备注
转到末尾 以下载完整示例代码。或者通过 Binder 在浏览器中运行此示例。
使用 RANSAC 进行稳健的线模型估计#
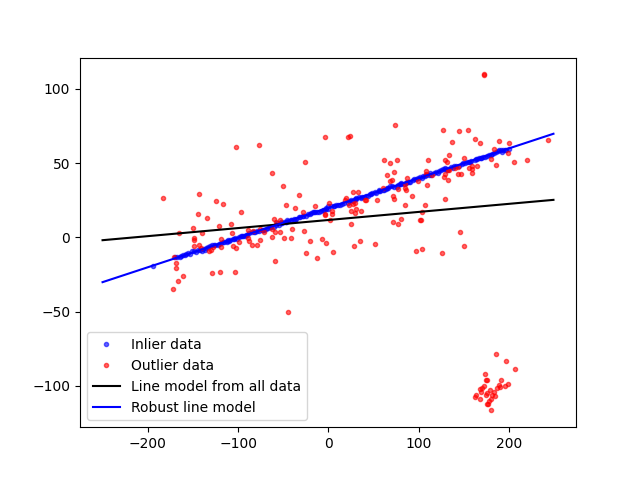
在这个例子中,我们看到了如何使用 RANSAC(随机样本一致性)算法来稳健地拟合一条线模型到有缺陷的数据。
首先,数据是通过向线性函数添加高斯噪声生成的。然后,离群点被添加到数据集中。
RANSAC 通过迭代从数据集中估计参数。在每次迭代中,执行以下步骤:
从原始数据中选择
min_samples个随机样本,并检查数据集是否有效(参见is_data_valid选项)。在随机子集上估计模型(
model_cls.estimate(*data[random_subset])并检查估计的模型是否有效(参见is_model_valid选项)。通过使用估计模型(
model_cls.residuals(*data))计算残差,将所有数据点分类为内点或离群点 - 所有残差小于residual_threshold的数据样本被视为内点。如果内点样本的数量比以往任何时候都多,则将估计的模型保存为最佳模型。如果当前估计的模型具有相同数量的内点,则仅当残差之和小于当前最佳模型时,才将其视为最佳模型。
这些步骤要么执行最大次数,要么直到满足其中一个特殊停止标准。最终模型是使用先前确定的最佳模型的所有内点样本估计的。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skimage.measure import LineModelND, ransac
rng = np.random.default_rng()
# generate coordinates of line
x = np.arange(-200, 200)
y = 0.2 * x + 20
data = np.column_stack([x, y])
# add gaussian noise to coordinates
noise = rng.normal(size=data.shape)
data += 0.5 * noise
data[::2] += 5 * noise[::2]
data[::4] += 20 * noise[::4]
# add faulty data
faulty = np.array(30 * [(180.0, -100)])
faulty += 10 * rng.normal(size=faulty.shape)
data[: faulty.shape[0]] = faulty
# fit line using all data
model = LineModelND()
model.estimate(data)
# robustly fit line only using inlier data with RANSAC algorithm
model_robust, inliers = ransac(
data, LineModelND, min_samples=2, residual_threshold=1, max_trials=1000
)
outliers = inliers == False
# generate coordinates of estimated models
line_x = np.arange(-250, 250)
line_y = model.predict_y(line_x)
line_y_robust = model_robust.predict_y(line_x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(data[inliers, 0], data[inliers, 1], '.b', alpha=0.6, label='Inlier data')
ax.plot(data[outliers, 0], data[outliers, 1], '.r', alpha=0.6, label='Outlier data')
ax.plot(line_x, line_y, '-k', label='Line model from all data')
ax.plot(line_x, line_y_robust, '-b', label='Robust line model')
ax.legend(loc='lower left')
plt.show()
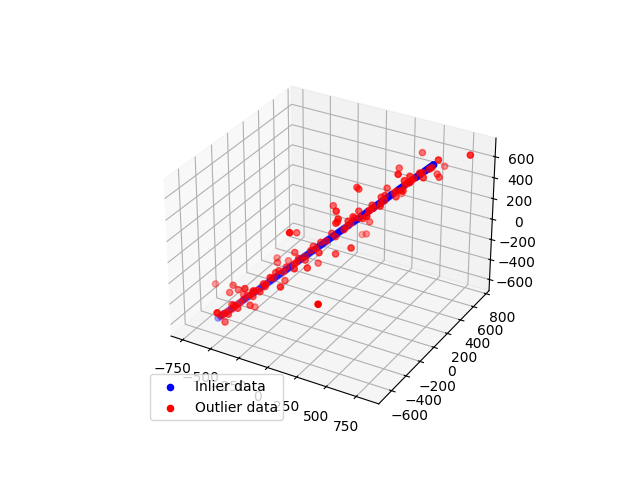
现在,我们将这个例子推广到三维点。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skimage.measure import LineModelND, ransac
# generate coordinates of line
point = np.array([0, 0, 0], dtype='float')
direction = np.array([1, 1, 1], dtype='float') / np.sqrt(3)
xyz = point + 10 * np.arange(-100, 100)[..., np.newaxis] * direction
# add gaussian noise to coordinates
noise = rng.normal(size=xyz.shape)
xyz += 0.5 * noise
xyz[::2] += 20 * noise[::2]
xyz[::4] += 100 * noise[::4]
# robustly fit line only using inlier data with RANSAC algorithm
model_robust, inliers = ransac(
xyz, LineModelND, min_samples=2, residual_threshold=1, max_trials=1000
)
outliers = inliers == False
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(
xyz[inliers][:, 0],
xyz[inliers][:, 1],
xyz[inliers][:, 2],
c='b',
marker='o',
label='Inlier data',
)
ax.scatter(
xyz[outliers][:, 0],
xyz[outliers][:, 1],
xyz[outliers][:, 2],
c='r',
marker='o',
label='Outlier data',
)
ax.legend(loc='lower left')
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.114 秒)
