备注
转到末尾 下载完整示例代码。或在浏览器中通过 Binder 运行此示例。
使用 RANSAC 进行鲁棒匹配#
在这个简化的示例中,我们首先生成两张合成图像,就好像它们是从不同的视角拍摄的一样。
在下一步中,我们在两幅图像中找到兴趣点,并基于它们周围小邻域的加权平方差和找到对应关系。注意,这种度量仅对线性辐射畸变稳健,而对几何畸变不稳健,因此仅适用于轻微的视点变化。
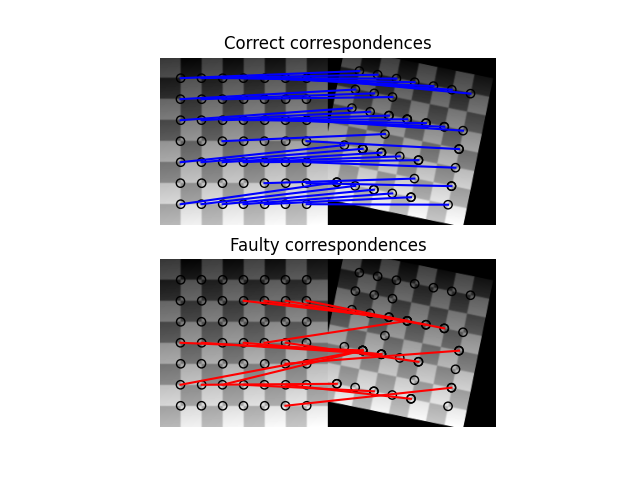
在找到对应关系后,我们最终得到一组源坐标和目标坐标,这些坐标可以用来估计两幅图像之间的几何变换。然而,许多对应关系是错误的,仅使用所有坐标估计参数集是不够的。因此,在正常模型之上使用RANSAC算法,通过检测异常值来稳健地估计参数集。
Ground truth:
Scale: (0.9000, 0.9000), Translation: (-10.0000, 20.0000), Rotation: -0.2000
Affine transform:
Scale: (0.9015, 0.8904), Translation: (-9.3136, 14.9768), Rotation: -0.1678
RANSAC:
Scale: (0.8999, 0.9001), Translation: (-10.0005, 19.9744), Rotation: -0.1999
/Users/cw/baidu/code/fin_tool/github/scikit-image/doc/examples/transform/plot_matching.py:150: FutureWarning:
`plot_matches` is deprecated since version 0.23 and will be removed in version 0.25. Use `skimage.feature.plot_matched_features` instead.
/Users/cw/baidu/code/fin_tool/github/scikit-image/doc/examples/transform/plot_matching.py:163: FutureWarning:
`plot_matches` is deprecated since version 0.23 and will be removed in version 0.25. Use `skimage.feature.plot_matched_features` instead.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage.util import img_as_float
from skimage.feature import corner_harris, corner_subpix, corner_peaks, plot_matches
from skimage.transform import warp, AffineTransform
from skimage.exposure import rescale_intensity
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.measure import ransac
# generate synthetic checkerboard image and add gradient for the later matching
checkerboard = img_as_float(data.checkerboard())
img_orig = np.zeros(list(checkerboard.shape) + [3])
img_orig[..., 0] = checkerboard
gradient_r, gradient_c = np.mgrid[0 : img_orig.shape[0], 0 : img_orig.shape[1]] / float(
img_orig.shape[0]
)
img_orig[..., 1] = gradient_r
img_orig[..., 2] = gradient_c
img_orig = rescale_intensity(img_orig)
img_orig_gray = rgb2gray(img_orig)
# warp synthetic image
tform = AffineTransform(scale=(0.9, 0.9), rotation=0.2, translation=(20, -10))
img_warped = warp(img_orig, tform.inverse, output_shape=(200, 200))
img_warped_gray = rgb2gray(img_warped)
# extract corners using Harris' corner measure
coords_orig = corner_peaks(
corner_harris(img_orig_gray), threshold_rel=0.001, min_distance=5
)
coords_warped = corner_peaks(
corner_harris(img_warped_gray), threshold_rel=0.001, min_distance=5
)
# determine sub-pixel corner position
coords_orig_subpix = corner_subpix(img_orig_gray, coords_orig, window_size=9)
coords_warped_subpix = corner_subpix(img_warped_gray, coords_warped, window_size=9)
def gaussian_weights(window_ext, sigma=1):
y, x = np.mgrid[-window_ext : window_ext + 1, -window_ext : window_ext + 1]
g = np.zeros(y.shape, dtype=np.double)
g[:] = np.exp(-0.5 * (x**2 / sigma**2 + y**2 / sigma**2))
g /= 2 * np.pi * sigma * sigma
return g
def match_corner(coord, window_ext=5):
r, c = np.round(coord).astype(np.intp)
window_orig = img_orig[
r - window_ext : r + window_ext + 1, c - window_ext : c + window_ext + 1, :
]
# weight pixels depending on distance to center pixel
weights = gaussian_weights(window_ext, 3)
weights = np.dstack((weights, weights, weights))
# compute sum of squared differences to all corners in warped image
SSDs = []
for cr, cc in coords_warped:
window_warped = img_warped[
cr - window_ext : cr + window_ext + 1,
cc - window_ext : cc + window_ext + 1,
:,
]
SSD = np.sum(weights * (window_orig - window_warped) ** 2)
SSDs.append(SSD)
# use corner with minimum SSD as correspondence
min_idx = np.argmin(SSDs)
return coords_warped_subpix[min_idx]
# find correspondences using simple weighted sum of squared differences
src = []
dst = []
for coord in coords_orig_subpix:
src.append(coord)
dst.append(match_corner(coord))
src = np.array(src)
dst = np.array(dst)
# estimate affine transform model using all coordinates
model = AffineTransform()
model.estimate(src, dst)
# robustly estimate affine transform model with RANSAC
model_robust, inliers = ransac(
(src, dst), AffineTransform, min_samples=3, residual_threshold=2, max_trials=100
)
outliers = inliers == False
# compare "true" and estimated transform parameters
print("Ground truth:")
print(
f'Scale: ({tform.scale[1]:.4f}, {tform.scale[0]:.4f}), '
f'Translation: ({tform.translation[1]:.4f}, '
f'{tform.translation[0]:.4f}), '
f'Rotation: {-tform.rotation:.4f}'
)
print("Affine transform:")
print(
f'Scale: ({model.scale[0]:.4f}, {model.scale[1]:.4f}), '
f'Translation: ({model.translation[0]:.4f}, '
f'{model.translation[1]:.4f}), '
f'Rotation: {model.rotation:.4f}'
)
print("RANSAC:")
print(
f'Scale: ({model_robust.scale[0]:.4f}, {model_robust.scale[1]:.4f}), '
f'Translation: ({model_robust.translation[0]:.4f}, '
f'{model_robust.translation[1]:.4f}), '
f'Rotation: {model_robust.rotation:.4f}'
)
# visualize correspondence
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=1)
plt.gray()
inlier_idxs = np.nonzero(inliers)[0]
plot_matches(
ax[0],
img_orig_gray,
img_warped_gray,
src,
dst,
np.column_stack((inlier_idxs, inlier_idxs)),
matches_color='b',
)
ax[0].axis('off')
ax[0].set_title('Correct correspondences')
outlier_idxs = np.nonzero(outliers)[0]
plot_matches(
ax[1],
img_orig_gray,
img_warped_gray,
src,
dst,
np.column_stack((outlier_idxs, outlier_idxs)),
matches_color='r',
)
ax[1].axis('off')
ax[1].set_title('Faulty correspondences')
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.111 秒)
