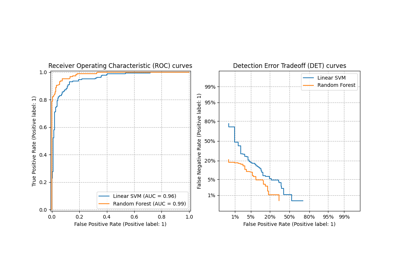
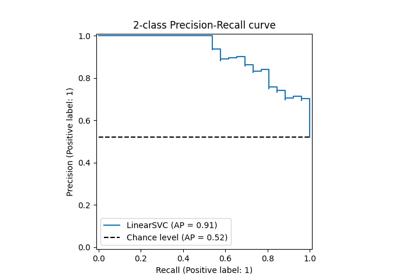
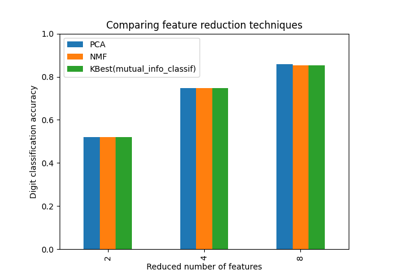
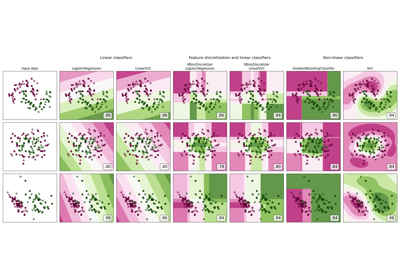
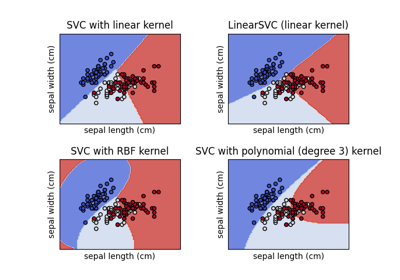
LinearSVC#
- class sklearn.svm.LinearSVC(penalty='l2', loss='squared_hinge', *, dual='auto', tol=0.0001, C=1.0, multi_class='ovr', fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1, class_weight=None, verbose=0, random_state=None, max_iter=1000)#
线性支持向量分类。
类似于带有参数 kernel=’linear’ 的 SVC,但其实现基于 liblinear 而不是 libsvm,因此在选择惩罚和损失函数方面具有更大的灵活性,并且应该更好地扩展到大量样本。
LinearSVC和SVC之间的主要区别在于默认使用的损失函数,以及在这两种实现之间处理截距正则化的方式。此类支持密集和稀疏输入,并且多类支持根据一对一的方案处理。
更多信息请参阅 用户指南 。
- Parameters:
- penalty{‘l1’, ‘l2’}, default=’l2’
指定在惩罚中使用的范数。’l2’ 惩罚是 SVC 中使用的标准。’l1’ 会导致
coef_向量稀疏。- loss{‘hinge’, ‘squared_hinge’}, default=’squared_hinge’
指定损失函数。’hinge’ 是标准的 SVM 损失(例如,由 SVC 类使用),而 ‘squared_hinge’ 是 hinge 损失的平方。不支持
penalty='l1'和loss='hinge'的组合。- dual“auto” 或 bool, default=”auto”
选择算法来解决对偶或原始优化问题。当 n_samples > n_features 时,首选 dual=False。
dual="auto"将根据n_samples、n_features、loss、multi_class和penalty的值自动选择参数的值。如果n_samples<n_features且优化器支持所选的loss、multi_class和penalty,则 dual 将设置为 True,否则将设置为 False。Changed in version 1.3: 在版本 1.3 中添加了
"auto"选项,并将在版本 1.5 中成为默认值。- tolfloat, default=1e-4
停止准则的容差。
- Cfloat, default=1.0
正则化参数。正则化的强度与 C 成反比。必须严格为正。有关直观显示正则化参数 C 缩放效果的示例,请参见 缩放SVC的正则化参数 。
- multi_class{‘ovr’, ‘crammer_singer’}, default=’ovr’
如果
y包含两个以上类,则确定多类策略。"ovr"训练 n_classes 个一对一分类器,而"crammer_singer"优化所有类的联合目标。虽然crammer_singer从理论角度来看很有趣,因为它是一致的,但在实践中很少使用,因为它很少能提高准确性,并且计算成本更高。如果选择"crammer_singer",则将忽略选项 loss、penalty 和 dual。- fit_interceptbool, default=True
是否拟合截距。如果设置为 True,则特征向量将扩展以包含截距项:
[x_1, ..., x_n, 1],其中 1 对应于截距。如果设置为 False,则在计算中不使用截距(即数据应已中心化)。- intercept_scalingfloat, default=1.0
当
fit_intercept为 True 时,实例向量 x 变为[x_1, ..., x_n, intercept_scaling],即一个具有恒定值等于intercept_scaling的“合成”特征被附加到实例向量。截距变为 intercept_scaling * 合成特征权重。注意,liblinear 内部对截距进行惩罚,将其视为特征向量中的任何其他项。为了减少正则化对截距的影响,可以将intercept_scaling参数设置为大于 1 的值;intercept_scaling的值越高,正则化对其的影响越小。然后,权重变为[w_x_1, ..., w_x_n, w_intercept*intercept_scaling],其中w_x_1, ..., w_x_n表示特征权重,截距权重按intercept_scaling缩放。这种缩放允许截距项具有与其他特征不同的正则化行为。- class_weightdict 或 ‘balanced’, default=None
将类 i 的参数 C 设置为
class_weight[i]*C。如果未给出,则所有类都被认为具有相同的权重。“balanced”模式使用 y 的值自动调整权重,与输入数据中的类频率成反比,即n_samples / (n_classes * np.bincount(y))。- verboseint, default=0
启用详细输出。请注意,此设置利用了 liblinear 中的每个进程运行时设置,如果在多线程上下文中启用,可能无法正常工作。
- random_stateint, RandomState 实例或 None, default=None
控制用于对偶坐标下降(如果
dual=True)的数据洗牌的伪随机数生成。当dual=False时,LinearSVC的底层实现不是随机的,random_state对结果没有影响。传递一个 int 以在多次函数调用中获得可重复的输出。参见 Glossary 。- max_iterint, default=1000
要运行的最大迭代次数。
- Attributes:
- coef_ndarray of shape (1, n_features) if n_classes == 2 else (n_classes, n_features)
分配给特征的权重(在原始问题中的系数)。
coef_是从raw_coef_派生的只读属性,遵循 liblinear 的内部内存布局。- intercept_ndarray of shape (1,) if n_classes == 2 else (n_classes,)
决策函数中的常数。
- classes_ndarray of shape (n_classes,)
唯一的类标签。
- n_features_in_int
在 fit 期间看到的特征数量。
Added in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) 在 fit 期间看到的特征名称。仅当
X的特征名称均为字符串时定义。Added in version 1.0.
- n_iter_int
在所有类中运行的最大迭代次数。
See also
SVC使用 libsvm 实现的支持向量机分类器: 内核可以是非线性的,但其 SMO 算法不能像 LinearSVC 那样扩展到大量样本。 此外,SVC 多类模式使用一对一方案实现,而 LinearSVC 使用一对一方案。可以使用
OneVsRestClassifier包装器实现一对一方案。 最后,SVC 可以在不复制内存的情况下拟合密集数据,如果输入是 C-contiguous 的。稀疏数据仍会导致内存复制。sklearn.linear_model.SGDClassifierSGDClassifier 可以通过调整惩罚和损失参数来优化与 LinearSVC 相同的成本函数。此外,它需要更少的内存,允许增量(在线)学习,并实现各种损失函数和正则化机制。
Notes
底层 C 实现使用随机数生成器在拟合模型时选择特征。因此,对于相同输入数据,结果略有不同并不罕见。如果发生这种情况,请尝试使用较小的
tol参数。底层实现 liblinear 使用稀疏的内部数据表示,这将导致内存复制。
预测输出在某些情况下可能与独立的 liblinear 不匹配。请参阅 narrative documentation 中的差异。
References
LIBLINEAR: A Library for Large Linear Classification _
Examples
>>> from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC >>> from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline >>> from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> X, y = make_classification(n_features=4, random_state=0) >>> clf = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), ... LinearSVC(random_state=0, tol=1e-5)) >>> clf.fit(X, y) Pipeline(steps=[('standardscaler', StandardScaler()), ('linearsvc', LinearSVC(random_state=0, tol=1e-05))])
>>> print(clf.named_steps['linearsvc'].coef_) [[0.141... 0.526... 0.679... 0.493...]]
>>> print(clf.named_steps['linearsvc'].intercept_) [0.1693...] >>> print(clf.predict([[0, 0, 0, 0]])) [1]
- decision_function(X)#
预测样本的置信度分数。
样本的置信度分数与其到超平面的有符号距离成正比。
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix},形状为 (n_samples, n_features)
我们想要获取置信度分数的数据矩阵。
- Returns:
- scoresndarray,形状为 (n_samples,) 或 (n_samples, n_classes)
每个
(n_samples, n_classes)组合的置信度分数。在二分类情况下,self.classes_[1]的置信度分数,其中 >0 表示会预测这个类别。
- densify()#
将系数矩阵转换为密集数组格式。
将
coef_成员(回)转换为 numpy.ndarray。这是coef_的默认格式,并且是拟合所必需的,因此只有在之前已经稀疏化的模型上才需要调用此方法;否则,它是一个空操作。- Returns:
- self
拟合的估计器。
- fit(X, y, sample_weight=None)#
拟合模型根据给定的训练数据。
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix},形状为 (n_samples, n_features)
训练向量,其中
n_samples是样本的数量,n_features是特征的数量。- y形状为 (n_samples,) 的 array-like
相对于 X 的目标向量。
- sample_weight形状为 (n_samples,) 的 array-like,默认=None
分配给单个样本的权重数组。如果没有提供, 则每个样本被赋予单位权重。
Added in version 0.18.
- Returns:
- selfobject
估计器的一个实例。
- get_metadata_routing()#
获取此对象的元数据路由。
请查看 用户指南 以了解路由机制的工作原理。
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
MetadataRequest封装的 路由信息。
- get_params(deep=True)#
获取此估计器的参数。
- Parameters:
- deepbool, 默认=True
如果为True,将返回此估计器和包含的子对象(也是估计器)的参数。
- Returns:
- paramsdict
参数名称映射到它们的值。
- predict(X)#
预测X中的样本类别标签。
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix},形状为 (n_samples, n_features)
我们希望获取预测的数据矩阵。
- Returns:
- y_predndarray,形状为 (n_samples,)
包含每个样本类别标签的向量。
- score(X, y, sample_weight=None)#
返回给定测试数据和标签的平均准确率。
在多标签分类中,这是子集准确率,这是一个严格的指标,因为你要求每个样本的每个标签集都被正确预测。
- Parameters:
- X形状为 (n_samples, n_features) 的类数组
测试样本。
- y形状为 (n_samples,) 或 (n_samples, n_outputs) 的类数组
` X`的真实标签。
- sample_weight形状为 (n_samples,) 的类数组,默认=None
样本权重。
- Returns:
- scorefloat
self.predict(X)相对于y的平均准确率。
- set_fit_request(*, sample_weight: bool | None | str = '$UNCHANGED$') LinearSVC#
Request metadata passed to the
fitmethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed tofitif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it tofit.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.Added in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- sample_weightstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
sample_weightparameter infit.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_params(**params)#
设置此估计器的参数。
该方法适用于简单估计器以及嵌套对象(例如
Pipeline)。后者具有形式为<component>__<parameter>的参数,以便可以更新嵌套对象的每个组件。- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
估计器参数。
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
估计器实例。
- set_score_request(*, sample_weight: bool | None | str = '$UNCHANGED$') LinearSVC#
Request metadata passed to the
scoremethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed toscoreif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it toscore.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.Added in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- sample_weightstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
sample_weightparameter inscore.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- sparsify()#
将系数矩阵转换为稀疏格式。
将
coef_成员转换为 scipy.sparse 矩阵,对于 L1 正则化模型来说,这种格式在内存和存储方面比通常的 numpy.ndarray 表示更高效。intercept_成员不会被转换。- Returns:
- self
拟合的估计器。
Notes
对于非稀疏模型,即当
coef_中没有很多零时,这实际上可能会增加内存使用量,因此请谨慎使用此方法。一个经验法则是,零元素的数量,可以通过(coef_ == 0).sum()计算,必须超过 50% 才能提供显著的效益。调用此方法后,进一步使用 partial_fit 方法(如果有)进行拟合将不起作用,直到您调用 densify。