Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
本示例在特征空间中通过结果比较直观地展示了两种不同成分分析技术的对比。
独立成分分析(ICA) vs 主成分分析(PCA) 。
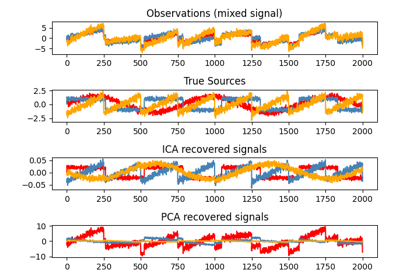
在特征空间中表示ICA可以得到“几何ICA”的视图: ICA是一种在特征空间中找到对应于高非高斯性投影方向的算法。这些方向在原始特征空间中不需要是正交的,但在白化特征空间中它们是正交的,在白化特征空间中所有方向对应于相同的方差。
另一方面,PCA在原始特征空间中找到对应于最大方差方向的正交方向。
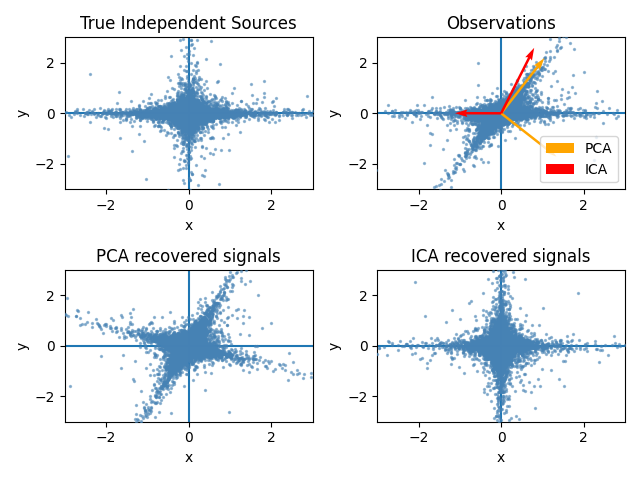
在这里,我们使用高度非高斯过程(自由度较低的2个学生T分布)模拟独立源(左上图)。我们将它们混合以创建观测值(右上图)。 在这个原始观测空间中,PCA识别的方向用橙色向量表示。我们在PCA空间中表示信号,通过对应于PCA向量的方差进行白化(左下图)。运行ICA相当于在这个空间中找到一个旋转,以识别最大非高斯性方向(右下图)。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
生成示例数据#
import numpy as np
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA, FastICA
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
S = rng.standard_t(1.5, size=(20000, 2))
S[:, 0] *= 2.0
# Mix data
A = np.array([[1, 1], [0, 2]]) # Mixing matrix
X = np.dot(S, A.T) # Generate observations
pca = PCA()
S_pca_ = pca.fit(X).transform(X)
ica = FastICA(random_state=rng, whiten="arbitrary-variance")
S_ica_ = ica.fit(X).transform(X) # Estimate the sources
绘制结果#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_samples(S, axis_list=None):
plt.scatter(
S[:, 0], S[:, 1], s=2, marker="o", zorder=10, color="steelblue", alpha=0.5
)
if axis_list is not None:
for axis, color, label in axis_list:
axis /= axis.std()
x_axis, y_axis = axis
plt.quiver(
(0, 0),
(0, 0),
x_axis,
y_axis,
zorder=11,
width=0.01,
scale=6,
color=color,
label=label,
)
plt.hlines(0, -3, 3)
plt.vlines(0, -3, 3)
plt.xlim(-3, 3)
plt.ylim(-3, 3)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plot_samples(S / S.std())
plt.title("True Independent Sources")
axis_list = [(pca.components_.T, "orange", "PCA"), (ica.mixing_, "red", "ICA")]
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plot_samples(X / np.std(X), axis_list=axis_list)
legend = plt.legend(loc="lower right")
legend.set_zorder(100)
plt.title("Observations")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plot_samples(S_pca_ / np.std(S_pca_, axis=0))
plt.title("PCA recovered signals")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plot_samples(S_ica_ / np.std(S_ica_))
plt.title("ICA recovered signals")
plt.subplots_adjust(0.09, 0.04, 0.94, 0.94, 0.26, 0.36)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.155 seconds)
Related examples