Mistral
概述
Mistral 是由 Albert Jiang、Alexandre Sablayrolles、Arthur Mensch、Chris Bamford、Devendra Singh Chaplot、Diego de las Casas、Florian Bressand、Gianna Lengyel、Guillaume Lample、Lélio Renard Lavaud、Lucile Saulnier、Marie-Anne Lachaux、Pierre Stock、Teven Le Scao、Thibaut Lavril、Thomas Wang、Timothée Lacroix、William El Sayed 在 这篇博客文章 中介绍的。
博客文章的引言说:
Mistral AI 团队自豪地发布了 Mistral 7B,这是迄今为止其规模最强大的语言模型。
Mistral-7B 是由 mistral.ai 发布的第一个大型语言模型(LLM)。
架构细节
Mistral-7B 是一个仅解码器的 Transformer,具有以下架构选择:
- 滑动窗口注意力 - 使用8k上下文长度和固定缓存大小进行训练,理论注意力跨度为128K个标记
- GQA(分组查询注意力) - 允许更快的推理和更低的缓存大小。
- 字节回退BPE分词器 - 确保字符永远不会映射到词汇表外的标记。
更多详情请参阅发布博客文章。
许可证
Mistral-7B 是根据 Apache 2.0 许可证发布的。
使用提示
Mistral 团队已经发布了 3 个检查点:
- 一个基础模型,Mistral-7B-v0.1,它已经经过预训练,用于预测互联网规模数据中的下一个标记。
- 一个经过指令调优的模型,Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1,这是通过监督微调(SFT)和直接偏好优化(DPO)优化的基础模型,专为聊天目的而设计。
- 一个改进的指令调优模型,Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2,它在v1的基础上有所改进。
基础模型可以如下使用:
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"My favourite condiment is to ..."调整后的指令模型可以如下使用:
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2")
>>> messages = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "What is your favourite condiment?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "Well, I'm quite partial to a good squeeze of fresh lemon juice. It adds just the right amount of zesty flavour to whatever I'm cooking up in the kitchen!"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "Do you have mayonnaise recipes?"}
... ]
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"Mayonnaise can be made as follows: (...)"可以看出,指令调优模型需要应用聊天模板,以确保输入以正确的格式准备。
通过使用Flash Attention加速Mistral
上面的代码片段展示了没有任何优化技巧的推理。然而,通过利用Flash Attention,可以显著加快模型的速度,这是模型中使用的注意力机制的更快实现。
首先,确保安装最新版本的 Flash Attention 2 以包含滑动窗口注意力功能。
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
请确保您拥有与Flash-Attention 2兼容的硬件。更多信息请参阅flash attention repository的官方文档。同时,请确保以半精度(例如torch.float16)加载您的模型。
要使用Flash Attention-2加载并运行模型,请参考以下代码片段:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"My favourite condiment is to (...)"预期的加速
下面是一个预期的加速图,比较了使用mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1检查点的transformers原生实现与Flash Attention 2版本模型的纯推理时间。
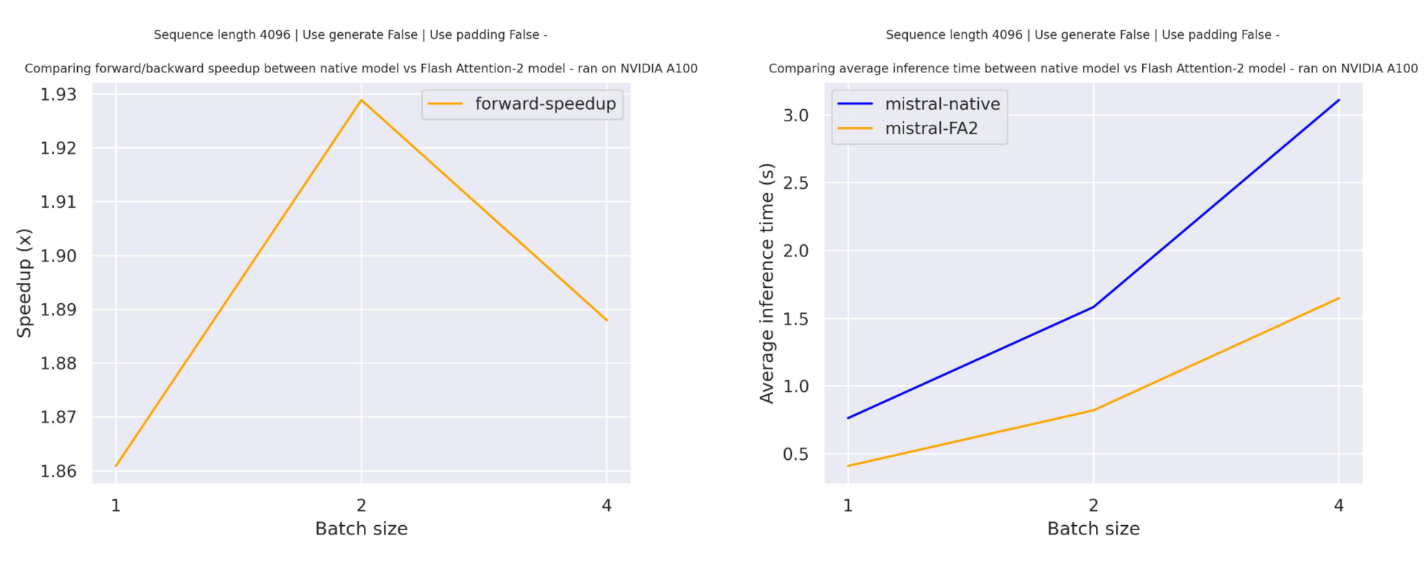
滑动窗口注意力
当前实现支持滑动窗口注意力机制和内存高效的缓存管理。
要启用滑动窗口注意力,只需确保拥有与滑动窗口注意力兼容的flash-attn版本(>=2.3.0)。
Flash Attention-2 模型还使用了更高效的内存缓存切片机制——正如 Mistral 模型的官方实现所建议的那样,我们使用滚动缓存机制保持缓存大小固定(self.config.sliding_window),仅支持 padding_side="left" 的批量生成,并使用当前 token 的绝对位置来计算位置嵌入。
使用量化缩小Mistral
由于Mistral模型有70亿个参数,这将需要大约14GB的GPU内存(半精度,float16),因为每个参数存储在2个字节中。然而,可以使用量化来缩小模型的大小。如果模型被量化为4位(或每个参数半字节),则仅需要大约3.5GB的内存。
量化模型就像将quantization_config传递给模型一样简单。下面,我们将利用BitsAndyBytes量化(但请参考此页面了解其他量化方法):
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
>>> # specify how to quantize the model
>>> quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
... load_in_4bit=True,
... bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
... bnb_4bit_compute_dtype="torch.float16",
... )
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", quantization_config=True, device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> messages = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "What is your favourite condiment?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "Well, I'm quite partial to a good squeeze of fresh lemon juice. It adds just the right amount of zesty flavour to whatever I'm cooking up in the kitchen!"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "Do you have mayonnaise recipes?"}
... ]
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"The expected output"该模型由Younes Belkada和Arthur Zucker贡献。 原始代码可以在这里找到。
资源
一份由Hugging Face官方和社区(由🌎表示)提供的资源列表,帮助您开始使用Mistral。如果您有兴趣提交资源以包含在此处,请随时打开一个Pull Request,我们将进行审核!理想情况下,资源应展示一些新内容,而不是重复现有资源。
- 一个用于执行Mistral-7B监督微调(SFT)的演示笔记本可以在这里找到。🌎
- 一篇关于如何在2024年使用Hugging Face工具微调LLMs的博客文章。🌎
- Hugging Face 的 Alignment Handbook 包含了使用 Mistral-7B 进行监督微调(SFT)和直接偏好优化的脚本和配方。这包括用于全微调、单 GPU 上的 QLoRa 以及多 GPU 微调的脚本。
- 因果语言建模任务指南
MistralConfig
类 transformers.MistralConfig
< source >( vocab_size = 32000 hidden_size = 4096 intermediate_size = 14336 num_hidden_layers = 32 num_attention_heads = 32 num_key_value_heads = 8 head_dim = None hidden_act = 'silu' max_position_embeddings = 131072 initializer_range = 0.02 rms_norm_eps = 1e-06 use_cache = True pad_token_id = None bos_token_id = 1 eos_token_id = 2 tie_word_embeddings = False rope_theta = 10000.0 sliding_window = 4096 attention_dropout = 0.0 **kwargs )
参数
- vocab_size (
int, 可选, 默认为 32000) — Mistral 模型的词汇量大小。定义了调用 MistralModel 时传递的inputs_ids可以表示的不同标记的数量 - hidden_size (
int, optional, 默认为 4096) — 隐藏表示的维度。 - intermediate_size (
int, optional, 默认为 14336) — MLP 表示的维度。 - num_hidden_layers (
int, 可选, 默认为 32) — Transformer 编码器中的隐藏层数量。 - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — Transformer编码器中每个注意力层的注意力头数量。 - num_key_value_heads (
int, 可选, 默认为 8) — 这是用于实现分组查询注意力(Grouped Query Attention)的键值头数量。如果num_key_value_heads=num_attention_heads,模型将使用多头注意力(MHA),如果num_key_value_heads=1,模型将使用多查询注意力(MQA),否则将使用GQA。当 将多头检查点转换为GQA检查点时,每个组的键和值头应通过对该组内所有原始头进行平均池化来构建。更多详细信息请查看这篇 论文。如果未指定,将默认为8. - head_dim (
int, 可选, 默认为hidden_size // num_attention_heads) — 注意力头的维度. - hidden_act (
str或function, 可选, 默认为"silu") — 解码器中的非线性激活函数(函数或字符串)。 - max_position_embeddings (
int, 可选, 默认为4096*32) — 该模型可能使用的最大序列长度。Mistral的滑动窗口注意力机制允许最多4096*32个标记的序列。 - initializer_range (
float, 可选, 默认为 0.02) — 用于初始化所有权重矩阵的截断正态初始化器的标准差。 - rms_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-06) — rms归一化层使用的epsilon值。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选, 默认为True) — 模型是否应返回最后的键/值注意力(并非所有模型都使用)。仅在config.is_decoder=True时相关。 - pad_token_id (
int, optional) — 填充令牌的ID。 - bos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — “序列开始”标记的ID。 - eos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 2) — “序列结束”标记的ID。 - tie_word_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — 是否应该将模型的输入和输出词嵌入绑定在一起。 - rope_theta (
float, optional, 默认为 10000.0) — RoPE 嵌入的基础周期。 - sliding_window (
int, 可选, 默认为 4096) — 滑动窗口注意力窗口大小。如果未指定,将默认为4096. - attention_dropout (
float, optional, 默认为 0.0) — 注意力概率的丢弃比率。
这是用于存储MistralModel配置的配置类。它用于根据指定的参数实例化Mistral模型,定义模型架构。使用默认值实例化配置将产生类似于Mistral-7B-v0.1或Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1的配置。
mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1 mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1
配置对象继承自PretrainedConfig,可用于控制模型输出。阅读PretrainedConfig的文档以获取更多信息。
>>> from transformers import MistralModel, MistralConfig
>>> # Initializing a Mistral 7B style configuration
>>> configuration = MistralConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model from the Mistral 7B style configuration
>>> model = MistralModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configMistralModel
类 transformers.MistralModel
< source >( config: MistralConfig )
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 模型配置类,包含模型的所有参数。使用配置文件初始化时不会加载与模型相关的权重,仅加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
- config — MistralConfig
裸的Mistral模型输出原始的隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。 该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
Transformer解码器由config.num_hidden_layers层组成。每一层都是一个MistralDecoderLayer
前进
< source >( input_ids: LongTensor = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.List[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None cache_position: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None )
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 指示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids不同, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。
MistralModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
MistralForCausalLM
前进
< source >( input_ids: LongTensor = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.List[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None cache_position: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None num_logits_to_keep: int = 0 ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), 可选) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个ModelOutput而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 指示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids不同, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - Args —
labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional): Labels for computing the masked language modeling loss. Indices should either be in[0, ..., config.vocab_size]or -100 (seeinput_idsdocstring). Tokens with indices set to-100are ignored (masked), the loss is only computed for the tokens with labels in[0, ..., config.vocab_size].num_logits_to_keep (
int, 可选): 计算最后num_logits_to_keep个token的logits。如果为0,则计算所有input_ids的logits(特殊情况)。生成时只需要最后一个token的logits,仅计算该token的logits可以节省内存,这对于长序列或大词汇量来说非常重要。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithPast 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(MistralConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 语言建模损失(用于下一个标记预测)。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax 之前每个词汇标记的分数)。 -
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)),可选,当传递use_cache=True或当config.use_cache=True时返回) — 长度为config.n_layers的tuple(torch.FloatTensor)元组,每个元组包含 2 个形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)的张量包含预先计算的隐藏状态(自注意力块中的键和值),可用于(参见
past_key_values输入)加速顺序解码。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
MistralForCausalLM 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, MistralForCausalLM
>>> model = MistralForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "Hey, are you conscious? Can you talk to me?"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> # Generate
>>> generate_ids = model.generate(inputs.input_ids, max_length=30)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
"Hey, are you conscious? Can you talk to me?\nI'm not conscious, but I can talk to you."MistralForSequenceClassification
类 transformers.MistralForSequenceClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 模型配置类,包含模型的所有参数。使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Mistral 模型转换器,顶部带有序列分类头(线性层)。
MistralForSequenceClassification 使用最后一个标记进行分类,就像其他因果模型(例如 GPT-2)所做的那样。
由于它对最后一个标记进行分类,因此需要知道最后一个标记的位置。如果在配置中定义了pad_token_id,它会在每一行中找到不是填充标记的最后一个标记。如果没有定义pad_token_id,它只需取批次中每一行的最后一个值。由于在传递inputs_embeds而不是input_ids时无法猜测填充标记,它会执行相同的操作(取批次中每一行的最后一个值)。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.List[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None )
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制权,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 指示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids不同, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor形状为(batch_size,), 可选) — 用于计算序列分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
MistralForSequenceClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
MistralForTokenClassification
类 transformers.MistralForTokenClassification
< source >( config )
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 模型配置类,包含模型的所有参数。使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Mistral模型转换器,顶部带有标记分类头(在隐藏状态输出之上的线性层),例如用于命名实体识别(NER)任务。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.List[torch.FloatTensor]] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.TokenClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 指示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids不同, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - labels (
torch.LongTensor形状为(batch_size,), 可选) — 用于计算序列分类/回归损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]范围内。如果config.num_labels == 1,则计算回归损失(均方损失),如果config.num_labels > 1,则计算分类损失(交叉熵)。
返回
transformers.modeling_outputs.TokenClassifierOutput 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_outputs.TokenClassifierOutput 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(MistralConfig)和输入。
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(1,),可选,当提供labels时返回) — 分类损失。 -
logits (
torch.FloatTensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.num_labels)) — 分类分数(在 SoftMax 之前)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,如果模型有嵌入层,+ 一个用于每一层的输出)形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上可选的初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor),可选,当传递output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由torch.FloatTensor组成的元组(每一层一个)形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
MistralForTokenClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, MistralForTokenClassification
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> model = MistralForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(
... "HuggingFace is a company based in Paris and New York", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt"
... )
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> predicted_token_class_ids = logits.argmax(-1)
>>> # Note that tokens are classified rather then input words which means that
>>> # there might be more predicted token classes than words.
>>> # Multiple token classes might account for the same word
>>> predicted_tokens_classes = [model.config.id2label[t.item()] for t in predicted_token_class_ids[0]]
>>> labels = predicted_token_class_ids
>>> loss = model(**inputs, labels=labels).lossMistralForQuestionAnswering
类 transformers.MistralForQuestionAnswering
< source >( config )
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 模型配置类,包含模型的所有参数。使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,仅加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Mistral模型转换器,顶部带有跨度分类头,用于抽取式问答任务,如SQuAD(在隐藏状态输出顶部有一个线性层,用于计算span start logits和span end logits)。
该模型继承自PreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个PyTorch torch.nn.Module 子类。 将其作为常规的PyTorch模块使用,并参考PyTorch文档以获取与一般使用和行为相关的所有信息。
前进
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Union[transformers.cache_utils.Cache, typing.List[torch.FloatTensor], NoneType] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None start_positions: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None end_positions: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None **kwargs )
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,可以选择只输入最后的input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许两种格式:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — 指示输入序列标记在序列中的位置的索引。与position_ids不同, 这个张量不受填充的影响。它用于在正确的位置更新缓存并推断 完整的序列长度。 - start_positions (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算标记分类损失的标记跨度起始位置(索引)的标签。 位置被限制在序列长度内(sequence_length)。序列之外的位置不会用于计算损失。 - end_positions (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — 用于计算标记分类损失的标记跨度结束位置(索引)的标签。 位置被限制在序列长度内(sequence_length)。序列之外的位置不会被考虑用于计算损失。
MistralForQuestionAnswering 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
- 前进
FlaxMistralModel
类 transformers.FlaxMistralModel
< source >( config: MistralConfig input_shape: typing.Tuple = (1, 1) seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype =
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16, orjax.numpy.bfloat16.这可以用于在GPU或TPU上启用混合精度训练或半精度推理。如果指定,所有计算将使用给定的
dtype执行。请注意,这仅指定了计算的数据类型,并不影响模型参数的数据类型。
裸的Mistral模型变压器输出原始隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。
该模型继承自FlaxPreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头等)。
该模型也是一个Flax Linen flax.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的Flax模块使用,并参考Flax文档以获取与一般用法和行为相关的所有信息。
最后,该模型支持JAX的固有特性,例如:
__call__
< source >( input_ids attention_mask = None position_ids = None params: dict = None past_key_values: dict = None dropout_rng: tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,则可以选择性地仅输入最后一个decoder_input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Dict[str, np.ndarray], 可选, 由init_cache返回或传递先前的past_key_values) — 预计算的隐藏状态字典(注意力块中的键和值),可用于快速自回归解码。预计算的键和值隐藏状态的形状为 [batch_size, max_length]. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组.
返回
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutputWithPast 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutputWithPast 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(MistralConfig)和输入。
-
last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarray形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — 模型最后一层输出的隐藏状态序列。 -
past_key_values (
Dict[str, jnp.ndarray]) — 预先计算的隐藏状态的字典(注意力块中的键和值),可用于快速 自回归解码。预先计算的键和值隐藏状态的形状为 [batch_size, max_length]。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), 可选, 当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(一个用于嵌入层的输出,一个用于每一层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每一层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), 可选, 当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(每一层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力权重在注意力 softmax 之后,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
FlaxMistralPreTrainedModel 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
这个例子使用了一个随机模型,因为真实的模型都非常大。为了获得正确的结果,你应该使用
mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1 而不是 ksmcg/Mistral-tiny。如果在加载该检查点时出现内存不足的情况,你可以尝试
在 from_pretrained 调用中添加 device_map="auto"。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, FlaxMistralModel
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("ksmcg/Mistral-tiny")
>>> model = FlaxMistralModel.from_pretrained("ksmcg/Mistral-tiny")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="jax")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_stateFlaxMistralForCausalLM
类 transformers.FlaxMistralForCausalLM
< source >( config: MistralConfig input_shape: typing.Tuple = (1, 1) seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype =
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16, orjax.numpy.bfloat16.这可以用于在GPU或TPU上启用混合精度训练或半精度推理。如果指定,所有计算将使用给定的
dtype执行。请注意,这仅指定了计算的数据类型,并不影响模型参数的数据类型。
Mistral 模型变压器,顶部带有语言建模头(线性层)。
该模型继承自FlaxPreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头等)。
该模型也是一个Flax Linen flax.nn.Module 子类。将其作为常规的Flax模块使用,并参考Flax文档以获取与一般用法和行为相关的所有信息。
最后,该模型支持JAX的固有特性,例如:
__call__
< source >( input_ids attention_mask = None position_ids = None params: dict = None past_key_values: dict = None dropout_rng: tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
参数
- input_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,则可以选择性地仅输入最后一个decoder_input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
numpy.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Dict[str, np.ndarray], 可选, 由init_cache返回或传递先前的past_key_values) — 预计算的隐藏状态字典(注意力块中的键和值),可用于快速自回归解码。预计算的键和值隐藏状态的形状为 [batch_size, max_length]. - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
返回
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxCausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions 或 tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
一个 transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxCausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions 或一个由
torch.FloatTensor 组成的元组(如果传递了 return_dict=False 或当 config.return_dict=False 时),包含各种
元素,具体取决于配置(MistralConfig)和输入。
-
logits (
jnp.ndarray,形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — 语言建模头的预测分数(SoftMax 之前的每个词汇标记的分数)。 -
hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray),可选,当传递了output_hidden_states=True或当config.output_hidden_states=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(一个用于嵌入的输出 + 一个用于每层的输出),形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)。模型在每层输出处的隐藏状态加上初始嵌入输出。
-
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray),可选,当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。注意力 softmax 后的注意力权重,用于计算自注意力头中的加权平均值。
-
cross_attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray),可选,当传递了output_attentions=True或当config.output_attentions=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray组成的元组(每层一个),形状为(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length)。交叉注意力 softmax 后的交叉注意力权重,用于计算交叉注意力头中的加权平均值。
-
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(jnp.ndarray)),可选,当传递了use_cache=True或当config.use_cache=True时返回) — 由jnp.ndarray元组组成的元组,长度为config.n_layers,每个元组包含自注意力和交叉注意力层的缓存键、值 状态,如果模型用于编码器-解码器设置。 仅在config.is_decoder = True时相关。包含预计算的隐藏状态(注意力块中的键和值),可用于(参见
past_key_values输入)以加速顺序解码。
FlaxMistralPreTrainedModel 的 forward 方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
此示例使用随机模型,因为真实模型都非常大。要获得正确的结果,您应该使用
mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1 而不是 ksmcg/Mistral-tiny。如果在加载该检查点时出现内存不足的情况,您可以尝试
在 from_pretrained 调用中添加 device_map="auto"。
示例:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, FlaxMistralForCausalLM
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("ksmcg/Mistral-tiny")
>>> model = FlaxMistralForCausalLM.from_pretrained("ksmcg/Mistral-tiny")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="np")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # retrieve logts for next token
>>> next_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1]TFMistralModel
class transformers.TFMistralModel
< source >( config: MistralConfig *inputs **kwargs )
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
裸的Mistral模型输出原始隐藏状态,没有任何特定的头部。
该模型继承自 TFPreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个keras.Model子类。可以将其作为常规的TF 2.0 Keras模型使用,并参考TF 2.0文档以了解与一般使用和行为相关的所有事项。
TensorFlow 模型和层在 model 中接受两种格式作为输入:
- 将所有输入作为关键字参数(如PyTorch模型),或
- 将所有输入作为列表、元组或字典放在第一个位置参数中。
支持第二种格式的原因是,Keras 方法在将输入传递给模型和层时更喜欢这种格式。由于这种支持,当使用像 model.fit() 这样的方法时,事情应该“正常工作”——只需以 model.fit() 支持的任何格式传递你的输入和标签!然而,如果你想在 Keras 方法之外使用第二种格式,比如在使用 Keras Functional API 创建自己的层或模型时,有三种方法可以用来将所有输入张量收集到第一个位置参数中:
- 仅包含
input_ids的单个张量,没有其他内容:model(input_ids) - 一个长度不定的列表,包含一个或多个输入张量,按照文档字符串中给出的顺序:
model([input_ids, attention_mask])或model([input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids]) - 一个字典,包含一个或多个与文档字符串中给出的输入名称相关联的输入张量:
model({"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids})
请注意,当使用子类化创建模型和层时,您不需要担心这些,因为您可以像传递任何其他Python函数一样传递输入!
调用
< source >( input_ids: Tensor = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.List[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor]] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None )
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,则可以选择性地仅输入最后一个decoder_input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(tf.Tensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许一种格式:
- Tuple of
tuple(tf.Tensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - Tuple of
- inputs_embeds (
tf.Tensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), 可选) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。
TFMistralModel 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
TFMistralForCausalLM
调用
< source >( input_ids: Tensor = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.List[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor]] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None )
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,则可以选择性地仅输入最后一个decoder_input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(tf.Tensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许一种格式:
- Tuple of
tuple(tf.Tensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - Tuple of
- inputs_embeds (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量中的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - 参数 —
labels (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), 可选): 用于计算掩码语言建模损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.vocab_size]或 -100(参见input_ids文档字符串)。索引设置为-100的标记将被忽略 (掩码),损失仅针对标签在[0, ..., config.vocab_size]中的标记计算。
TFMistralForCausalLM 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。
TFMistralForSequenceClassification
类 transformers.TFMistralForSequenceClassification
< source >( config *inputs **kwargs )
参数
- config (MistralConfig) — 包含模型所有参数的模型配置类。 使用配置文件初始化不会加载与模型相关的权重,只会加载配置。查看 from_pretrained() 方法以加载模型权重。
Mistral 模型转换器,顶部带有序列分类头(线性层)。
MistralForSequenceClassification 使用最后一个标记进行分类,就像其他因果模型(例如 GPT-2)所做的那样。
由于它对最后一个标记进行分类,因此需要知道最后一个标记的位置。如果在配置中定义了pad_token_id,它会在每一行中找到不是填充标记的最后一个标记。如果没有定义pad_token_id,它只需取批次中每一行的最后一个值。由于在传递inputs_embeds而不是input_ids时无法猜测填充标记,它会执行相同的操作(取批次中每一行的最后一个值)。
该模型继承自 TFPreTrainedModel。请查看超类文档以了解库为其所有模型实现的通用方法(如下载或保存、调整输入嵌入的大小、修剪头部等)。
该模型也是一个keras.Model子类。可以将其作为常规的TF 2.0 Keras模型使用,并参考TF 2.0文档以了解与一般使用和行为相关的所有事项。
TensorFlow 模型和层在 model 中接受两种格式作为输入:
- 将所有输入作为关键字参数(如PyTorch模型),或
- 将所有输入作为列表、元组或字典放在第一个位置参数中。
支持第二种格式的原因是,Keras 方法在将输入传递给模型和层时更喜欢这种格式。由于这种支持,当使用像 model.fit() 这样的方法时,事情应该“正常工作”——只需以 model.fit() 支持的任何格式传递你的输入和标签!然而,如果你想在 Keras 方法之外使用第二种格式,比如在使用 Keras Functional API 创建自己的层或模型时,有三种方法可以用来将所有输入张量收集到第一个位置参数中:
- 仅包含
input_ids的单个张量,没有其他内容:model(input_ids) - 一个长度不定的列表,包含一个或多个输入张量,按照文档字符串中给出的顺序:
model([input_ids, attention_mask])或model([input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids]) - 一个字典,包含一个或多个与文档字符串中给出的输入名称相关联的输入张量:
model({"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids})
请注意,当使用子类化创建模型和层时,您不需要担心这些,因为您可以像传递任何其他Python函数一样传递输入!
调用
< source >( input_ids: Tensor = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.List[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor]] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[tensorflow.python.framework.tensor.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None )
参数
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
- attention_mask (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
可以使用AutoTokenizer获取索引。详情请参见PreTrainedTokenizer.encode()和 PreTrainedTokenizer.call()。
如果使用了
past_key_values,则可以选择性地仅输入最后一个decoder_input_ids(参见past_key_values)。如果你想改变填充行为,你应该阅读
modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask并根据你的需求进行修改。有关默认策略的更多信息,请参见论文中的图1。- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
Cacheortuple(tuple(tf.Tensor)), optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.允许一种格式:
- Tuple of
tuple(tf.Tensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
模型将输出与输入相同的缓存格式。如果没有传递
past_key_values,将返回旧的缓存格式。如果使用了
past_key_values,用户可以选择只输入形状为(batch_size, 1)的最后input_ids(那些没有将其过去键值状态提供给此模型的input_ids),而不是形状为(batch_size, sequence_length)的所有input_ids。 - Tuple of
- inputs_embeds (
tf.Tensor形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), 可选) — 可选地,您可以选择直接传递嵌入表示,而不是传递input_ids。如果您希望对如何将input_ids索引转换为相关向量有更多控制权,而不是使用模型的内部嵌入查找矩阵,这将非常有用。 - use_cache (
bool, 可选) — 如果设置为True,past_key_values键值状态将被返回,并可用于加速解码(参见past_key_values)。 - output_attentions (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回所有注意力层的注意力张量。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的attentions。 - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — 是否返回所有层的隐藏状态。有关更多详细信息,请参见返回张量下的hidden_states。 - return_dict (
bool, 可选) — 是否返回一个 ModelOutput 而不是一个普通的元组。 - 参数 —
labels (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), 可选): 用于计算掩码语言建模损失的标签。索引应在[0, ..., config.vocab_size]或 -100 之间(参见input_ids文档字符串)。索引设置为-100的标记将被忽略 (掩码),损失仅针对标签在[0, ..., config.vocab_size]之间的标记计算。
TFMistralForSequenceClassification 的前向方法,重写了 __call__ 特殊方法。
尽管前向传递的配方需要在此函数内定义,但之后应该调用Module实例而不是这个,因为前者负责运行预处理和后处理步骤,而后者会默默地忽略它们。