X-CLIP
概述
X-CLIP模型由Bolin Ni、Houwen Peng、Minghao Chen、Songyang Zhang、Gaofeng Meng、Jianlong Fu、Shiming Xiang和Haibin Ling在Expanding Language-Image Pretrained Models for General Video Recognition中提出。 X-CLIP是CLIP的一个最小扩展,用于视频。该模型由一个文本编码器、一个跨帧视觉编码器、一个多帧集成Transformer和一个视频特定的提示生成器组成。
论文的摘要如下:
对比语言-图像预训练在从网络规模数据中学习视觉-文本联合表示方面取得了巨大成功,展示了在各种图像任务中的显著“零样本”泛化能力。然而,如何有效地将这种新的语言-图像预训练方法扩展到视频领域仍然是一个开放的问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,直接将预训练的语言-图像模型适应于视频识别,而不是从头开始预训练一个新模型。更具体地说,为了捕捉时间维度上帧的长程依赖关系,我们提出了一种跨帧注意力机制,明确地在帧之间交换信息。这种模块轻量级,并且可以无缝地插入到预训练的语言-图像模型中。此外,我们提出了一种视频特定的提示方案,利用视频内容信息生成具有区分性的文本提示。大量实验表明,我们的方法是有效的,并且可以推广到不同的视频识别场景。特别是在全监督设置下,我们的方法在Kinectics-400上达到了87.1%的top-1准确率,同时使用的FLOPs比Swin-L和ViViT-H少12倍。在零样本实验中,我们的方法在两种流行协议下的top-1准确率分别比当前最先进的方法高出+7.6%和+14.9%。在少样本场景中,当标记数据极其有限时,我们的方法比之前最好的方法高出+32.1%和+23.1%。
提示:
- X-CLIP 的使用与 CLIP 相同。
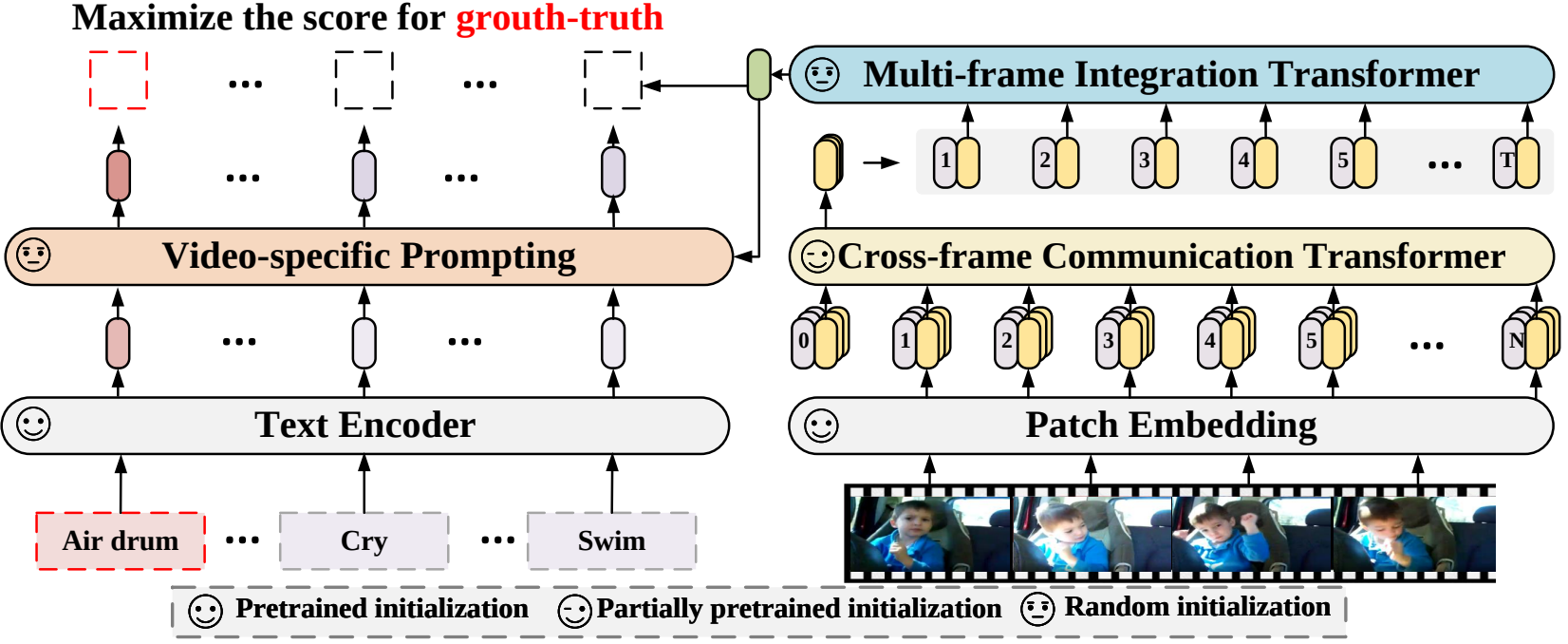 X-CLIP architecture. Taken from the original paper.
X-CLIP architecture. Taken from the original paper. 资源
以下是官方Hugging Face和社区(由🌎表示)提供的资源列表,帮助您开始使用X-CLIP。
- X-CLIP 的演示笔记本可以在 这里 找到。
如果您有兴趣提交资源以包含在此处,请随时打开一个 Pull Request,我们将进行审核!理想情况下,资源应展示一些新内容,而不是重复现有资源。
XCLIPProcessor
类 transformers.XCLIPProcessor
< source >( image_processor = 无 tokenizer = 无 **kwargs )
参数
- image_processor (VideoMAEImageProcessor, 可选) — 图像处理器是一个必需的输入。
- tokenizer (CLIPTokenizerFast, 可选) — tokenizer 是一个必需的输入。
构建一个X-CLIP处理器,它将VideoMAE图像处理器和CLIP分词器封装到一个单一的处理器中。
XCLIPProcessor 提供了 VideoMAEImageProcessor 和 CLIPTokenizerFast 的所有功能。更多信息请参见
__call__() 和 decode()。
此方法将其所有参数转发给CLIPTokenizerFast的batch_decode()。请参考该方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
此方法将其所有参数转发给CLIPTokenizerFast的decode()。请参考该方法的文档字符串以获取更多信息。
XCLIPConfig
类 transformers.XCLIPConfig
< source >( text_config = 无 vision_config = 无 projection_dim = 512 prompt_layers = 2 prompt_alpha = 0.1 prompt_hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' prompt_num_attention_heads = 8 prompt_attention_dropout = 0.0 prompt_projection_dropout = 0.0 logit_scale_init_value = 2.6592 **kwargs )
参数
- text_config (
dict, optional) — 用于初始化 XCLIPTextConfig 的配置选项字典。 - vision_config (
dict, optional) — 用于初始化XCLIPVisionConfig的配置选项字典。 - projection_dim (
int, 可选, 默认为 512) — 文本和视觉投影层的维度。 - prompt_layers (
int, optional, 默认为 2) — 视频特定提示生成器中的层数。 - prompt_alpha (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.1) — 用于视频特定提示生成器的Alpha值。 - prompt_hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"quick_gelu") — 视频特定提示生成器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串, 支持"gelu","relu","selu"和"gelu_new""quick_gelu". - prompt_num_attention_heads (
int, optional, 默认为 8) — 视频特定提示生成器的交叉注意力中的注意力头数。 - prompt_attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 视频特定提示生成器中注意力层的丢弃概率。 - prompt_projection_dropout (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.0) — 视频特定提示生成器中投影层的丢弃概率。 - logit_scale_init_value (
float, optional, 默认为 2.6592) — logit_scale 参数的初始值。默认值根据原始 XCLIP 实现使用。 - kwargs (可选) — 关键字参数字典。
XCLIPConfig 是用于存储 XCLIPModel 配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化 X-CLIP 模型,定义文本模型和视觉模型的配置。 使用默认值实例化配置将生成与 X-CLIP microsoft/xclip-base-patch32 架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
from_text_vision_configs
< source >( text_config: XCLIPTextConfig vision_config: XCLIPVisionConfig **kwargs ) → XCLIPConfig
从xclip文本模型配置和xclip视觉模型配置实例化一个XCLIPConfig(或派生类)。
XCLIPTextConfig
类 transformers.XCLIPTextConfig
< source >( vocab_size = 49408 hidden_size = 512 intermediate_size = 2048 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 8 max_position_embeddings = 77 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 pad_token_id = 1 bos_token_id = 0 eos_token_id = 2 **kwargs )
参数
- vocab_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 49408) — X-CLIP 文本模型的词汇表大小。定义了可以通过调用 XCLIPModel 时传递的inputs_ids表示的不同标记的数量。 - hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 512) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 2048) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Transformer编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, 默认为 77) — 此模型可能使用的最大序列长度。通常将其设置为较大的值以防万一(例如,512 或 1024 或 2048)。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"quick_gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"selu"和"gelu_new""quick_gelu"。 - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - attention_dropout (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比例。 - initializer_range (
float, optional, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - initializer_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为 1) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的因子(应保持为1,内部用于初始化测试)。
这是用于存储XCLIPModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化X-CLIP模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与X-CLIP microsoft/xclip-base-patch32架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import XCLIPTextModel, XCLIPTextConfig
>>> # Initializing a XCLIPTextModel with microsoft/xclip-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> configuration = XCLIPTextConfig()
>>> # Initializing a XCLIPTextConfig from the microsoft/xclip-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> model = XCLIPTextModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configXCLIPVisionConfig
类 transformers.XCLIPVisionConfig
< source >( hidden_size = 768 intermediate_size = 3072 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 mit_hidden_size = 512 mit_intermediate_size = 2048 mit_num_hidden_layers = 1 mit_num_attention_heads = 8 num_channels = 3 image_size = 224 patch_size = 32 num_frames = 8 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 drop_path_rate = 0.0 **kwargs )
参数
- hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 768) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 3072) — Transformer 编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, 默认为 12) — Transformer 编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - mit_hidden_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 512) — 多帧集成变换器(MIT)编码器层的维度。 - mit_intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 2048) — 多维集成变换器(MIT)中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - mit_num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — 多帧集成变换器(MIT)中的隐藏层数量。 - mit_num_attention_heads (
int, optional, 默认为 8) — 多帧集成变换器(MIT)中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - image_size (
int, optional, 默认为 224) — 每张图片的大小(分辨率)。 - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — 每个补丁的大小(分辨率)。 - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"quick_gelu") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu","relu","selu","gelu_new"和"quick_gelu". - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - attention_dropout (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比例。 - initializer_range (
float, optional, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - initializer_factor (
float, 可选, 默认为 1) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的因子(应保持为1,内部用于初始化测试)。 - drop_path_rate (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 随机深度率.
这是用于存储XCLIPModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化X-CLIP模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与X-CLIP microsoft/xclip-base-patch32架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import XCLIPVisionModel, XCLIPVisionConfig
>>> # Initializing a XCLIPVisionModel with microsoft/xclip-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> configuration = XCLIPVisionConfig()
>>> # Initializing a XCLIPVisionModel model from the microsoft/xclip-base-patch32 style configuration
>>> model = XCLIPVisionModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configXCLIPModel
类 transformers.XCLIPModel
< source >( config: XCLIPConfig )
参数
- config (XCLIPConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
该模型是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。将其用作常规的PyTorch模块,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None return_loss: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.x_clip.modeling_x_clip.XCLIPOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。默认情况下,如果您提供了填充,它将被忽略。像素值可以使用 AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见CLIPImageProcessor.call(). - return_loss (
bool, optional) — 是否返回对比损失。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaultsFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.models.x_clip.modeling_x_clip.XCLIPOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.models.x_clip.modeling_x_clip.XCLIPOutput 或一个由 torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含根据配置(
- loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当return_loss为True时返回) — 视频-文本相似度的对比损失。 - logits_per_video (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(video_batch_size, text_batch_size)) —video_embeds和text_embeds之间的缩放点积分数。这表示视频-文本相似度分数。 - logits_per_text (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(text_batch_size, video_batch_size)) —text_embeds和video_embeds之间的缩放点积分数。这表示文本-视频相似度分数。 - text_embeds(
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, output_dim) — 通过将投影层应用于 XCLIPTextModel 的池化输出获得的文本嵌入。 - video_embeds(
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, output_dim) — 通过将投影层应用于 XCLIPVisionModel 的池化输出获得的视频嵌入。 - text_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — XCLIPTextModel 的输出。 - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — XCLIPVisionModel 的输出。 - mit_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) —XCLIPMultiframeIntegrationTransformer(简称 MIT)的输出。
XCLIPModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import av
>>> import torch
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModel
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>> def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
... '''
... Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
... Args:
... container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
... indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
... Returns:
... result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
... '''
... frames = []
... container.seek(0)
... start_index = indices[0]
... end_index = indices[-1]
... for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
... if i > end_index:
... break
... if i >= start_index and i in indices:
... frames.append(frame)
... return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
>>> def sample_frame_indices(clip_len, frame_sample_rate, seg_len):
... '''
... Sample a given number of frame indices from the video.
... Args:
... clip_len (`int`): Total number of frames to sample.
... frame_sample_rate (`int`): Sample every n-th frame.
... seg_len (`int`): Maximum allowed index of sample's last frame.
... Returns:
... indices (`List[int]`): List of sampled frame indices
... '''
... converted_len = int(clip_len * frame_sample_rate)
... end_idx = np.random.randint(converted_len, seg_len)
... start_idx = end_idx - converted_len
... indices = np.linspace(start_idx, end_idx, num=clip_len)
... indices = np.clip(indices, start_idx, end_idx - 1).astype(np.int64)
... return indices
>>> # video clip consists of 300 frames (10 seconds at 30 FPS)
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(
... repo_id="nielsr/video-demo", filename="eating_spaghetti.mp4", repo_type="dataset"
... )
>>> container = av.open(file_path)
>>> # sample 8 frames
>>> indices = sample_frame_indices(clip_len=8, frame_sample_rate=1, seg_len=container.streams.video[0].frames)
>>> video = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = processor(
... text=["playing sports", "eating spaghetti", "go shopping"],
... videos=list(video),
... return_tensors="pt",
... padding=True,
... )
>>> # forward pass
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits_per_video = outputs.logits_per_video # this is the video-text similarity score
>>> probs = logits_per_video.softmax(dim=1) # we can take the softmax to get the label probabilities
>>> print(probs)
tensor([[1.9496e-04, 9.9960e-01, 2.0825e-04]])get_text_features
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → 文本特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
文本特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
通过将投影层应用于XCLIPTextModel的池化输出获得的文本嵌入。
XCLIPModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> text_features = model.get_text_features(**inputs)获取视频特征
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → 视频特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。默认情况下,如果您提供了填充,它将被忽略。可以使用 AutoImageProcessor获取像素值。详情请参见CLIPImageProcessor.call(). - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaultsFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
视频特征 (torch.FloatTensor 形状为 (batch_size, output_dim)
通过将投影层应用于XCLIPVisionModel和XCLIPMultiframeIntegrationTransformer的池化输出获得的视频嵌入。
XCLIPModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import av
>>> import torch
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModel
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>> def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
... '''
... Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
... Args:
... container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
... indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
... Returns:
... result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
... '''
... frames = []
... container.seek(0)
... start_index = indices[0]
... end_index = indices[-1]
... for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
... if i > end_index:
... break
... if i >= start_index and i in indices:
... frames.append(frame)
... return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
>>> def sample_frame_indices(clip_len, frame_sample_rate, seg_len):
... '''
... Sample a given number of frame indices from the video.
... Args:
... clip_len (`int`): Total number of frames to sample.
... frame_sample_rate (`int`): Sample every n-th frame.
... seg_len (`int`): Maximum allowed index of sample's last frame.
... Returns:
... indices (`List[int]`): List of sampled frame indices
... '''
... converted_len = int(clip_len * frame_sample_rate)
... end_idx = np.random.randint(converted_len, seg_len)
... start_idx = end_idx - converted_len
... indices = np.linspace(start_idx, end_idx, num=clip_len)
... indices = np.clip(indices, start_idx, end_idx - 1).astype(np.int64)
... return indices
>>> # video clip consists of 300 frames (10 seconds at 30 FPS)
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(
... repo_id="nielsr/video-demo", filename="eating_spaghetti.mp4", repo_type="dataset"
... )
>>> container = av.open(file_path)
>>> # sample 8 frames
>>> indices = sample_frame_indices(clip_len=8, frame_sample_rate=1, seg_len=container.streams.video[0].frames)
>>> video = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = processor(videos=list(video), return_tensors="pt")
>>> video_features = model.get_video_features(**inputs)XCLIPTextModel
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, hidden_size)) — 序列的第一个标记(分类标记)在经过用于辅助预训练任务的层进一步处理后的最后一层隐藏状态。例如,对于BERT系列模型,这返回经过线性层和tanh激活函数处理后的分类标记。线性层的权重是在预训练期间通过下一句预测(分类)目标训练的。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力softmax后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
XCLIPTextModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, XCLIPTextModel
>>> model = XCLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled (EOS token) statesXCLIPVisionModel
前进
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — 像素值。默认情况下,如果您提供了填充,它将被忽略。像素值可以使用 AutoImageProcessor获取。详情请参见CLIPImageProcessor.call(). - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaultsFalse) — 是否插值预训练的位置编码. - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, hidden_size)) — 序列的第一个标记(分类标记)在经过用于辅助预训练任务的层进一步处理后的最后一层隐藏状态。例如,对于BERT系列模型,这返回经过线性层和tanh激活函数处理后的分类标记。线性层的权重是在预训练期间通过下一个句子预测(分类)目标训练的。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力softmax之后,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
XCLIPVisionModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import av
>>> import torch
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, XCLIPVisionModel
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>> def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
... '''
... Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
... Args:
... container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
... indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
... Returns:
... result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
... '''
... frames = []
... container.seek(0)
... start_index = indices[0]
... end_index = indices[-1]
... for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
... if i > end_index:
... break
... if i >= start_index and i in indices:
... frames.append(frame)
... return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
>>> def sample_frame_indices(clip_len, frame_sample_rate, seg_len):
... '''
... Sample a given number of frame indices from the video.
... Args:
... clip_len (`int`): Total number of frames to sample.
... frame_sample_rate (`int`): Sample every n-th frame.
... seg_len (`int`): Maximum allowed index of sample's last frame.
... Returns:
... indices (`List[int]`): List of sampled frame indices
... '''
... converted_len = int(clip_len * frame_sample_rate)
... end_idx = np.random.randint(converted_len, seg_len)
... start_idx = end_idx - converted_len
... indices = np.linspace(start_idx, end_idx, num=clip_len)
... indices = np.clip(indices, start_idx, end_idx - 1).astype(np.int64)
... return indices
>>> # video clip consists of 300 frames (10 seconds at 30 FPS)
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(
... repo_id="nielsr/video-demo", filename="eating_spaghetti.mp4", repo_type="dataset"
... )
>>> container = av.open(file_path)
>>> # sample 16 frames
>>> indices = sample_frame_indices(clip_len=8, frame_sample_rate=1, seg_len=container.streams.video[0].frames)
>>> video = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> model = XCLIPVisionModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
>>> pixel_values = processor(videos=list(video), return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width = pixel_values.shape
>>> pixel_values = pixel_values.reshape(-1, num_channels, height, width)
>>> outputs = model(pixel_values)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state