Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
在 LinearSVC 中绘制支持向量#
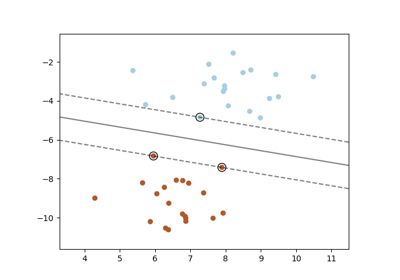
与基于 LIBSVM 的 SVC 不同,基于 LIBLINEAR 的 LinearSVC 不提供支持向量。此示例演示了如何在 LinearSVC 中获取支持向量。
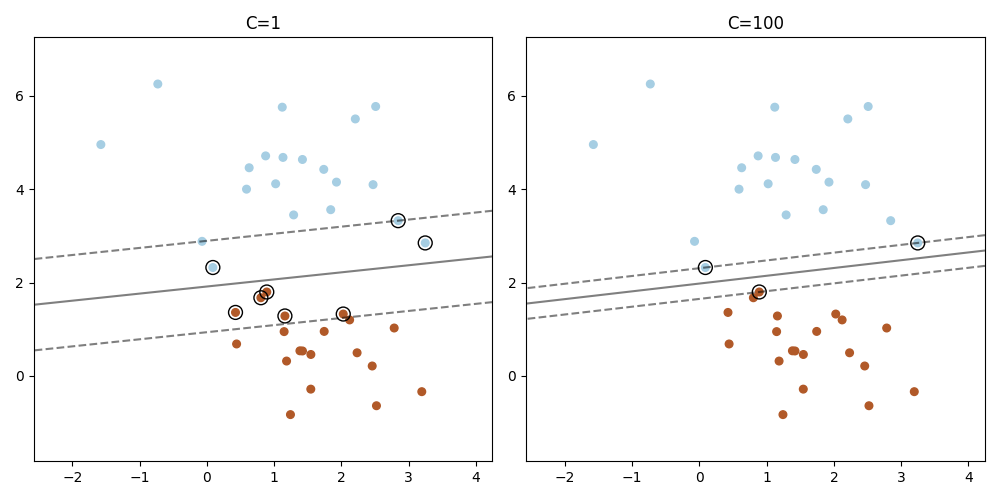
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=40, centers=2, random_state=0)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
for i, C in enumerate([1, 100]):
# “hinge” 是标准的 SVM 损失函数
clf = LinearSVC(C=C, loss="hinge", random_state=42).fit(X, y)
# 通过决策函数获得支持向量
decision_function = clf.decision_function(X)
# 我们也可以手动计算决策函数
# decision_function = np.dot(X, clf.coef_[0]) + clf.intercept_[0]
# 支持向量是位于边界内的样本,其大小通常限制为1
support_vector_indices = np.where(np.abs(decision_function) <= 1 + 1e-15)[0]
support_vectors = X[support_vector_indices]
plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=30, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
ax = plt.gca()
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
clf,
X,
ax=ax,
grid_resolution=50,
plot_method="contour",
colors="k",
levels=[-1, 0, 1],
alpha=0.5,
linestyles=["--", "-", "--"],
)
plt.scatter(
support_vectors[:, 0],
support_vectors[:, 1],
s=100,
linewidth=1,
facecolors="none",
edgecolors="k",
)
plt.title("C=" + str(C))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.076 seconds)
Related examples