备注
前往结尾 下载完整示例代码。或者通过 Binder 在浏览器中运行此示例。
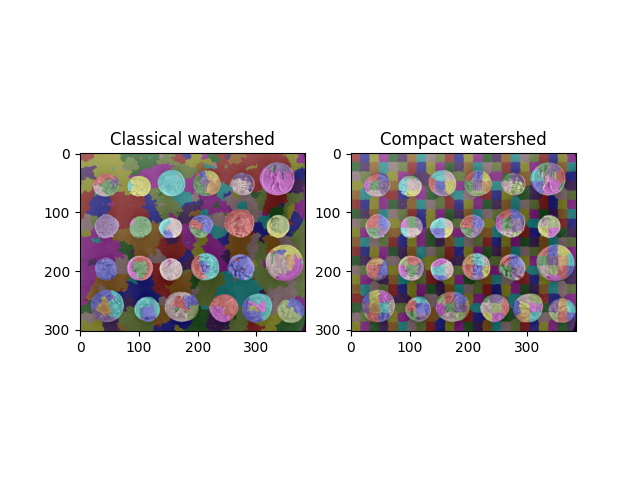
使用紧凑分水岭查找常规段#
分水岭变换通常被用作许多分割算法的起点。然而,如果没有明智地选择种子,它可能会产生非常不均匀的片段大小,这在下游分析中可能难以处理。
通过倾向于选择靠近被考虑像素的种子,*紧凑*分水岭变换解决了这个问题。
这两种算法都在 skimage.segmentation.watershed() 函数中实现。要使用紧凑形式,只需传递一个大于 0 的 compactness 值。
import numpy as np
from skimage import data, util, filters, color
from skimage.segmentation import watershed
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
coins = data.coins()
edges = filters.sobel(coins)
grid = util.regular_grid(coins.shape, n_points=468)
seeds = np.zeros(coins.shape, dtype=int)
seeds[grid] = np.arange(seeds[grid].size).reshape(seeds[grid].shape) + 1
w0 = watershed(edges, seeds)
w1 = watershed(edges, seeds, compactness=0.01)
fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax0.imshow(color.label2rgb(w0, coins, bg_label=-1))
ax0.set_title('Classical watershed')
ax1.imshow(color.label2rgb(w1, coins, bg_label=-1))
ax1.set_title('Compact watershed')
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.160 秒)
