Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
使用RANSAC进行稳健的线性模型估计#
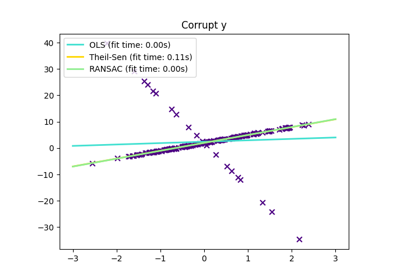
在这个例子中,我们将看到如何使用:ref:RANSAC <ransac_regression> 算法稳健地拟合一个线性模型到有缺陷的数据。
普通的线性回归对异常值很敏感,拟合的直线很容易偏离数据的真实底层关系。
RANSAC回归器会自动将数据分为内点和外点,拟合的直线仅由识别出的内点决定。
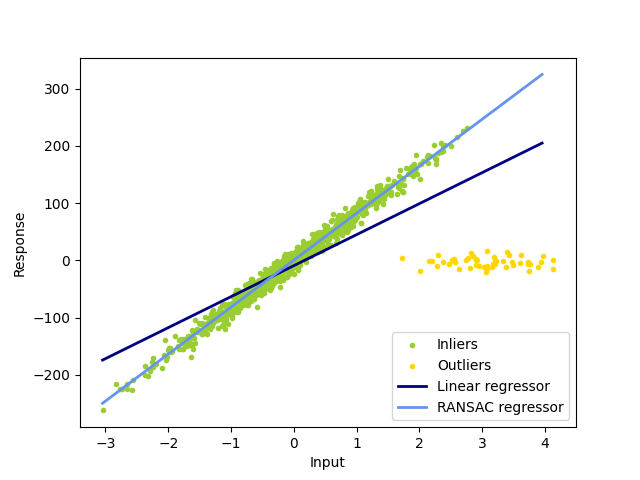
Estimated coefficients (true, linear regression, RANSAC):
82.1903908407869 [54.17236387] [82.08533159]
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets, linear_model
n_samples = 1000
n_outliers = 50
X, y, coef = datasets.make_regression(
n_samples=n_samples,
n_features=1,
n_informative=1,
noise=10,
coef=True,
random_state=0,
)
# 添加异常数据
np.random.seed(0)
X[:n_outliers] = 3 + 0.5 * np.random.normal(size=(n_outliers, 1))
y[:n_outliers] = -3 + 10 * np.random.normal(size=n_outliers)
# 使用所有数据拟合直线
#
#
lr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X, y)
# 使用RANSAC算法稳健地拟合线性模型
ransac = linear_model.RANSACRegressor()
ransac.fit(X, y)
inlier_mask = ransac.inlier_mask_
outlier_mask = np.logical_not(inlier_mask)
# 预测估计模型的数据
line_X = np.arange(X.min(), X.max())[:, np.newaxis]
line_y = lr.predict(line_X)
line_y_ransac = ransac.predict(line_X)
# 比较估计系数
print("Estimated coefficients (true, linear regression, RANSAC):")
print(coef, lr.coef_, ransac.estimator_.coef_)
lw = 2
plt.scatter(
X[inlier_mask], y[inlier_mask], color="yellowgreen", marker=".", label="Inliers"
)
plt.scatter(
X[outlier_mask], y[outlier_mask], color="gold", marker=".", label="Outliers"
)
plt.plot(line_X, line_y, color="navy", linewidth=lw, label="Linear regressor")
plt.plot(
line_X,
line_y_ransac,
color="cornflowerblue",
linewidth=lw,
label="RANSAC regressor",
)
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.xlabel("Input")
plt.ylabel("Response")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.046 seconds)
Related examples