备注
转到结尾 以下载完整示例代码。或在您的浏览器中通过 Binder 运行此示例。
相位解包裹#
某些信号只能在模 2*pi 的情况下观察到,这同样适用于二维和三维图像。在这些情况下,需要进行相位解缠以恢复底层未解缠的信号。在这个例子中,我们将演示一个在 skimage 中实现的算法 [1] 如何解决此类问题。一维、二维和三维图像都可以使用 skimage 进行解缠。这里我们将演示二维情况下的相位解缠。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skimage import data, img_as_float, color, exposure
from skimage.restoration import unwrap_phase
# Load an image as a floating-point grayscale
image = color.rgb2gray(img_as_float(data.chelsea()))
# Scale the image to [0, 4*pi]
image = exposure.rescale_intensity(image, out_range=(0, 4 * np.pi))
# Create a phase-wrapped image in the interval [-pi, pi)
image_wrapped = np.angle(np.exp(1j * image))
# Perform phase unwrapping
image_unwrapped = unwrap_phase(image_wrapped)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4 = ax.ravel()
fig.colorbar(ax1.imshow(image, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=4 * np.pi), ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title('Original')
fig.colorbar(ax2.imshow(image_wrapped, cmap='gray', vmin=-np.pi, vmax=np.pi), ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title('Wrapped phase')
fig.colorbar(ax3.imshow(image_unwrapped, cmap='gray'), ax=ax3)
ax3.set_title('After phase unwrapping')
fig.colorbar(ax4.imshow(image_unwrapped - image, cmap='gray'), ax=ax4)
ax4.set_title('Unwrapped minus original')
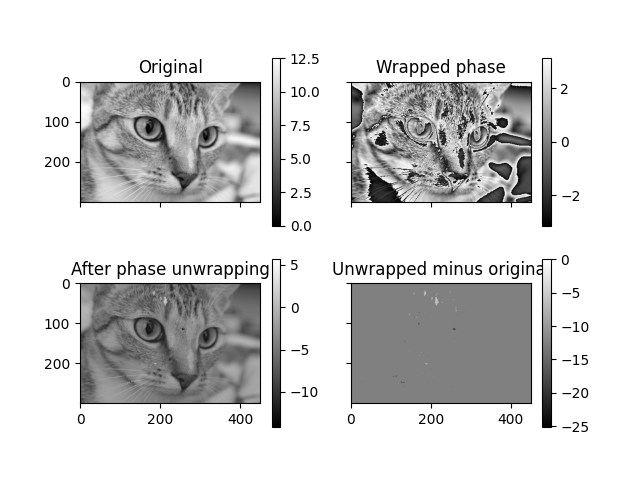
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Unwrapped minus original')
解包过程接受掩码数组,并且可以选择假设循环边界以连接图像的边缘。在下面的示例中,我们研究了一个简单的相位斜坡,该斜坡被掩码图像的一行分割成两部分。
# Create a simple ramp
image = np.ones((100, 100)) * np.linspace(0, 8 * np.pi, 100).reshape((-1, 1))
# Mask the image to split it in two horizontally
mask = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool)
mask[image.shape[0] // 2, :] = True
image_wrapped = np.ma.array(np.angle(np.exp(1j * image)), mask=mask)
# Unwrap image without wrap around
image_unwrapped_no_wrap_around = unwrap_phase(image_wrapped, wrap_around=(False, False))
# Unwrap with wrap around enabled for the 0th dimension
image_unwrapped_wrap_around = unwrap_phase(image_wrapped, wrap_around=(True, False))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2)
ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4 = ax.ravel()
fig.colorbar(ax1.imshow(np.ma.array(image, mask=mask), cmap='rainbow'), ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title('Original')
fig.colorbar(ax2.imshow(image_wrapped, cmap='rainbow', vmin=-np.pi, vmax=np.pi), ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title('Wrapped phase')
fig.colorbar(ax3.imshow(image_unwrapped_no_wrap_around, cmap='rainbow'), ax=ax3)
ax3.set_title('Unwrapped without wrap_around')
fig.colorbar(ax4.imshow(image_unwrapped_wrap_around, cmap='rainbow'), ax=ax4)
ax4.set_title('Unwrapped with wrap_around')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
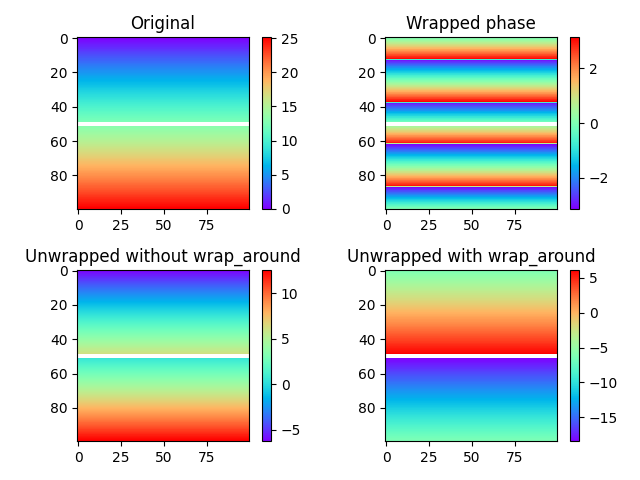
在上面的图中,可以看到被遮罩的行在图像中呈现为一条白线。底部两幅展开图像之间的差异很明显:如果没有展开(左下),被遮罩边界上下的区域完全不相互作用,导致两个区域之间存在一个任意整数倍的两倍的偏移。我们也可以将这些区域作为两幅独立的图像展开。当启用垂直方向的环绕(右下)时,情况发生了变化:展开路径现在允许从图像底部到顶部,反之亦然,实际上提供了一种确定两个区域之间偏移的方法。
参考文献#
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.349 秒)
