Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
物种分布建模#
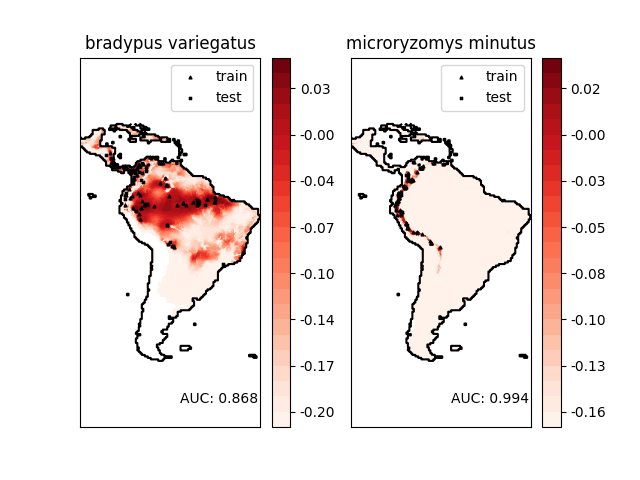
建模物种的地理分布是保护生物学中的一个重要问题。在这个例子中,我们根据过去的观察和14个环境变量来建模两种南美洲哺乳动物的地理分布。由于我们只有正样本(没有不成功的观察),我们将这个问题视为一个密度估计问题,并使用 OneClassSVM 作为我们的建模工具。数据集由Phillips等人(2006)提供。如果可用,示例使用 basemap 来绘制南美洲的海岸线和国家边界。
这两种物种是:
“Bradypus variegatus” , 棕喉树懒。
“Microryzomys minutus” , 也被称为森林小稻鼠,一种生活在秘鲁、哥伦比亚、厄瓜多尔、秘鲁和委内瑞拉的啮齿动物。
参考文献#
“物种地理分布的最大熵建模” S. J. Phillips, R. P. Anderson, R. E. Schapire - 生态建模, 190:231-259, 2006.
________________________________________________________________________________
Modeling distribution of species 'bradypus variegatus'
- fit OneClassSVM ... done.
- plot coastlines from coverage
- predict species distribution
Area under the ROC curve : 0.868443
________________________________________________________________________________
Modeling distribution of species 'microryzomys minutus'
- fit OneClassSVM ... done.
- plot coastlines from coverage
- predict species distribution
Area under the ROC curve : 0.993919
time elapsed: 3.00s
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import metrics, svm
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_species_distributions
from sklearn.utils import Bunch
# 如果 basemap 可用,我们将使用它。
# 否则,我们稍后将即兴处理……
try:
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
basemap = True
except ImportError:
basemap = False
def construct_grids(batch):
"""从批处理对象构建地图网格
Parameters
----------
batch : 批处理对象
由 :func:`fetch_species_distributions` 返回的对象
返回
-------
(xgrid, ygrid) : 一维数组
与 batch.coverages 中的值对应的网格
"""
# 角落单元的 x,y 坐标
xmin = batch.x_left_lower_corner + batch.grid_size
xmax = xmin + (batch.Nx * batch.grid_size)
ymin = batch.y_left_lower_corner + batch.grid_size
ymax = ymin + (batch.Ny * batch.grid_size)
# 网格单元的 x 坐标
xgrid = np.arange(xmin, xmax, batch.grid_size)
# 网格单元的 y 坐标
ygrid = np.arange(ymin, ymax, batch.grid_size)
return (xgrid, ygrid)
def create_species_bunch(species_name, train, test, coverages, xgrid, ygrid):
"""创建一个包含特定生物信息的集合
这将使用测试/训练记录数组来提取特定物种名称的数据。
"""
bunch = Bunch(name=" ".join(species_name.split("_")[:2]))
species_name = species_name.encode("ascii")
points = dict(test=test, train=train)
for label, pts in points.items():
# 选择与所需物种相关的点
pts = pts[pts["species"] == species_name]
bunch["pts_%s" % label] = pts
# 确定每个训练和测试点的覆盖值
ix = np.searchsorted(xgrid, pts["dd long"])
iy = np.searchsorted(ygrid, pts["dd lat"])
bunch["cov_%s" % label] = coverages[:, -iy, ix].T
return bunch
def plot_species_distribution(
species=("bradypus_variegatus_0", "microryzomys_minutus_0")
):
"""
绘制物种分布图。
"""
if len(species) > 2:
print(
"Note: when more than two species are provided,"
" only the first two will be used"
)
t0 = time()
# 加载压缩数据
data = fetch_species_distributions()
# 设置数据网格
xgrid, ygrid = construct_grids(data)
# x,y坐标系中的网格
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xgrid, ygrid[::-1])
# 为每个物种创建一组
BV_bunch = create_species_bunch(
species[0], data.train, data.test, data.coverages, xgrid, ygrid
)
MM_bunch = create_species_bunch(
species[1], data.train, data.test, data.coverages, xgrid, ygrid
)
# 评估用背景点(网格坐标)
np.random.seed(13)
background_points = np.c_[
np.random.randint(low=0, high=data.Ny, size=10000),
np.random.randint(low=0, high=data.Nx, size=10000),
].T
# 我们将利用coverages[6]在所有陆地区域都有测量值这一事实。这将帮助我们在陆地和水域之间做出判断。
land_reference = data.coverages[6]
# 拟合、预测和绘制每个物种的图表。
for i, species in enumerate([BV_bunch, MM_bunch]):
print("_" * 80)
print("Modeling distribution of species '%s'" % species.name)
# 标准化特征
mean = species.cov_train.mean(axis=0)
std = species.cov_train.std(axis=0)
train_cover_std = (species.cov_train - mean) / std
# Fit OneClassSVM
print(" - fit OneClassSVM ... ", end="")
clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.1, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.5)
clf.fit(train_cover_std)
print("done.")
# 绘制南美洲地图
plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
if basemap:
print(" - plot coastlines using basemap")
m = Basemap(
projection="cyl",
llcrnrlat=Y.min(),
urcrnrlat=Y.max(),
llcrnrlon=X.min(),
urcrnrlon=X.max(),
resolution="c",
)
m.drawcoastlines()
m.drawcountries()
else:
print(" - plot coastlines from coverage")
plt.contour(
X, Y, land_reference, levels=[-9998], colors="k", linestyles="solid"
)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
print(" - predict species distribution")
# 使用训练数据预测物种分布
Z = np.ones((data.Ny, data.Nx), dtype=np.float64)
# 我们只会预测陆地上的点。
idx = np.where(land_reference > -9999)
coverages_land = data.coverages[:, idx[0], idx[1]].T
pred = clf.decision_function((coverages_land - mean) / std)
Z *= pred.min()
Z[idx[0], idx[1]] = pred
levels = np.linspace(Z.min(), Z.max(), 25)
Z[land_reference == -9999] = -9999
# 绘制预测的等高线图
plt.contourf(X, Y, Z, levels=levels, cmap=plt.cm.Reds)
plt.colorbar(format="%.2f")
# 散点训练/测试点
plt.scatter(
species.pts_train["dd long"],
species.pts_train["dd lat"],
s=2**2,
c="black",
marker="^",
label="train",
)
plt.scatter(
species.pts_test["dd long"],
species.pts_test["dd lat"],
s=2**2,
c="black",
marker="x",
label="test",
)
plt.legend()
plt.title(species.name)
plt.axis("equal")
# 计算相对于背景点的AUC
pred_background = Z[background_points[0], background_points[1]]
pred_test = clf.decision_function((species.cov_test - mean) / std)
scores = np.r_[pred_test, pred_background]
y = np.r_[np.ones(pred_test.shape), np.zeros(pred_background.shape)]
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(y, scores)
roc_auc = metrics.auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.text(-35, -70, "AUC: %.3f" % roc_auc, ha="right")
print("\n Area under the ROC curve : %f" % roc_auc)
print("\ntime elapsed: %.2fs" % (time() - t0))
plot_species_distribution()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.081 seconds)
Related examples