备注
转到末尾 下载完整的示例代码。或在您的浏览器中通过 Binder 运行此示例。
边缘运算符#
边缘算子在边缘检测算法中用于图像处理。它们是离散微分算子,计算图像强度函数的梯度的近似值。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import filters
from skimage.data import camera
from skimage.util import compare_images
image = camera()
edge_roberts = filters.roberts(image)
edge_sobel = filters.sobel(image)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(8, 4))
axes[0].imshow(edge_roberts, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
axes[0].set_title('Roberts Edge Detection')
axes[1].imshow(edge_sobel, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
axes[1].set_title('Sobel Edge Detection')
for ax in axes:
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

不同的算子计算梯度的不同有限差分近似。例如,Scharr滤波器比Sobel滤波器具有更少的旋转方差,而Sobel滤波器又优于Prewitt滤波器[1]_ [2] [3]。Prewitt和Sobel滤波器与Scharr滤波器之间的差异通过一个图像来说明,该图像是旋转不变连续函数的离散化。Prewitt和Sobel滤波器与Scharr滤波器之间的差异在图像的梯度方向接近对角线的区域以及具有高空间频率的区域中更为明显。对于示例图像,滤波器结果之间的差异非常小,滤波器结果在视觉上几乎无法区分。
x, y = np.ogrid[:100, :100]
# Creating a rotation-invariant image with different spatial frequencies.
image_rot = np.exp(1j * np.hypot(x, y) ** 1.3 / 20.0).real
edge_sobel = filters.sobel(image_rot)
edge_scharr = filters.scharr(image_rot)
edge_prewitt = filters.prewitt(image_rot)
diff_scharr_prewitt = compare_images(edge_scharr, edge_prewitt)
diff_scharr_sobel = compare_images(edge_scharr, edge_sobel)
max_diff = np.max(np.maximum(diff_scharr_prewitt, diff_scharr_sobel))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(8, 8))
axes = axes.ravel()
axes[0].imshow(image_rot, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
axes[0].set_title('Original image')
axes[1].imshow(edge_scharr, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
axes[1].set_title('Scharr Edge Detection')
axes[2].imshow(diff_scharr_prewitt, cmap=plt.cm.gray, vmax=max_diff)
axes[2].set_title('Scharr - Prewitt')
axes[3].imshow(diff_scharr_sobel, cmap=plt.cm.gray, vmax=max_diff)
axes[3].set_title('Scharr - Sobel')
for ax in axes:
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

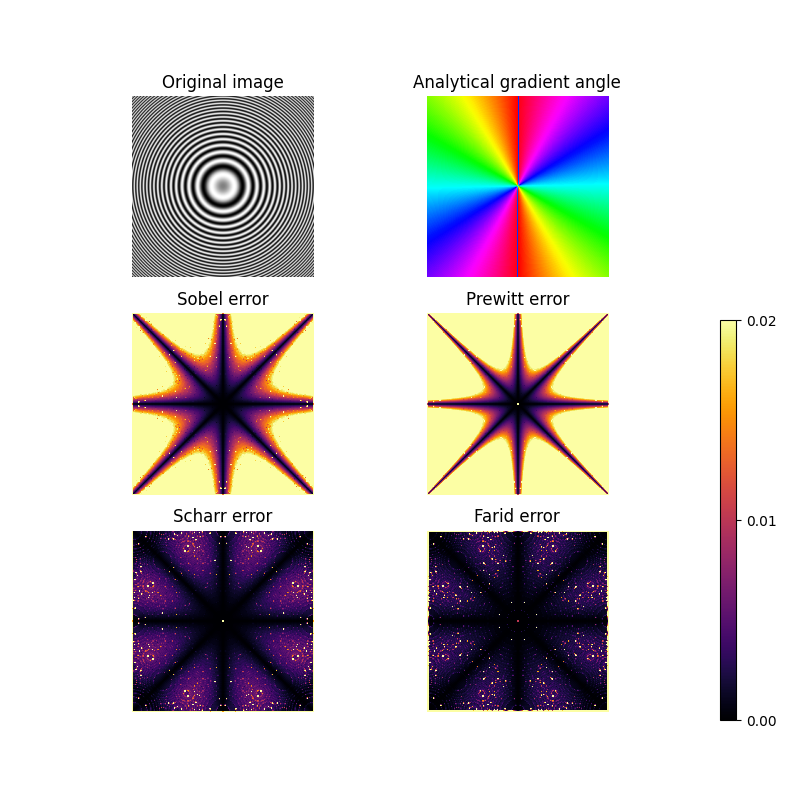
与前面的例子一样,这里我们展示了滤波器的旋转不变性。第一行显示了一个旋转不变的图像及其分析梯度的角度。其他两行包含了不同梯度近似(Sobel、Prewitt、Scharr & Farid)与分析梯度之间的差异。
Farid & Simoncelli 导数滤波器 [4], [5] 是最具旋转不变性的,但需要一个 5x5 的核,这在计算上比 3x3 的核更密集。
Farid, H. 和 Simoncelli, E. P., “离散多维信号的微分”, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 13(4): 496-508, 2004. DOI:10.1109/TIP.2004.823819
维基百科,“Farid 和 Simoncelli 导数。” 可访问于:<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_derivatives#Farid_and_Simoncelli_Derivatives>
x, y = np.mgrid[-10:10:255j, -10:10:255j]
image_rotinv = np.sin(x**2 + y**2)
image_x = 2 * x * np.cos(x**2 + y**2)
image_y = 2 * y * np.cos(x**2 + y**2)
def angle(dx, dy):
"""Calculate the angles between horizontal and vertical operators."""
return np.mod(np.arctan2(dy, dx), np.pi)
true_angle = angle(image_x, image_y)
angle_farid = angle(filters.farid_h(image_rotinv), filters.farid_v(image_rotinv))
angle_sobel = angle(filters.sobel_h(image_rotinv), filters.sobel_v(image_rotinv))
angle_scharr = angle(filters.scharr_h(image_rotinv), filters.scharr_v(image_rotinv))
angle_prewitt = angle(filters.prewitt_h(image_rotinv), filters.prewitt_v(image_rotinv))
def diff_angle(angle_1, angle_2):
"""Calculate the differences between two angles."""
return np.minimum(np.pi - np.abs(angle_1 - angle_2), np.abs(angle_1 - angle_2))
diff_farid = diff_angle(true_angle, angle_farid)
diff_sobel = diff_angle(true_angle, angle_sobel)
diff_scharr = diff_angle(true_angle, angle_scharr)
diff_prewitt = diff_angle(true_angle, angle_prewitt)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(8, 8))
axes = axes.ravel()
axes[0].imshow(image_rotinv, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
axes[0].set_title('Original image')
axes[1].imshow(true_angle, cmap=plt.cm.hsv)
axes[1].set_title('Analytical gradient angle')
axes[2].imshow(diff_sobel, cmap=plt.cm.inferno, vmin=0, vmax=0.02)
axes[2].set_title('Sobel error')
axes[3].imshow(diff_prewitt, cmap=plt.cm.inferno, vmin=0, vmax=0.02)
axes[3].set_title('Prewitt error')
axes[4].imshow(diff_scharr, cmap=plt.cm.inferno, vmin=0, vmax=0.02)
axes[4].set_title('Scharr error')
color_ax = axes[5].imshow(diff_farid, cmap=plt.cm.inferno, vmin=0, vmax=0.02)
axes[5].set_title('Farid error')
fig.subplots_adjust(right=0.8)
colorbar_ax = fig.add_axes([0.90, 0.10, 0.02, 0.50])
fig.colorbar(color_ax, cax=colorbar_ax, ticks=[0, 0.01, 0.02])
for ax in axes:
ax.axis('off')
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.439 秒)
