Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
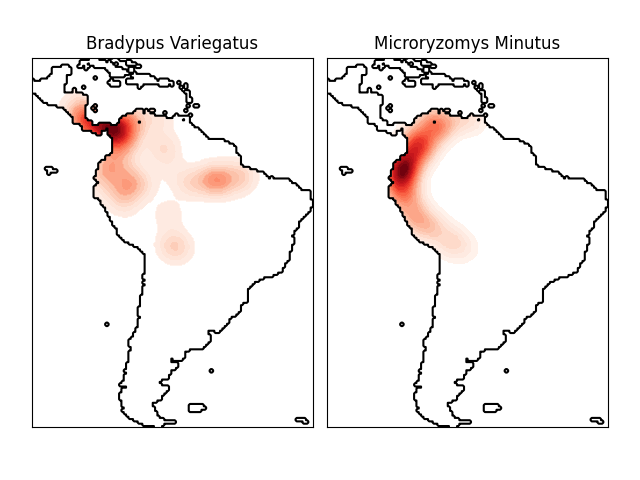
物种分布的核密度估计#
这展示了一个基于邻居查询(特别是核密度估计)的地理空间数据示例,使用基于哈弗赛因距离度量构建的球树——即经纬度点之间的距离。数据集由Phillips等人(2006)提供。 如果可用,示例使用 basemap 绘制南美洲的海岸线和国界。
此示例不对数据进行任何学习(有关基于此数据集属性的分类示例,请参见:ref:sphx_glr_auto_examples_applications_plot_species_distribution_modeling.py )。它只是显示地理空间坐标中观测数据点的核密度估计。
这两种物种是:
“Bradypus variegatus” , 棕喉树懒。
“Microryzomys minutus” , 也被称为森林小稻鼠,一种生活在秘鲁、哥伦比亚、厄瓜多尔、秘鲁和委内瑞拉的啮齿动物。
参考文献#
“物种地理分布的最大熵建模” S. J. Phillips, R. P. Anderson, R. E. Schapire - 生态建模, 190:231-259, 2006.
- computing KDE in spherical coordinates
- plot coastlines from coverage
- computing KDE in spherical coordinates
- plot coastlines from coverage
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_species_distributions
from sklearn.neighbors import KernelDensity
# 如果 basemap 可用,我们将使用它。
# 否则,我们稍后将进行改进……
try:
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
basemap = True
except ImportError:
basemap = False
def construct_grids(batch):
"""构建地图网格从批处理对象
Parameters
----------
batch : 批处理对象
由 :func:`fetch_species_distributions` 返回的对象
返回
-------
(xgrid, ygrid) : 一维数组
对应于 batch.coverages 中值的网格
"""
# 角落单元格的 x,y 坐标
xmin = batch.x_left_lower_corner + batch.grid_size
xmax = xmin + (batch.Nx * batch.grid_size)
ymin = batch.y_left_lower_corner + batch.grid_size
ymax = ymin + (batch.Ny * batch.grid_size)
# 网格单元的 x 坐标
xgrid = np.arange(xmin, xmax, batch.grid_size)
# 网格单元的y坐标
ygrid = np.arange(ymin, ymax, batch.grid_size)
return (xgrid, ygrid)
# 获取物种ID和位置的矩阵/数组
data = fetch_species_distributions()
species_names = ["Bradypus Variegatus", "Microryzomys Minutus"]
Xtrain = np.vstack([data["train"]["dd lat"], data["train"]["dd long"]]).T
ytrain = np.array(
[d.decode("ascii").startswith("micro") for d in data["train"]["species"]],
dtype="int",
)
Xtrain *= np.pi / 180.0 # Convert lat/long to radians
# 设置数据网格以绘制等高线图
xgrid, ygrid = construct_grids(data)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xgrid[ : :5], ygrid[::5][::-1])
land_reference = data.coverages[6][ : :5, ::5]
land_mask = (land_reference > -9999).ravel()
xy = np.vstack([Y.ravel(), X.ravel()]).T
xy = xy[land_mask]
xy *= np.pi / 180.0
# 绘制南美洲地图并标注每个物种的分布情况
fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.05, right=0.95, wspace=0.05)
for i in range(2):
plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
# 构建分布的核密度估计
print(" - computing KDE in spherical coordinates")
kde = KernelDensity(
bandwidth=0.04, metric="haversine", kernel="gaussian", algorithm="ball_tree"
)
kde.fit(Xtrain[ytrain == i])
# 仅在陆地上评估:-9999 表示海洋
Z = np.full(land_mask.shape[0], -9999, dtype="int")
Z[land_mask] = np.exp(kde.score_samples(xy))
Z = Z.reshape(X.shape)
# 绘制密度的等高线
levels = np.linspace(0, Z.max(), 25)
plt.contourf(X, Y, Z, levels=levels, cmap=plt.cm.Reds)
if basemap:
print(" - plot coastlines using basemap")
m = Basemap(
projection="cyl",
llcrnrlat=Y.min(),
urcrnrlat=Y.max(),
llcrnrlon=X.min(),
urcrnrlon=X.max(),
resolution="c",
)
m.drawcoastlines()
m.drawcountries()
else:
print(" - plot coastlines from coverage")
plt.contour(
X, Y, land_reference, levels=[-9998], colors="k", linestyles="solid"
)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title(species_names[i])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.095 seconds)
Related examples