GPT Neo
概述
GPTNeo模型由Sid Black、Stella Biderman、Leo Gao、Phil Wang和Connor Leahy在EleutherAI/gpt-neo仓库中发布。它是一个类似于GPT2的因果语言模型,基于Pile数据集进行训练。
该架构与GPT2类似,不同之处在于GPT Neo在每隔一层中使用局部注意力,窗口大小为256个标记。
该模型由valhalla贡献。
使用示例
generate() 方法可用于使用 GPT Neo 模型生成文本。
>>> from transformers import GPTNeoForCausalLM, GPT2Tokenizer
>>> model = GPTNeoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> prompt = (
... "In a shocking finding, scientists discovered a herd of unicorns living in a remote, "
... "previously unexplored valley, in the Andes Mountains. Even more surprising to the "
... "researchers was the fact that the unicorns spoke perfect English."
... )
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
>>> gen_tokens = model.generate(
... input_ids,
... do_sample=True,
... temperature=0.9,
... max_length=100,
... )
>>> gen_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(gen_tokens)[0]结合 GPT-Neo 和 Flash Attention 2
首先,确保安装最新版本的 Flash Attention 2 以包含滑动窗口注意力功能,并确保您的硬件与 Flash-Attention 2 兼容。有关安装的更多详细信息,请参阅此处。
确保以半精度加载模型(例如 torch.float16)。
要使用Flash Attention 2加载并运行模型,请参考以下代码片段:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> device = "cuda" # the device to load the model onto
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-2.7B", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-2.7B")
>>> prompt = "def hello_world():"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to(device)
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
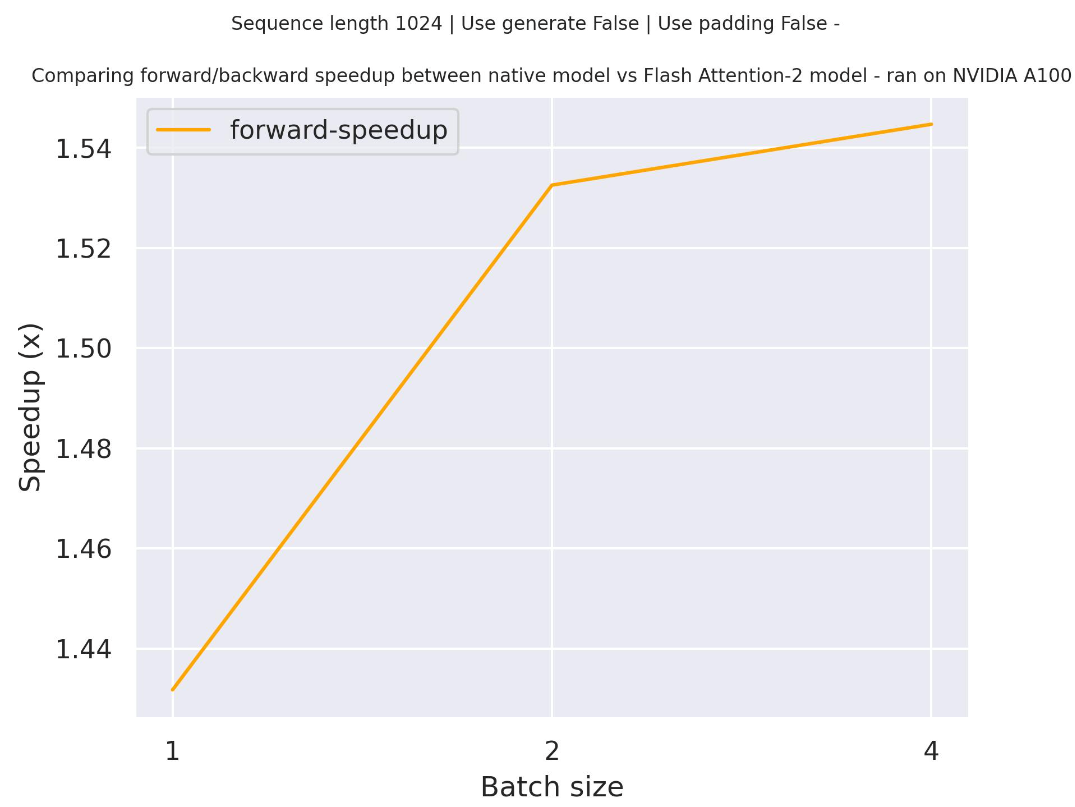
"def hello_world():\n >>> run_script("hello.py")\n >>> exit(0)\n<|endoftext|>"预期的加速
下面是一个预期的加速图,比较了使用EleutherAI/gpt-neo-2.7B检查点的transformers原生实现与Flash Attention 2版本模型的纯推理时间。
请注意,对于GPT-Neo来说,无法在非常长的上下文中进行训练/运行,因为最大位置嵌入限制为2048 - 但这适用于所有gpt-neo模型,并非特定于FA-2。
资源
GPTNeoConfig
类 transformers.GPTNeoConfig
< source >( vocab_size = 50257 max_position_embeddings = 2048 hidden_size = 2048 num_layers = 24 attention_types = [[['global', 'local'], 12]] num_heads = 16 intermediate_size = None window_size = 256 activation_function = 'gelu_new' resid_dropout = 0.0 embed_dropout = 0.0 attention_dropout = 0.0 classifier_dropout = 0.1 layer_norm_epsilon = 1e-05 initializer_range = 0.02 use_cache = True bos_token_id = 50256 eos_token_id = 50256 **kwargs )
参数
- vocab_size (
int, optional, 默认为 50257) — GPT Neo 模型的词汇量大小。定义了调用 GPTNeoModel 时传递的inputs_ids可以表示的不同标记的数量。模型的词汇量大小。定义了传递给 GPTNeoModel 的 inputs_ids 可以表示的不同标记的数量。 - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, 默认为 2048) — 此模型可能使用的最大序列长度。通常将其设置为较大的值以防万一(例如,512 或 1024 或 2048)。 - hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — 编码器层和池化层的维度。 - num_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 24) — Transformer编码器中的隐藏层数。 - attention_types (
List, 可选, 默认为[[['global', 'local'], 12]]) — 每一层的注意力类型,格式为List,格式如下[[["attention_type"], num_layerss]]例如,对于一个24层的模型[[["global"], 24]]或[[["global", "local"], 12]]从["global", "local"]中选择attention_type的值 - num_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 8192) — Transformer编码器中“中间”(即前馈)层的维度。 - window_size (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — 局部注意力的滑动窗口大小。 - activation_function (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"gelu_new") — 编码器和池化器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。如果是字符串,支持"gelu"、"relu"、"selu"和"gelu_new"。 - resid_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 用于注意力模式中的残差丢弃率。 - embed_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 嵌入层、编码器和池化器中所有全连接层的dropout概率。 - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比率。 - classifier_dropout (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.1) — 用于进行标记分类时的参数,在模型 GPTNeoForTokenClassification 中使用。隐藏层的丢弃比例。 - layer_norm_epsilon (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — 层归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - initializer_range (
float, optional, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的 truncated_normal_initializer 的标准差。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 模型是否应返回最后的键/值注意力(并非所有模型都使用)。仅在config.is_decoder=True时相关。 - bos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 50256) — 词汇表中句子开始标记的id. - eos_token_id (
int, 可选, 默认为 50256) — 词汇表中句子结束标记的id.
这是用于存储GPTNeoModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化GPT Neo模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生与GPTNeo EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B架构类似的配置。
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
示例:
>>> from transformers import GPTNeoConfig, GPTNeoModel
>>> # Initializing a GPTNeo EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B style configuration
>>> configuration = GPTNeoConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B style configuration
>>> model = GPTNeoModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configGPTNeoModel
类 transformers.GPTNeoModel
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
裸的GPT Neo模型变压器输出原始隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None cache_position: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.如果使用了
past_key_values,则只应将未计算其过去的input_ids作为input_ids传递。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- token_type_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的inputs_embeds(参见past_key_values)。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 表示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids相反, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。如果使用了
past_key_values,则只输出形状为(batch_size, 1, hidden_size)的序列的最后一个隐藏状态。 -
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), 可选, 当传递了use_cache=True或当config.use_cache=True时返回) — 长度为config.n_layers的tuple(torch.FloatTensor)元组,每个元组包含 2 个形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)的张量,并且如果config.is_encoder_decoder=True,则还包含 2 个形状为(batch_size, num_heads, encoder_sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)的额外张量。包含预先计算的隐藏状态(自注意力块中的键和值,并且如果
config.is_encoder_decoder=True,则还包含交叉注意力块中的键和值),可以用于(参见past_key_values输入)加速顺序解码。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
-
cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True和config.add_cross_attention=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。解码器的交叉注意力层的注意力权重,在注意力 softmax 后,用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
GPTNeoModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTNeoModel
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = GPTNeoModel.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_stateGPTNeoForCausalLM
类 transformers.GPTNeoForCausalLM
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
GPT Neo 模型变压器,顶部带有语言建模头(线性层,权重与输入嵌入绑定)。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None cache_position: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.如果使用了
past_key_values,则只应将未计算其过去的input_ids作为input_ids传递。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- token_type_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的inputs_embeds(参见past_key_values)。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 表示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids相反, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — 用于语言建模的标签。请注意,标签在模型内部被移位,即你可以设置labels = input_ids索引在[-100, 0, ..., config.vocab_size]中选择。所有设置为-100的标签 将被忽略(掩码),损失仅针对[0, ..., config.vocab_size]中的标签计算
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 语言建模损失(用于下一个词的预测)。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax 之前的每个词汇标记的分数)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
-
cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的交叉注意力权重,用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
-
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)),可选,当传递use_cache=True或当config.use_cache=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor元组组成的元组,长度为config.n_layers,每个元组包含自注意力和交叉注意力层的缓存键, 值状态,如果模型用于编码器-解码器设置。仅在config.is_decoder = True时相关。包含预计算的隐藏状态(注意力块中的键和值),可用于(参见
past_key_values输入)以加速顺序解码。
GPTNeoForCausalLM 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTNeoForCausalLM
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = GPTNeoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, labels=inputs["input_ids"])
>>> loss = outputs.loss
>>> logits = outputs.logitsGPTNeoForQuestionAnswering
类 transformers.GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
GPT-Neo模型转换器,顶部带有用于抽取式问答任务的跨度分类头,例如SQuAD(在隐藏状态输出顶部添加一个线性层来计算span start logits和span end logits)。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None start_positions: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None end_positions: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.QuestionAnsweringModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.如果使用了
past_key_values,则只应将未计算其过去的input_ids作为input_ids传递。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- token_type_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的inputs_embeds(参见past_key_values)。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 表示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids相反, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - start_positions (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算标记分类损失的标记跨度起始位置(索引)的标签。 位置被限制在序列长度内(sequence_length)。序列之外的位置不会被考虑用于计算损失。 - end_positions (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算标记分类损失的标记跨度结束位置(索引)的标签。 位置被限制在序列长度内(sequence_length)。序列之外的位置不会被考虑用于计算损失。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.QuestionAnsweringModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.QuestionAnsweringModelOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,), 可选, 当提供labels时返回) — 总跨度提取损失是起始和结束位置的交叉熵之和。 -
start_logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)) — 跨度起始分数(在 SoftMax 之前)。 -
end_logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)) — 跨度结束分数(在 SoftMax 之前)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
此示例使用随机模型,因为真实模型都非常大。为了获得正确的结果,您应该使用
EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B 而不是 EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B。如果在加载该检查点时出现内存不足的情况,您可以尝试
在 from_pretrained 调用中添加 device_map="auto"。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> question, text = "Who was Jim Henson?", "Jim Henson was a nice puppet"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(question, text, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> answer_start_index = outputs.start_logits.argmax()
>>> answer_end_index = outputs.end_logits.argmax()
>>> predict_answer_tokens = inputs.input_ids[0, answer_start_index : answer_end_index + 1]
>>> # target is "nice puppet"
>>> target_start_index = torch.tensor([14])
>>> target_end_index = torch.tensor([15])
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, start_positions=target_start_index, end_positions=target_end_index)
>>> loss = outputs.lossGPTNeoForSequenceClassification
类 transformers.GPTNeoForSequenceClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
GPTNeo模型转换器,顶部带有序列分类头(线性层)。
GPTNeoForSequenceClassification 使用最后一个标记进行分类,就像其他因果模型(例如 GPT-1)所做的那样。
由于它对最后一个标记进行分类,因此需要知道最后一个标记的位置。如果在配置中定义了pad_token_id,它会在每一行中找到不是填充标记的最后一个标记。如果没有定义pad_token_id,它只需取批次中每一行的最后一个值。由于在传递inputs_embeds而不是input_ids时无法猜测填充标记,它会执行相同的操作(取批次中每一行的最后一个值)。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.SequenceClassifierOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.如果使用了
past_key_values,则只应将未计算其过去的input_ids作为input_ids传递。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- token_type_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的inputs_embeds(参见past_key_values)。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 表示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids相反, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor形状为(batch_size,), 可选) — 用于计算序列分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.SequenceClassifierOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.SequenceClassifierOutputWithPast 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)损失。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — 分类(或回归,如果 config.num_labels==1)得分(在 SoftMax 之前)。 -
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)),可选,当传递use_cache=True或当config.use_cache=True时返回) — 长度为config.n_layers的tuple(torch.FloatTensor)元组,每个元组包含 2 个形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)的张量)包含预先计算的隐藏状态(自注意力块中的键和值),可用于(参见
past_key_values输入)加速顺序解码。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) —torch.FloatTensor元组(每层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
GPTNeoForSequenceClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
单标签分类示例:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTNeoForSequenceClassification
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = GPTNeoForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> predicted_class_id = logits.argmax().item()
>>> # To train a model on `num_labels` classes, you can pass `num_labels=num_labels` to `.from_pretrained(...)`
>>> num_labels = len(model.config.id2label)
>>> model = GPTNeoForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B", num_labels=num_labels)
>>> labels = torch.tensor([1])
>>> loss = model(**inputs, labels=labels).loss多标签分类示例:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTNeoForSequenceClassification
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = GPTNeoForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B", problem_type="multi_label_classification")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> predicted_class_ids = torch.arange(0, logits.shape[-1])[torch.sigmoid(logits).squeeze(dim=0) > 0.5]
>>> # To train a model on `num_labels` classes, you can pass `num_labels=num_labels` to `.from_pretrained(...)`
>>> num_labels = len(model.config.id2label)
>>> model = GPTNeoForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
... "EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B", num_labels=num_labels, problem_type="multi_label_classification"
... )
>>> labels = torch.sum(
... torch.nn.functional.one_hot(predicted_class_ids[None, :].clone(), num_classes=num_labels), dim=1
... ).to(torch.float)
>>> loss = model(**inputs, labels=labels).lossGPTNeoForTokenClassification
类 transformers.GPTNeoForTokenClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
GPT Neo模型,顶部带有标记分类头(在隐藏状态输出之上的线性层),例如用于命名实体识别(NER)任务。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.Tuple[typing.Tuple[torch.Tensor]], NoneType] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.TokenClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.如果使用了
past_key_values,则只应将未计算其过去的input_ids作为input_ids传递。可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- token_type_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(num_heads,)或(num_layers, num_heads), 可选) — 用于屏蔽自注意力模块中选定的头部的掩码。掩码值在[0, 1]中选择:- 1 表示头部 未被屏蔽,
- 0 表示头部 被屏蔽.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的inputs_embeds(参见past_key_values)。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 表示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids不同, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length), 可选) — 用于计算序列分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.TokenClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.TokenClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,), 可选, 当提供labels时返回) — 分类损失。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.num_labels)) — 分类分数(在 SoftMax 之前)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), 可选, 当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
GPTNeoForTokenClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTNeoForTokenClassification
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125m")
>>> model = GPTNeoForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125m")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(
... "HuggingFace is a company based in Paris and New York", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt"
... )
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> predicted_token_class_ids = logits.argmax(-1)
>>> # Note that tokens are classified rather then input words which means that
>>> # there might be more predicted token classes than words.
>>> # Multiple token classes might account for the same word
>>> predicted_tokens_classes = [model.config.id2label[t.item()] for t in predicted_token_class_ids[0]]
>>> labels = predicted_token_class_ids
>>> loss = model(**inputs, labels=labels).loss
>>> round(loss.item(), 2)
0.25FlaxGPTNeoModel
类 transformers.FlaxGPTNeoModel
< source >( config: GPTNeoConfig input_shape: typing.Tuple = (1, 1) seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype =
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).这可以用于在GPU或TPU上启用混合精度训练或半精度推理。如果指定,所有计算将使用给定的
dtype执行。请注意,这仅指定了计算的数据类型,并不影响模型参数的数据类型。
裸的GPTNeo模型变压器输出原始隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。
该模型继承自FlaxPreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头等)。
该模型也是一个Flax Linen flax.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的Flax模块使用,并参考Flax文档以获取与一般用法和行为相关的所有信息。
最后,该模型支持JAX的固有特性,例如:
__call__
< source >( input_ids attention_mask = None position_ids = None params: dict = None past_key_values: dict = None dropout_rng: tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_length. Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
numpy.ndarray形状为(batch_size, sequence_length), 可选) — 每个输入序列标记在位置嵌入中的位置索引。选择范围在[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]. - past_key_values (
Dict[str, np.ndarray], 可选, 由init_cache返回或传递先前的past_key_values) — 预计算的隐藏状态字典(注意力块中的键和值),可用于快速自回归解码。预计算的键和值隐藏状态的形状为 [batch_size, max_length]. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutput 或一个包含各种元素的 torch.FloatTensor 元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarray形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)的jnp.ndarray元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,一个用于每一层的输出)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)的jnp.ndarray元组(每一层一个)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
FlaxGPTNeoPreTrainedModel 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, FlaxGPTNeoModel
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = FlaxGPTNeoModel.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="jax")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_stateFlaxGPTNeoForCausalLM
类 transformers.FlaxGPTNeoForCausalLM
< source >( config: GPTNeoConfig input_shape: typing.Tuple = (1, 1) seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype =
参数
- config (GPTNeoConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,仅加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).这可以用于在GPU或TPU上启用混合精度训练或半精度推理。如果指定,所有计算将使用给定的
dtype执行。请注意,这仅指定了计算的数据类型,并不影响模型参数的数据类型。
GPTNeo 模型变换器,顶部带有语言建模头(线性层,权重与输入嵌入绑定)。
该模型继承自FlaxPreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头等)。
该模型也是一个Flax Linen flax.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的Flax模块使用,并参考Flax文档以获取与一般用法和行为相关的所有信息。
最后,该模型支持JAX的固有特性,例如:
__call__
< source >( input_ids attention_mask = None position_ids = None params: dict = None past_key_values: dict = None dropout_rng: tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_length. Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — 每个输入序列标记在位置嵌入中的位置索引。选择范围在[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]之间。 - past_key_values (
Dict[str, np.ndarray], 可选, 由init_cache返回或传递先前的past_key_values) — 预计算的隐藏状态字典(注意力块中的键和值),可用于快速自回归解码。预计算的键和值隐藏状态的形状为 [batch_size, max_length]. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(GPTNeoConfig)和输入。
-
logits (
jnp.ndarray形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax 之前每个词汇标记的分数)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
FlaxGPTNeoPreTrainedModel 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, FlaxGPTNeoForCausalLM
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> model = FlaxGPTNeoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="np")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # retrieve logts for next token
>>> next_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1]