备注
转到末尾 以下载完整示例代码。或在您的浏览器中通过 Binder 运行此示例。
使用薄板样条进行图像变形#
要扭曲图像,我们从一组源坐标和目标坐标开始。目标是使图像变形,使得源点移动到目标位置。通常,我们只知道少数选定源点的目标位置。为了计算所有其他像素位置的目标位置,我们需要一个模型。存在各种这样的模型,例如 仿射或投影变换。
大多数变换是线性的(即,它们保持直线),但有时我们需要更多的灵活性。一种表示非线性变换的模型,即线条可以弯曲的变换,是薄板样条 [1] [2]。
薄板样条借鉴了金属板的类比,金属板具有固有的刚性。考虑我们的源点:每个点都必须沿x和y方向移动一定的距离,以到达其对应的目标位置。首先,仅检查x坐标。想象将一块薄金属板放在图像上方。现在弯曲它,使得在每个源点处,板的z偏移是该源点在x方向上必须移动的距离,无论是正还是负,以到达其目标位置。金属板抵抗弯曲,因此保持平滑。我们可以从板的位置读取非源点坐标的偏移量。同样的步骤可以重复用于y坐标。
这为我们提供了薄板样条模型,该模型将任何 (x, y) 坐标映射到目标位置。
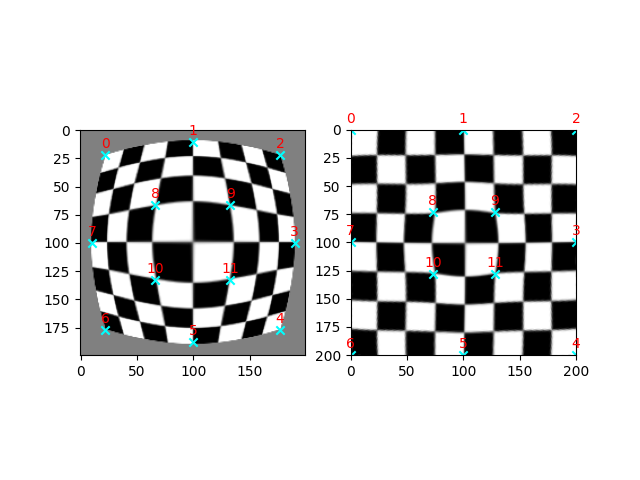
正确的桶形畸变#
在这个示例中,我们演示了如何使用薄板样条变换来校正桶形畸变 [3] 。桶形畸变会产生鱼眼效果,即图像放大率随距离图像中心的距离增加而减小。
我们首先生成一个示例数据集,通过对棋盘图像应用鱼眼扭曲,然后应用逆校正变换。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distortion_(optics)#Radial_distortion 的翻译
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import skimage as ski
def radial_distortion(xy, k1=0.9, k2=0.5):
"""Distort coordinates `xy` symmetrically around their own center."""
xy_c = xy.max(axis=0) / 2
xy = (xy - xy_c) / xy_c
radius = np.linalg.norm(xy, axis=1)
distortion_model = (1 + k1 * radius + k2 * radius**2) * k2
xy *= distortion_model.reshape(-1, 1)
xy = xy * xy_c + xy_c
return xy
image = ski.data.checkerboard()
image = ski.transform.warp(image, radial_distortion, cval=0.5)
# Pick a few `src` points by hand, and move the corresponding `dst` points to their
# expected positions.
# fmt: off
src = np.array([[22, 22], [100, 10], [177, 22], [190, 100], [177, 177], [100, 188],
[22, 177], [ 10, 100], [ 66, 66], [133, 66], [ 66, 133], [133, 133]])
dst = np.array([[ 0, 0], [100, 0], [200, 0], [200, 100], [200, 200], [100, 200],
[ 0, 200], [ 0, 100], [ 73, 73], [128, 73], [ 73, 128], [128, 128]])
# fmt: on
# Estimate the TPS transformation from these points and then warp the image.
# We switch `src` and `dst` here because `skimage.transform.warp` requires the
# inverse transformation!
tps = ski.transform.ThinPlateSplineTransform()
tps.estimate(dst, src)
warped = ski.transform.warp(image, tps)
# Plot the results
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2)
axs[0].imshow(image, cmap='gray')
axs[0].scatter(src[:, 0], src[:, 1], marker='x', color='cyan')
axs[1].imshow(warped, cmap='gray', extent=(0, 200, 200, 0))
axs[1].scatter(dst[:, 0], dst[:, 1], marker='x', color='cyan')
point_labels = [str(i) for i in range(len(src))]
for i, label in enumerate(point_labels):
axs[0].annotate(
label,
(src[:, 0][i], src[:, 1][i]),
textcoords="offset points",
xytext=(0, 5),
ha='center',
color='red',
)
axs[1].annotate(
label,
(dst[:, 0][i], dst[:, 1][i]),
textcoords="offset points",
xytext=(0, 5),
ha='center',
color='red',
)
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.078 秒)
