeddings = 2048 image_size = 56 train_size = [368, 496] num_frames = 16 audio_samples_per_frame = 1920 samples_per_patch = 16 output_shape = [1, 16, 224, 224] output_num_channels = 512 _label_trainable_num_channels = 1024 **kwargs )
参数
- num_latents (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — 潜在变量的数量。 - d_latents (
int, optional, 默认为 1280) — 潜在嵌入的维度。 - d_model (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 输入的维度。仅在使用了 [PerceiverTextPreprocessor] 或未提供预处理器的情况下提供。 - num_blocks (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — Transformer编码器中的块数。 - num_self_attends_per_block (
int, optional, 默认为 26) — 每个块中的自注意力层数。 - num_self_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Transformer编码器中每个自注意力层的注意力头数。 - num_cross_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Transformer编码器中每个交叉注意力层的注意力头数。 - qk_channels (
int, optional) — 在编码器的交叉注意力和自注意力层中应用注意力之前,将查询和键投影到的维度。如果未指定,将默认保留查询的维度。 - v_channels (
int, optional) — 在编码器的交叉注意力和自注意力层中应用注意力之前,将值投影到的维度。如果未指定,将默认保留查询的维度。 - cross_attention_shape_for_attention (
str, optional, defaults to"kv") — 在编码器的交叉注意力层中下采样查询和键时使用的维度。 - self_attention_widening_factor (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — Transformer编码器的交叉注意力层中前馈层的维度。 - cross_attention_widening_factor (
int, 可选, 默认为 1) — Transformer编码器的自注意力层中前馈层的维度。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"selu"和"gelu_new"。 - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, 默认为 0.1) — 注意力概率的丢弃比例。 - initializer_range (
float, optional, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - use_query_residual (
float, optional, defaults toTrue) — 是否在编码器的交叉注意力层中添加查询残差。 - vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 262) — 用于掩码语言建模模型的词汇表大小。 - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, 默认为 2048) — 掩码语言模型可能使用的最大序列长度。通常将其设置为较大的值以防万一(例如,512、1024 或 2048)。 - image_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 56) — 预处理后图像的大小,用于 PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned. - train_size (
List[int], optional, defaults to[368, 496]) — 光流模型图像的训练大小。 - num_frames (
int, optional, 默认为 16) — 用于多模态自动编码模型的视频帧数。 - audio_samples_per_frame (
int, optional, 默认为 1920) — 多模态自编码模型中每帧的音频样本数。 - samples_per_patch (
int, optional, 默认为 16) — 在为多模态自动编码模型预处理音频时,每个补丁的音频样本数。 - output_shape (
List[int], 可选, 默认为[1, 16, 224, 224]) — 输出的形状(batch_size, num_frames, height, width)用于多模态自动编码模型的视频解码器查询。这不包括通道维度。 - output_num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — 每个模态解码器的输出通道数。
这是用于存储PerceiverModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化Perceiver模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生类似于Perceiver deepmind/language-perceiver架构的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import PerceiverModel, PerceiverConfig
>>> # Initializing a Perceiver deepmind/language-perceiver style configuration
>>> configuration = PerceiverConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model from the deepmind/language-perceiver style configuration
>>> model = PerceiverModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configPerceiverTokenizer
类 transformers.PerceiverTokenizer
< source >( pad_token = '[PAD]' bos_token = '[BOS]' eos_token = '[EOS]' mask_token = '[MASK]' cls_token = '[CLS]' sep_token = '[SEP]' model_max_length = 2048 **kwargs )
参数
- pad_token (
str, optional, defaults to"[PAD]") — 用于填充的标记,例如在批处理不同长度的序列时使用。 - bos_token (
str, optional, defaults to"[BOS]") — BOS 令牌(在词汇表中保留,但实际上未使用)。 - eos_token (
str, optional, defaults to"[EOS]") — The end of sequence token (reserved in the vocab, but not actually used).在使用特殊标记构建序列时,这不是用于序列结束的标记。 使用的标记是
sep_token。 - mask_token (
str, optional, defaults to"[MASK]") — MASK 令牌,用于掩码语言建模。 - cls_token (
str, optional, defaults to"[CLS]") — CLS 令牌(在词汇表中保留,但实际上未使用)。 - sep_token (
str, optional, defaults to"[SEP]") — 分隔符标记,用于从两个序列构建一个序列时使用。
构建一个Perceiver分词器。Perceiver简单地使用原始字节的utf-8编码。
此分词器继承自PreTrainedTokenizer,其中包含了大部分主要方法。用户应参考此超类以获取有关这些方法的更多信息。
__call__
< source >( text: typing.Union[str, typing.List[str], typing.List[typing.List[str]]] = None text_pair: typing.Union[str, typing.List[str], typing.List[typing.List[str]], NoneType] = None text_target: typing.Union[str, typing.List[str], typing.List[typing.List[str]]] = None text_pair_target: typing.Union[str, typing.List[str], typing.List[typing.List[str]], NoneType] = None add_special_tokens: bool = True padding: typing.Union[bool, str, transformers.utils.generic.PaddingStrategy] = False truncation: typing.Union[bool, str, transformers.tokenization_utils_base.TruncationStrategy] = None max_length: typing.Optional[int] = None stride: int = 0 is_split_into_words: bool = False pad_to_multiple_of: typing.Optional[int] = None padding_side: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None return_token_type_ids: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_attention_mask: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_overflowing_tokens: bool = False return_special_tokens_mask: bool = False return_offsets_mapping: bool = False return_length: bool = False verbose: bool = True **kwargs ) → BatchEncoding
参数
- text (
str,List[str],List[List[str]], optional) — 要编码的序列或序列批次。每个序列可以是一个字符串或一个字符串列表(预分词的字符串)。如果序列以字符串列表(预分词)的形式提供,你必须设置is_split_into_words=True(以消除与序列批次的歧义)。 - text_pair (
str,List[str],List[List[str]], optional) — 要编码的序列或序列批次。每个序列可以是一个字符串或一个字符串列表(预分词的字符串)。如果序列以字符串列表(预分词)的形式提供,你必须设置is_split_into_words=True(以消除与序列批次的歧义)。 - text_target (
str,List[str],List[List[str]], optional) — 要编码为目标文本的序列或序列批次。每个序列可以是一个字符串或一个字符串列表(预分词的字符串)。如果序列以字符串列表(预分词)的形式提供,你必须设置is_split_into_words=True(以消除与序列批次的歧义)。 - text_pair_target (
str,List[str],List[List[str]], optional) — 要编码为目标文本的序列或序列批次。每个序列可以是一个字符串或一个字符串列表(预分词的字符串)。如果序列以字符串列表(预分词)的形式提供,你必须设置is_split_into_words=True(以消除与序列批次的歧义)。 - add_special_tokens (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否在编码序列时添加特殊标记。这将使用底层的PretrainedTokenizerBase.build_inputs_with_special_tokens函数,该函数定义了哪些标记会自动添加到输入ID中。如果您想自动添加bos或eos标记,这将非常有用。 - padding (
bool,stror PaddingStrategy, optional, defaults toFalse) — Activates and controls padding. Accepts the following values:Trueor'longest': Pad to the longest sequence in the batch (or no padding if only a single sequence if provided).'max_length': Pad to a maximum length specified with the argumentmax_lengthor to the maximum acceptable input length for the model if that argument is not provided.Falseor'do_not_pad'(default): No padding (i.e., can output a batch with sequences of different lengths).
- truncation (
bool,stror TruncationStrategy, optional, defaults toFalse) — Activates and controls truncation. Accepts the following values:Trueor'longest_first': Truncate to a maximum length specified with the argumentmax_lengthor to the maximum acceptable input length for the model if that argument is not provided. This will truncate token by token, removing a token from the longest sequence in the pair if a pair of sequences (or a batch of pairs) is provided.'only_first': Truncate to a maximum length specified with the argumentmax_lengthor to the maximum acceptable input length for the model if that argument is not provided. This will only truncate the first sequence of a pair if a pair of sequences (or a batch of pairs) is provided.'only_second': Truncate to a maximum length specified with the argumentmax_lengthor to the maximum acceptable input length for the model if that argument is not provided. This will only truncate the second sequence of a pair if a pair of sequences (or a batch of pairs) is provided.Falseor'do_not_truncate'(default): No truncation (i.e., can output batch with sequence lengths greater than the model maximum admissible input size).
- max_length (
int, optional) — Controls the maximum length to use by one of the truncation/padding parameters.如果未设置或设置为
None,则在需要截断/填充参数时,将使用预定义的模型最大长度。如果模型没有特定的最大输入长度(如XLNet),则截断/填充到最大长度的功能将被停用。 - stride (
int, 可选, 默认为 0) — 如果设置为一个数字并与max_length一起使用,当return_overflowing_tokens=True时返回的溢出标记将包含来自截断序列末尾的一些标记, 以提供截断序列和溢出序列之间的一些重叠。此参数的值定义了重叠标记的数量。 - is_split_into_words (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 输入是否已经预分词(例如,分割成单词)。如果设置为True,分词器会假设输入已经分割成单词(例如,通过空格分割),然后进行分词。这对于NER或分词分类非常有用。 - pad_to_multiple_of (
int, 可选) — 如果设置,将序列填充到提供的值的倍数。需要激活padding。 这对于在计算能力>= 7.5(Volta)的NVIDIA硬件上启用Tensor Cores特别有用。 - padding_side (
str, optional) — 模型应应用填充的一侧。应在['right', 'left']之间选择。 默认值从同名的类属性中选取。 - return_tensors (
str或 TensorType, 可选) — 如果设置,将返回张量而不是Python整数列表。可接受的值有:'tf': 返回 TensorFlowtf.constant对象。'pt': 返回 PyTorchtorch.Tensor对象。'np': 返回 Numpynp.ndarray对象。
- return_token_type_ids (
bool, optional) — Whether to return token type IDs. If left to the default, will return the token type IDs according to the specific tokenizer’s default, defined by thereturn_outputsattribute. - return_attention_mask (
bool, optional) — Whether to return the attention mask. If left to the default, will return the attention mask according to the specific tokenizer’s default, defined by thereturn_outputsattribute. - return_overflowing_tokens (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否返回溢出的令牌序列。如果提供了一对输入ID序列(或一批对),并且使用了truncation_strategy = longest_first或True,则会引发错误,而不是返回溢出的令牌。 - return_special_tokens_mask (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 是否返回特殊令牌掩码信息。 - return_offsets_mapping (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to return(char_start, char_end)for each token.这仅在继承自PreTrainedTokenizerFast的快速分词器上可用,如果使用Python的分词器,此方法将引发
NotImplementedError。 - return_length (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否返回编码输入的长度。 - verbose (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否打印更多信息和警告。 - **kwargs — 传递给
self.tokenize()方法
一个BatchEncoding包含以下字段:
-
input_ids — 要输入模型的令牌ID列表。
-
token_type_ids — 要输入模型的令牌类型ID列表(当
return_token_type_ids=True或 如果“token_type_ids”在self.model_input_names中)。 -
attention_mask — 指定模型应关注哪些令牌的索引列表(当
return_attention_mask=True或如果“attention_mask”在self.model_input_names中)。 -
overflowing_tokens — 溢出令牌序列列表(当指定了
max_length并且return_overflowing_tokens=True)。 -
num_truncated_tokens — 截断的令牌数量(当指定了
max_length并且return_overflowing_tokens=True)。 -
special_tokens_mask — 0和1的列表,1表示添加的特殊令牌,0表示 常规序列令牌(当
add_special_tokens=True和return_special_tokens_mask=True)。 -
length — 输入的长度(当
return_length=True)
主要方法,用于将一个或多个序列或一个或多个序列对进行标记化并准备供模型使用。
PerceiverFeatureExtractor
预处理一张图像或一批图像。
PerceiverImageProcessor
class transformers.PerceiverImageProcessor
< source >( do_center_crop: bool = True crop_size: typing.Dict[str, int] = None do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Dict[str, int] = None resample: Resampling =
参数
- do_center_crop (
bool,optional, 默认为True) — 是否对图像进行中心裁剪。如果输入尺寸在任何一边小于crop_size,图像将用零填充,然后进行中心裁剪。可以通过preprocess方法中的do_center_crop参数进行覆盖。 - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], 可选, 默认为{"height" -- 256, "width": 256}): 应用中心裁剪时的期望输出大小。可以在preprocess方法中通过crop_size参数进行覆盖。 - do_resize (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否将图像调整为(size["height"], size["width"])。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_resize参数覆盖此设置。 - size (
Dict[str, int]optional, 默认为{"height" -- 224, "width": 224}): 调整大小后图像的尺寸。可以通过preprocess方法中的size参数进行覆盖。 - resample (
PILImageResampling, 可选, 默认为PILImageResampling.BICUBIC) — 定义在调整图像大小时使用的重采样过滤器。可以在preprocess方法中通过resample参数覆盖此设置。 - do_rescale (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否通过指定的比例rescale_factor重新缩放图像。可以在preprocess方法中通过do_rescale参数覆盖此设置。 - rescale_factor (
int或float, 可选, 默认为1/255) — 定义在重新缩放图像时使用的比例因子。可以在preprocess方法中通过rescale_factor参数覆盖此值。 - do_normalize —
是否对图像进行归一化。可以在
preprocess方法中通过do_normalize参数进行覆盖。 - image_mean (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — 如果对图像进行归一化,则使用的均值。这是一个浮点数或与图像通道数长度相同的浮点数列表。可以通过preprocess方法中的image_mean参数进行覆盖。 - image_std (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为IMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — 如果对图像进行归一化,则使用的标准差。这是一个浮点数或与图像通道数长度相同的浮点数列表。可以在preprocess方法中通过image_std参数进行覆盖。
构建一个Perceiver图像处理器。
预处理
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]] do_center_crop: typing.Optional[bool] = None crop_size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None resample: Resampling = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: ChannelDimension =
参数
- 图像 (
ImageInput) — 要预处理的图像。期望输入单个或批量的图像,像素值范围在0到255之间。如果传入的图像像素值在0到1之间,请设置do_rescale=False. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_center_crop) — 是否将图像中心裁剪到crop_size. - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — 应用中心裁剪后所需的输出大小。 - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — 是否调整图像大小. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — 调整大小后的图像尺寸。 - resample (
int, 可选, 默认为self.resample) — 如果调整图像大小,则使用的重采样过滤器。这可以是枚举PILImageResampling中的一个,只有在do_resize设置为True时才会生效。 - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — 是否对图像进行重新缩放. - rescale_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为self.rescale_factor) — 如果do_rescale设置为True,则用于重新缩放图像的重新缩放因子。 - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — 是否对图像进行归一化处理。 - image_mean (
float或List[float], 可选, 默认为self.image_mean) — 图像均值. - image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — 图像标准差. - return_tensors (
str或TensorType, 可选) — 返回的张量类型。可以是以下之一:- 未设置:返回一个
np.ndarray列表。 TensorType.TENSORFLOW或'tf':返回一个类型为tf.Tensor的批次。TensorType.PYTORCH或'pt':返回一个类型为torch.Tensor的批次。TensorType.NUMPY或'np':返回一个类型为np.ndarray的批次。TensorType.JAX或'jax':返回一个类型为jax.numpy.ndarray的批次。
- 未设置:返回一个
- data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选, 默认为ChannelDimension.FIRST) — 输出图像的通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimension或str, 可选) — 输入图像的通道维度格式。如果未设置,则从输入图像推断通道维度格式。可以是以下之一:"channels_first"或ChannelDimension.FIRST: 图像格式为 (num_channels, height, width)。"channels_last"或ChannelDimension.LAST: 图像格式为 (height, width, num_channels)。"none"或ChannelDimension.NONE: 图像格式为 (height, width)。
预处理一张图像或一批图像。
PerceiverTextPreprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverTextPreprocessor
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 模型配置.
用于Perceiver编码器的文本预处理。可用于嵌入inputs并添加位置编码。
嵌入的维度由配置的d_model属性决定。
PerceiverImagePreprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverImagePreprocessor
< source >( config prep_type = 'conv' spatial_downsample: int = 4 temporal_downsample: int = 1 position_encoding_type: str = 'fourier' in_channels: int = 3 out_channels: int = 64 conv_after_patching: bool = False conv_after_patching_in_channels: int = 54 conv2d_use_batchnorm: bool = True concat_or_add_pos: str = 'concat' project_pos_dim: int = -1 **position_encoding_kwargs )
参数
- config ([PerceiverConfig]) — 模型配置.
- prep_type (
str, optional, defaults to"conv") — 预处理类型。可以是“conv1x1”、“conv”、“patches”、“pixels”。 - spatial_downsample (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — 空间下采样因子. - temporal_downsample (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — 时间下采样因子(仅在存在时间维度时相关)。 - position_encoding_type (
str, optional, defaults to"fourier") — 位置编码类型。可以是“fourier”或“trainable”。 - in_channels (
int, optional, 默认为 3) — 输入中的通道数。 - out_channels (
int, optional, 默认为 64) — 输出中的通道数。 - conv_after_patching (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 是否在打补丁后应用卷积层。 - conv_after_patching_in_channels (
int, 可选, 默认为 54) — 卷积层在修补后的输入通道数。 - conv2d_use_batchnorm (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否在卷积层中使用批量归一化。 - concat_or_add_pos (
str, optional, defaults to"concat") — 如何将位置编码连接到输入。可以是“concat”或“add”。 - project_pos_dim (
int, optional, 默认为 -1) — 位置编码的投影维度。如果为 -1,则不应用投影。 - **position_encoding_kwargs (
Dict, optional) — 位置编码的关键字参数。
Perceiver Encoder 的图像预处理。
注意:out_channels参数指的是卷积层的输出通道,如果prep_type设置为“conv1x1”或“conv”。如果添加绝对位置嵌入,必须确保位置编码kwargs的num_channels设置为与out_channels相等。
PerceiverOneHotPreprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverOneHotPreprocessor
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 模型配置.
用于Perceiver编码器的One-hot预处理器。可用于向输入添加一个虚拟索引维度。
PerceiverAudioPreprocessor
class transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverAudioPreprocessor
< source >( config prep_type: str = 'patches' samples_per_patch: int = 96 position_encoding_type: str = 'fourier' concat_or_add_pos: str = 'concat' out_channels = 64 project_pos_dim = -1 **position_encoding_kwargs )
参数
- config ([PerceiverConfig]) — 模型配置.
- prep_type (
str, optional, defaults to"patches") — 使用的预处理器类型。仅支持“patches”。 - samples_per_patch (
int, optional, defaults to 96) — 每个补丁的样本数量. - position_encoding_type (
str, optional, defaults to"fourier") — 要使用的位置编码类型。可以是“trainable”或“fourier”。 - concat_or_add_pos (
str, 可选, 默认为"concat") — 如何将位置编码连接到输入。可以是“concat”或“add”。 - out_channels (
int, optional, 默认为 64) — 输出中的通道数。 - project_pos_dim (
int, optional, 默认为 -1) — 位置编码的投影维度。如果为 -1,则不应用投影。 - **position_encoding_kwargs (
Dict, optional) — 用于位置编码的关键字参数。
用于Perceiver编码器的音频预处理。
PerceiverMultimodalPreprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultimodalPreprocessor
< source >( modalities: typing.Mapping[str, typing.Callable[..., typing.Tuple[torch.Tensor, typing.Optional[torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor]]] mask_probs: typing.Optional[typing.Mapping[str, float]] = None min_padding_size: int = 2 )
Perceiver 编码器的多模态预处理。
每种模态的输入都经过预处理,然后用可训练的位置嵌入进行填充,以具有相同数量的通道。
PerceiverProjectionDecoder
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverProjectionDecoder
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 模型配置.
基线投影解码器(无交叉注意力)。
PerceiverBasicDecoder
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverBasicDecoder
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig output_num_channels: int position_encoding_type: typing.Optional[str] = 'trainable' output_index_dims: typing.Optional[int] = None num_channels: typing.Optional[int] = 128 subsampled_index_dims: typing.Optional[int] = None qk_channels: typing.Optional[int] = None v_channels: typing.Optional[int] = None num_heads: typing.Optional[int] = 1 widening_factor: typing.Optional[int] = 1 use_query_residual: typing.Optional[bool] = False concat_preprocessed_input: typing.Optional[bool] = False final_project: typing.Optional[bool] = True position_encoding_only: typing.Optional[bool] = False **position_encoding_kwargs )
参数
- config ([PerceiverConfig]) — 模型配置.
- output_num_channels (
int, optional) — 输出中的通道数。仅在 final_project 设置为True时使用。 - position_encoding_type (
str, optional, defaults to “trainable”) — 使用的位置编码类型。可以是“trainable”、“fourier”或“none”。 - output_index_dims (
int, optional) — 输出查询的维度数。如果‘position_encoding_type’ == ‘none’,则忽略此参数。 - num_channels (
int, 可选, 默认为 128) — 解码器查询的通道数。如果‘position_encoding_type’ == ‘none’,则忽略此参数。 - qk_channels (
int, optional) — 交叉注意力层中查询和键的通道数。 - v_channels (
int, optional) — 交叉注意力层中值的通道数。 - num_heads (
int, 可选, 默认为 1) — 交叉注意力层中的注意力头数。 - widening_factor (
int, optional, 默认为 1) — 交叉注意力层的扩展因子。 - use_query_residual (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 是否在查询和交叉注意力层的输出之间使用残差连接。 - concat_preprocessed_input (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否将预处理后的输入与查询连接起来。 - final_project (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 是否将交叉注意力层的输出投影到目标维度。 - position_encoding_only (
bool, 可选, 默认为False) — 是否仅使用此类来定义输出查询。
基于交叉注意力的解码器。该类可用于使用交叉注意力操作解码潜在变量的最终隐藏状态,其中潜在变量生成键和值。
此类的输出形状取决于如何定义输出查询(也称为解码器查询)。
PerceiverClassificationDecoder
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassificationDecoder
< source >( config **decoder_kwargs )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 模型配置.
基于交叉注意力的分类解码器。用于logit输出的PerceiverBasicDecoder的轻量级封装。
将Perceiver编码器的输出形状从(batch_size, num_latents, d_latents)转换为形状为(batch_size, num_labels)的张量。
查询的形状为(batch_size, 1, num_labels)。
PerceiverOpticalFlowDecoder
class transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverOpticalFlowDecoder
< source >( config output_image_shape output_num_channels = 2 rescale_factor = 100.0 **decoder_kwargs )
基于交叉注意力的光流解码器。
PerceiverBasicVideoAutoencodingDecoder
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverBasicVideoAutoencodingDecoder
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig output_shape: typing.List[int] position_encoding_type: str **decoder_kwargs )
基于交叉注意力的视频自动编码解码器。轻量级封装了[PerceiverBasicDecoder],并包含视频重塑逻辑。
PerceiverMultimodalDecoder
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultimodalDecoder
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig modalities: typing.Dict[str, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverAbstractDecoder] num_outputs: int output_num_channels: int min_padding_size: typing.Optional[int] = 2 subsampled_index_dims: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverAbstractDecoder]] = None **decoder_kwargs )
参数
- config ([PerceiverConfig]) — 模型配置.
- modalities (
Dict[str, PerceiverAbstractDecoder]) — 字典映射模态名称到该模态的解码器。 - num_outputs (
int) — 解码器的输出数量。 - output_num_channels (
int) — 输出中的通道数。 - min_padding_size (
int, optional, 默认为 2) — 所有模态的最小填充大小。最终输出将具有等于所有模态中最大通道数加上 min_padding_size 的 num_channels。 - subsampled_index_dims (
Dict[str, PerceiverAbstractDecoder], 可选) — 字典映射模态名称到用于该模态解码器查询的子采样索引维度。
通过组合单模态解码器进行多模态解码。构造函数的modalities参数是一个字典,将模态名称映射到该模态的解码器。该解码器将用于构建该模态的查询。特定模态的查询会填充可训练的特定模态参数,之后它们会沿时间维度连接起来。
接下来,有一个跨所有模态的共享交叉注意力操作。
PerceiverProjectionPostprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverProjectionPostprocessor
< source >( in_channels: int out_channels: int )
Perceiver的投影后处理。可用于将解码器输出的通道投影到较低的维度。
PerceiverAudioPostprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverAudioPostprocessor
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig in_channels: int postproc_type: str = 'patches' )
用于Perceiver的音频后处理。可用于将解码器输出转换为音频特征。
PerceiverClassificationPostprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassificationPostprocessor
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig in_channels: int )
用于Perceiver的分类后处理。可用于将解码器输出转换为分类logits。
PerceiverMultimodalPostprocessor
类 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultimodalPostprocessor
< source >( 模态: typing.Mapping[str, typing.Callable[..., typing.Any]] 输入是否为字典: bool = False )
用于Perceiver的多模态后处理。可用于将特定模态的后处理器组合成一个单一的后处理器。
PerceiverModel
类 transformers.PerceiverModel
< source >( config decoder = None input_preprocessor: typing.Callable[..., typing.Tuple[torch.Tensor, typing.Optional[torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor]] = None output_postprocessor: typing.Callable[..., typing.Any] = None )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
- decoder (DecoderType, optional) — 可选的解码器,用于解码编码器的潜在表示。示例包括 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverBasicDecoder, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassificationDecoder, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultimodalDecoder.
- input_preprocessor (PreprocessorType, optional) — 可选的输入预处理器。示例包括 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverImagePreprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverAudioPreprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverTextPreprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultimodalPreprocessor.
- output_postprocessor (PostprocessorType, optional) — 可选的输出后处理器。示例包括 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverImagePostprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverAudioPostprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassificationPostprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverProjectionPostprocessor, transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultimodalPostprocessor.
- 注意 你可以定义自己的解码器、预处理器和/或后处理器以适应你的使用场景。—
感知器:一种可扩展的、完全注意力的架构。
请注意,通过在模型的前向传播中将interpolate_pos_encoding设置为True,可以在比训练时更高分辨率的图像上微调Perceiver。这将把预训练的位置嵌入插值到更高的分辨率。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: FloatTensor attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None subsampled_output_points: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, torch.Tensor]] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverModelOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)分数(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层的隐藏状态序列。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每一层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import PerceiverConfig, PerceiverTokenizer, PerceiverImageProcessor, PerceiverModel
>>> from transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver import (
... PerceiverTextPreprocessor,
... PerceiverImagePreprocessor,
... PerceiverClassificationDecoder,
... )
>>> import torch
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> # EXAMPLE 1: using the Perceiver to classify texts
>>> # - we define a TextPreprocessor, which can be used to embed tokens
>>> # - we define a ClassificationDecoder, which can be used to decode the
>>> # final hidden states of the latents to classification logits
>>> # using trainable position embeddings
>>> config = PerceiverConfig()
>>> preprocessor = PerceiverTextPreprocessor(config)
>>> decoder = PerceiverClassificationDecoder(
... config,
... num_channels=config.d_latents,
... trainable_position_encoding_kwargs=dict(num_channels=config.d_latents, index_dims=1),
... use_query_residual=True,
... )
>>> model = PerceiverModel(config, input_preprocessor=preprocessor, decoder=decoder)
>>> # you can then do a forward pass as follows:
>>> tokenizer = PerceiverTokenizer()
>>> text = "hello world"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(inputs=inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 2]
>>> # to train, one can train the model using standard cross-entropy:
>>> criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
>>> labels = torch.tensor([1])
>>> loss = criterion(logits, labels)
>>> # EXAMPLE 2: using the Perceiver to classify images
>>> # - we define an ImagePreprocessor, which can be used to embed images
>>> config = PerceiverConfig(image_size=224)
>>> preprocessor = PerceiverImagePreprocessor(
... config,
... prep_type="conv1x1",
... spatial_downsample=1,
... out_channels=256,
... position_encoding_type="trainable",
... concat_or_add_pos="concat",
... project_pos_dim=256,
... trainable_position_encoding_kwargs=dict(
... num_channels=256,
... index_dims=config.image_size**2,
... ),
... )
>>> model = PerceiverModel(
... config,
... input_preprocessor=preprocessor,
... decoder=PerceiverClassificationDecoder(
... config,
... num_channels=config.d_latents,
... trainable_position_encoding_kwargs=dict(num_channels=config.d_latents, index_dims=1),
... use_query_residual=True,
... ),
... )
>>> # you can then do a forward pass as follows:
>>> image_processor = PerceiverImageProcessor()
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(inputs=inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 2]
>>> # to train, one can train the model using standard cross-entropy:
>>> criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
>>> labels = torch.tensor([1])
>>> loss = criterion(logits, labels)PerceiverForMaskedLM
类 transformers.PerceiverForMaskedLM
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 用于掩码语言建模的示例用法。 该模型是 PyTorch torch.nn.Module 的子类。将其作为常规的 PyTorch 模块使用,并参考 PyTorch 文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMaskedLMOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — 用于计算掩码语言建模损失的标签。索引应在[-100, 0, ..., config.vocab_size]范围内(参见input_ids文档字符串)。索引设置为-100的标记将被忽略(掩码), 损失仅针对标签在[0, ..., config.vocab_size]范围内的标记进行计算
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMaskedLMOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMaskedLMOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,), 可选, 当提供labels时返回) — 掩码语言建模(MLM)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax 之前每个词汇标记的分数)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, num_latents, num_latents)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 后,用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForMaskedLM 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, PerceiverForMaskedLM
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepmind/language-perceiver")
>>> model = PerceiverForMaskedLM.from_pretrained("deepmind/language-perceiver")
>>> # training
>>> text = "This is an incomplete sentence where some words are missing."
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt")
>>> # mask " missing."
>>> inputs["input_ids"][0, 52:61] = tokenizer.mask_token_id
>>> labels = tokenizer(text, padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt").input_ids
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, labels=labels)
>>> loss = outputs.loss
>>> round(loss.item(), 2)
19.87
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 2048, 262]
>>> # inference
>>> text = "This is an incomplete sentence where some words are missing."
>>> encoding = tokenizer(text, padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt")
>>> # mask bytes corresponding to " missing.". Note that the model performs much better if the masked span starts with a space.
>>> encoding["input_ids"][0, 52:61] = tokenizer.mask_token_id
>>> # forward pass
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**encoding)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 2048, 262]
>>> masked_tokens_predictions = logits[0, 52:61].argmax(dim=-1).tolist()
>>> tokenizer.decode(masked_tokens_predictions)
' missing.'PerceiverForSequenceClassification
类 transformers.PerceiverForSequenceClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 用于文本分类的示例。 该模型是 PyTorch torch.nn.Module 的子类。将其作为常规的 PyTorch 模块使用,并参考 PyTorch 文档以了解与一般使用和行为相关的所有事项。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 输入到感知器的内容。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForSequenceClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, PerceiverForSequenceClassification
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepmind/language-perceiver")
>>> model = PerceiverForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("deepmind/language-perceiver")
>>> text = "hello world"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
>>> outputs = model(inputs=inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 2]PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned
类 transformers.PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 用于图像分类的示例,适用于 ImageNet 等任务。
该模型使用了学习到的位置嵌入。换句话说,该模型没有获得任何关于图像结构的特权信息。如论文所示,该模型在ImageNet上可以达到72.7的top-1准确率。
PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned 使用 PerceiverImagePreprocessor
(带有 prep_type="conv1x1")来预处理输入图像,并使用
PerceiverClassificationDecoder 将
PerceiverModel 的潜在表示解码为分类 logits。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算图像分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-learned")
>>> model = PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-learned")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> outputs = model(inputs=inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 1000]
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
Predicted class: tabby, tabby catPerceiverForImageClassificationFourier
类 transformers.PerceiverForImageClassificationFourier
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 用于图像分类的示例,适用于 ImageNet 等任务。
该模型使用固定的2D傅里叶位置嵌入。如论文所示,该模型在ImageNet上可以达到79.0的top-1准确率,当在大规模数据集(即JFT)上进行预训练时,准确率可以达到84.5。
PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned 使用 PerceiverImagePreprocessor
(with prep_type="pixels") 来预处理输入图像,并使用
PerceiverClassificationDecoder 将
PerceiverModel 的潜在表示解码为分类 logits。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor形状为(batch_size,), 可选) — 用于计算图像分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForImageClassificationFourier 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, PerceiverForImageClassificationFourier
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-fourier")
>>> model = PerceiverForImageClassificationFourier.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-fourier")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> outputs = model(inputs=inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 1000]
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
Predicted class: tabby, tabby catPerceiverForImageClassificationConvProcessing
类 transformers.PerceiverForImageClassificationConvProcessing
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 用于图像分类的示例,适用于 ImageNet 等任务。
该模型使用了一个2D卷积+最大池化预处理网络。如论文所示,该模型在ImageNet上可以达到82.1的top-1准确率。
PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned 使用 PerceiverImagePreprocessor
(带有 prep_type="conv")来预处理输入图像,并使用
PerceiverClassificationDecoder 将
PerceiverModel 的潜在表示解码为分类 logits。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算图像分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForImageClassificationConvProcessing 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, PerceiverForImageClassificationConvProcessing
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-conv")
>>> model = PerceiverForImageClassificationConvProcessing.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-conv")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> outputs = model(inputs=inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 1000]
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
Predicted class: tabby, tabby catPerceiverForOpticalFlow
类 transformers.PerceiverForOpticalFlow
< source >( config )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 在光流任务中的使用示例,例如 Sintel 和 KITTI。PerceiverForOpticalFlow 使用 PerceiverImagePreprocessor(带有 prep_type=“patches”)来预处理 输入图像,并使用 PerceiverOpticalFlowDecoder 来解码 PerceiverModel 的潜在表示。
作为输入,将两个连续的帧沿通道维度连接,并在每个像素周围提取一个3 x 3的补丁(导致每个像素有3 x 3 x 3 x 2 = 54个值)。使用固定的傅里叶位置编码来编码补丁中每个像素的位置。接下来,应用Perceiver编码器。为了解码,使用与输入相同的编码查询潜在表示。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算光流损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForOpticalFlow 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import PerceiverForOpticalFlow
>>> import torch
>>> model = PerceiverForOpticalFlow.from_pretrained("deepmind/optical-flow-perceiver")
>>> # in the Perceiver IO paper, the authors extract a 3 x 3 patch around each pixel,
>>> # leading to 3 x 3 x 3 = 27 values for each pixel (as each pixel also has 3 color channels)
>>> # patches have shape (batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)
>>> # the authors train on resolutions of 368 x 496
>>> patches = torch.randn(1, 2, 27, 368, 496)
>>> outputs = model(inputs=patches)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 368, 496, 2]PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding
类 transformers.PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding
< source >( config: PerceiverConfig )
参数
- config (PerceiverConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Perceiver 在多模态(视频)自动编码中的示例使用,适用于 Kinetics-700 等任务。
PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding 使用 PerceiverMultimodalPreprocessor 来预处理三种模态:图像、音频和类别标签。该预处理器使用特定模态的预处理器分别对每种模态进行预处理,然后将它们连接起来。可训练的位置嵌入用于将每种模态填充到相同数量的通道,以便在时间维度上进行连接。接下来,应用Perceiver编码器。
PerceiverMultimodalDecoder 用于解码 PerceiverModel 的潜在表示。该解码器使用每个模态特定的解码器来构建查询。解码器查询是基于预处理后的输入创建的。然而,在单次前向传递中对整个视频进行自动编码在计算上是不可行的,因此只使用部分解码器查询与潜在表示进行交叉注意力。这是由每个模态的子采样索引决定的,可以作为 PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding 前向传递的额外输入提供。
PerceiverMultimodalDecoder 还将不同模态的解码器查询填充到相同数量的通道,以便沿时间维度将它们连接起来。接下来,与 PerceiverModel 的潜在表示进行交叉注意力操作。
最后,~models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverMultiModalPostprocessor 用于将这个张量转换为实际的视频。它首先将输出分割成不同的模态,然后为每个模态应用相应的后处理器。
请注意,通过在评估期间屏蔽分类标签(即仅为“标签”模态提供一个零张量),这个自动编码模型就变成了一个Kinetics 700视频分类器。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( inputs: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None subsampled_output_points: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, torch.Tensor]] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- inputs (
torch.FloatTensor) — 感知器的输入。可以是任何东西:图像、文本、音频、视频等。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shapebatch_size, sequence_length, optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算图像分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.perceiver.modeling_perceiver.PerceiverClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(PerceiverConfig)和输入。
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 - logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态 加上初始嵌入输出。 - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算 自注意力头中的加权平均值。 - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 之后, 用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding
>>> import torch
>>> import numpy as np
>>> # create multimodal inputs
>>> images = torch.randn((1, 16, 3, 224, 224))
>>> audio = torch.randn((1, 30720, 1))
>>> inputs = dict(image=images, audio=audio, label=torch.zeros((images.shape[0], 700)))
>>> model = PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding.from_pretrained("deepmind/multimodal-perceiver")
>>> # in the Perceiver IO paper, videos are auto-encoded in chunks
>>> # each chunk subsamples different index dimensions of the image and audio modality decoder queries
>>> nchunks = 128
>>> image_chunk_size = np.prod((16, 224, 224)) // nchunks
>>> audio_chunk_size = audio.shape[1] // model.config.samples_per_patch // nchunks
>>> # process the first chunk
>>> chunk_idx = 0
>>> subsampling = {
... "image": torch.arange(image_chunk_size * chunk_idx, image_chunk_size * (chunk_idx + 1)),
... "audio": torch.arange(audio_chunk_size * chunk_idx, audio_chunk_size * (chunk_idx + 1)),
... "label": None,
... }
>>> outputs = model(inputs=inputs, subsampled_output_points=subsampling)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> list(logits["audio"].shape)
[1, 240]
>>> list(logits["image"].shape)
[1, 6272, 3]
>>> list(logits["label"].shape)
[1, 700]