GIT
概述
GIT模型由Jianfeng Wang、Zhengyuan Yang、Xiaowei Hu、Linjie Li、Kevin Lin、Zhe Gan、Zicheng Liu、Ce Liu、Lijuan Wang在GIT: A Generative Image-to-text Transformer for Vision and Language中提出。GIT是一个仅解码器的Transformer,它利用CLIP的视觉编码器来在文本之外的条件模型上处理视觉输入。该模型在图像描述和视觉问答基准测试中获得了最先进的结果。
论文的摘要如下:
在本文中,我们设计并训练了一个生成式图像到文本转换器(GIT),以统一视觉语言任务,如图像/视频字幕生成和问答。虽然生成模型在预训练和微调之间提供了一致的网络架构,但现有工作通常包含复杂的结构(单/多模态编码器/解码器),并依赖于外部模块,如对象检测器/标记器和光学字符识别(OCR)。在GIT中,我们将架构简化为一个图像编码器和一个文本解码器,在单一语言建模任务下进行。我们还扩大了预训练数据和模型规模,以提升模型性能。无需花哨的技巧,我们的GIT在12个具有挑战性的基准测试中大幅领先,建立了新的技术水平。例如,我们的模型首次在TextCaps上超越了人类表现(CIDEr得分138.2 vs. 125.5)。此外,我们提出了一种新的基于生成的图像分类和场景文本识别方案,在标准基准测试中取得了不错的性能。
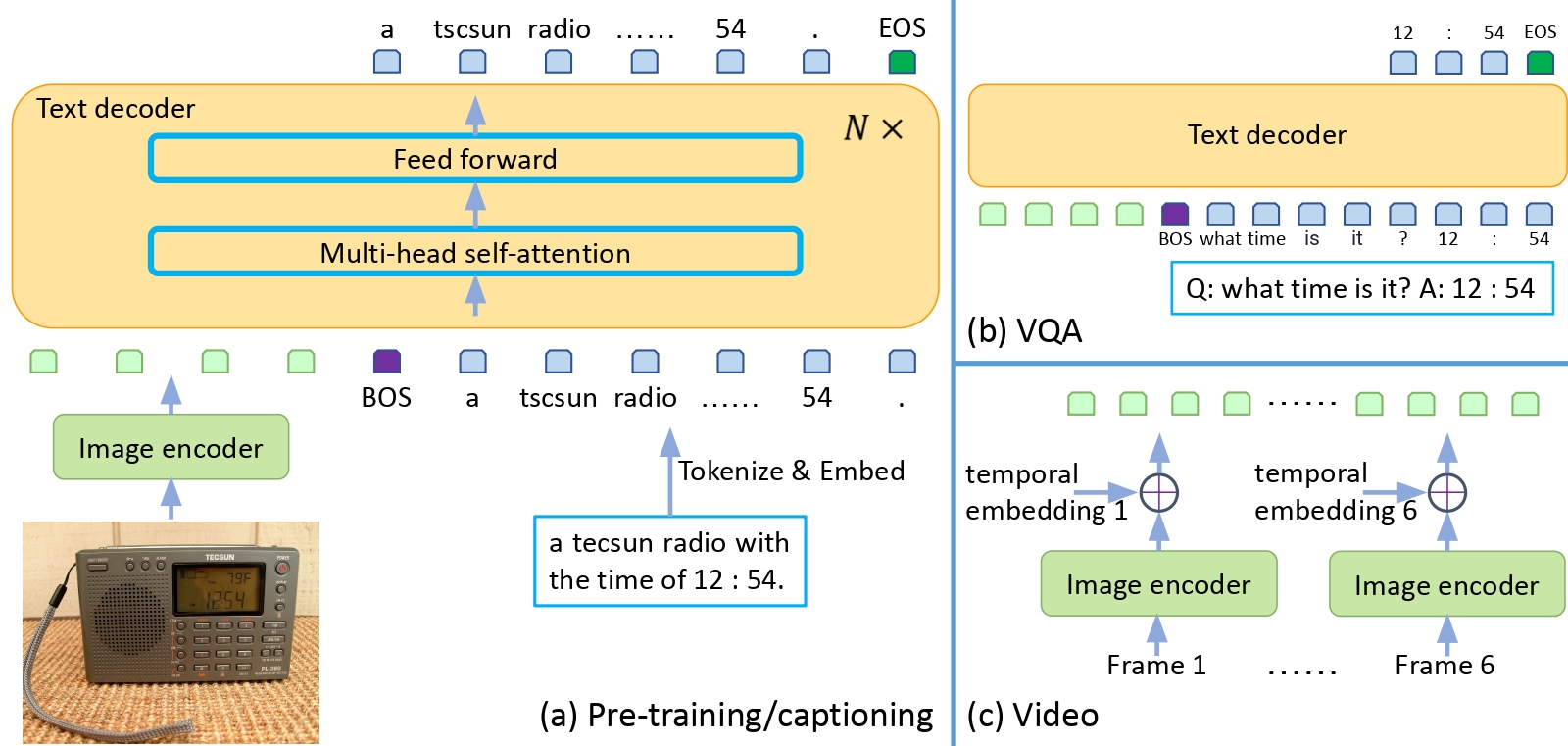 GIT architecture. Taken from the original paper.
GIT architecture. Taken from the original paper. 使用提示
- GIT 的实现方式与 GPT-2 非常相似,唯一的区别在于模型还以
pixel_values为条件。
资源
一份官方的Hugging Face和社区(由🌎表示)资源列表,帮助您开始使用GIT。
- 关于在自定义数据上进行推理和微调GIT的演示笔记本可以在这里找到。
- 另请参阅:Causal language modeling task guide
如果您有兴趣提交资源以包含在此处,请随时打开一个Pull Request,我们将对其进行审查。 理想情况下,资源应展示一些新的内容,而不是重复现有的资源。
GitVisionConfig
类 transformers.GitVisionConfig
< source >( hidden_size = 768 intermediate_size = 3072 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 num_channels = 3 image_size = 224 patch_size = 16 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 **kwargs )
参数
- hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 3072) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — 每张图片的大小(分辨率)。 - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — 每个补丁的大小(分辨率)。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"quick_gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"selu"和"gelu_new""quick_gelu"。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比率。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的截断正态初始化器的标准差。
这是用于存储GitVisionModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化一个GIT视觉编码器,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与GIT视觉编码器microsoft/git-base架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import GitVisionConfig, GitVisionModel
>>> # Initializing a GitVisionConfig with microsoft/git-base style configuration
>>> configuration = GitVisionConfig()
>>> # Initializing a GitVisionModel (with random weights) from the microsoft/git-base style configuration
>>> model = GitVisionModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configGitVisionModel
类 transformers.GitVisionModel
< source >( config: GitVisionConfig )
参数
- config (GitConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
来自CLIP的视觉模型,用于GIT,没有任何头部或顶部的投影。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。默认情况下,如果您提供了填充,它将被忽略。可以使用 AutoImageProcessor获取像素值。有关详细信息,请参见CLIPImageProcessor.call(). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参阅返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaultsFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层的隐藏状态序列。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
GitVisionModel 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, GitVisionModel
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base")
>>> model = GitVisionModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_stateGit配置
类 transformers.GitConfig
< source >( vision_config = None vocab_size = 30522 hidden_size = 768 num_hidden_layers = 6 num_attention_heads = 12 intermediate_size = 3072 hidden_act = 'gelu' hidden_dropout_prob = 0.1 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.1 max_position_embeddings = 1024 initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 pad_token_id = 0 position_embedding_type = 'absolute' use_cache = True tie_word_embeddings = False bos_token_id = 101 eos_token_id = 102 num_image_with_embedding = None **kwargs )
参数
- vision_config (
dict, 可选) — 用于初始化 GitVisionConfig 的配置选项字典。 - vocab_size (
int, optional, 默认为 30522) — GIT 模型的词汇表大小。定义了调用 GitModel 时传递的inputs_ids可以表示的不同标记的数量。 - hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, 默认为 6) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 3072) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(通常称为前馈)层的维度。 - hidden_act (
str或Callable, 可选, 默认为"gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"silu"和"gelu_new"。 - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, 默认为 0.1) — 嵌入层、编码器和池化器中所有全连接层的 dropout 概率。 - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — 注意力概率的丢弃比率。 - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, 默认为 1024) — 此模型可能使用的最大序列长度。通常将其设置为较大的值以防万一(例如,512 或 1024 或 2048)。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的截断正态初始化器的标准差。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - position_embedding_type (
str, optional, defaults to"absolute") — 位置嵌入的类型。选择"absolute","relative_key","relative_key_query"中的一个。对于 位置嵌入,使用"absolute"。有关"relative_key"的更多信息,请参阅 Self-Attention with Relative Position Representations (Shaw et al.)。 有关"relative_key_query"的更多信息,请参阅 Method 4 在 Improve Transformer Models with Better Relative Position Embeddings (Huang et al.) 中。 - use_cache (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — 模型是否应返回最后的键/值注意力(并非所有模型都使用)。 - num_image_with_embedding (
int, optional) — 要添加的时间嵌入数量,以防模型用于视频字幕/VQA。
这是用于存储GitModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化一个GIT模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与GIT microsoft/git-base架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import GitConfig, GitModel
>>> # Initializing a GIT microsoft/git-base style configuration
>>> configuration = GitConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the microsoft/git-base style configuration
>>> model = GitModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configGitProcessor
类 transformers.GitProcessor
< source >( image_processor tokenizer )
参数
- image_processor (AutoImageProcessor) — 图像处理器是一个必需的输入。
- tokenizer (AutoTokenizer) — 分词器是一个必需的输入。
构建一个GIT处理器,它将CLIP图像处理器和BERT分词器封装到一个单一的处理器中。
GitProcessor 提供了 CLIPImageProcessor 和 BertTokenizerFast 的所有功能。更多信息请参见
call() 和 decode()。
__call__
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')], NoneType] = None text: typing.Union[str, typing.List[str], typing.List[typing.List[str]], NoneType] = None audio = None videos = None **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.git.processing_git.GitProcessorKwargs] ) → BatchFeature
参数
- images (
PIL.Image.Image,np.ndarray,torch.Tensor,List[PIL.Image.Image],List[np.ndarray],List[torch.Tensor]) — 要准备的图像或图像批次。每个图像可以是PIL图像、NumPy数组或PyTorch张量。支持通道优先和通道最后的格式。 - 文本 (
TextInput,PreTokenizedInput,List[TextInput],List[PreTokenizedInput], 可选) — 要编码的序列或序列批次。每个序列可以是一个字符串或字符串列表(预分词的字符串)。如果序列以字符串列表(预分词)的形式提供,你必须设置is_split_into_words=True(以消除与序列批次的歧义)。 - return_tensors (
stror TensorType, 可选) — 如果设置,将返回特定框架的张量。可接受的值有:'tf': 返回 TensorFlowtf.constant对象。'pt': 返回 PyTorchtorch.Tensor对象。'np': 返回 NumPynp.ndarray对象。'jax': 返回 JAXjnp.ndarray对象。
返回
一个包含以下字段的BatchFeature:
- input_ids — 要输入模型的令牌ID列表。当
text不为None时返回。 - attention_mask — 指定模型应关注哪些令牌的索引列表(当
return_attention_mask=True或“attention_mask”在self.model_input_names中且text不为None时)。 - pixel_values — 要输入模型的像素值。当
images不为None时返回。
准备模型的一个或多个序列和图像的主要方法。如果text不为None,则此方法将text和kwargs参数转发给BertTokenizerFast的call()以编码文本。为了准备图像,如果images不为None,则此方法将images和kwrags参数转发给CLIPImageProcessor的call()。请参考上述两个方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
GitModel
类 transformers.GitModel
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GitConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
裸GIT模型转换器,由CLIP图像编码器和文本解码器组成,输出原始隐藏状态,顶部没有任何特定的头部。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.List[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 CLIPImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaultsFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GitConfig)和输入。
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, hidden_size)) — 序列的第一个标记(分类标记)在经过用于辅助预训练任务的层进一步处理后的最后一层隐藏状态。例如,对于BERT系列模型,这返回经过线性层和tanh激活函数处理后的分类标记。线性层的权重是在预训练期间通过下一个句子预测(分类)目标训练的。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力softmax后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
GitModel 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModel
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base")
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> text = "this is an image of two cats"
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, text=text, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_stateGitForCausalLM
类 transformers.GitForCausalLM
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GitConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
GIT 模型,顶部带有language modeling头,用于自回归语言建模。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.List[torch.Tensor], NoneType] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。像素值可以使用AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见 CLIPImageProcessor.call(). - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), 可选) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaultsFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组. - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — 用于计算从左到右语言建模损失(下一个词预测)的标签。索引应在[-100, 0, ..., config.vocab_size]范围内(参见input_ids文档字符串)。索引设置为-100的 标记将被忽略(掩码),损失仅计算标签在[0, ..., config.vocab_size]范围内的标记 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithPast 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GitConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 语言建模损失(用于下一个标记的预测)。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax 之前每个词汇标记的分数)。 -
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)),可选,当传递use_cache=True或当config.use_cache=True时返回) — 长度为config.n_layers的tuple(torch.FloatTensor)元组,每个元组包含 2 个形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)的张量包含预先计算的隐藏状态(自注意力块中的键和值),可用于(参见
past_key_values输入)加速顺序解码。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor的元组(每层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
GitForCausalLM 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
图像字幕示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base-coco")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base-coco")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> pixel_values = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(pixel_values=pixel_values, max_length=50)
>>> generated_caption = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
>>> print(generated_caption)
two cats sleeping on a pink blanket next to remotes.视觉问答(VQA)示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base-textvqa")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base-textvqa")
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(repo_id="nielsr/textvqa-sample", filename="bus.png", repo_type="dataset")
>>> image = Image.open(file_path).convert("RGB")
>>> pixel_values = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> question = "what does the front of the bus say at the top?"
>>> input_ids = processor(text=question, add_special_tokens=False).input_ids
>>> input_ids = [processor.tokenizer.cls_token_id] + input_ids
>>> input_ids = torch.tensor(input_ids).unsqueeze(0)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(pixel_values=pixel_values, input_ids=input_ids, max_length=50)
>>> print(processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True))
['what does the front of the bus say at the top? special']视频字幕示例:
>>> import av
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base-vatex")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("microsoft/git-base-vatex")
>>> # set seed for reproducability
>>> np.random.seed(45)
>>> def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
... '''
... Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
... Args:
... container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
... indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
... Returns:
... result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
... '''
... frames = []
... container.seek(0)
... start_index = indices[0]
... end_index = indices[-1]
... for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
... if i > end_index:
... break
... if i >= start_index and i in indices:
... frames.append(frame)
... return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
>>> def sample_frame_indices(clip_len, frame_sample_rate, seg_len):
... '''
... Sample a given number of frame indices from the video.
... Args:
... clip_len (`int`): Total number of frames to sample.
... frame_sample_rate (`int`): Sample every n-th frame.
... seg_len (`int`): Maximum allowed index of sample's last frame.
... Returns:
... indices (`List[int]`): List of sampled frame indices
... '''
... converted_len = int(clip_len * frame_sample_rate)
... end_idx = np.random.randint(converted_len, seg_len)
... start_idx = end_idx - converted_len
... indices = np.linspace(start_idx, end_idx, num=clip_len)
... indices = np.clip(indices, start_idx, end_idx - 1).astype(np.int64)
... return indices
>>> # load video
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(
... repo_id="nielsr/video-demo", filename="eating_spaghetti.mp4", repo_type="dataset"
... )
>>> container = av.open(file_path)
>>> # sample frames
>>> num_frames = model.config.num_image_with_embedding
>>> indices = sample_frame_indices(
... clip_len=num_frames, frame_sample_rate=4, seg_len=container.streams.video[0].frames
... )
>>> frames = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
>>> pixel_values = processor(images=list(frames), return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(pixel_values=pixel_values, max_length=50)
>>> print("Generated caption:", processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True))
Generated caption: ['a woman is sitting at a table and she is talking about the food she is holding.']