Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
比较交叉分解方法#
各种交叉分解算法的简单用法:
PLSCanonical
PLS回归,具有多变量响应,又称PLS2
PLS回归,具有单变量响应,又称PLS1
CCA
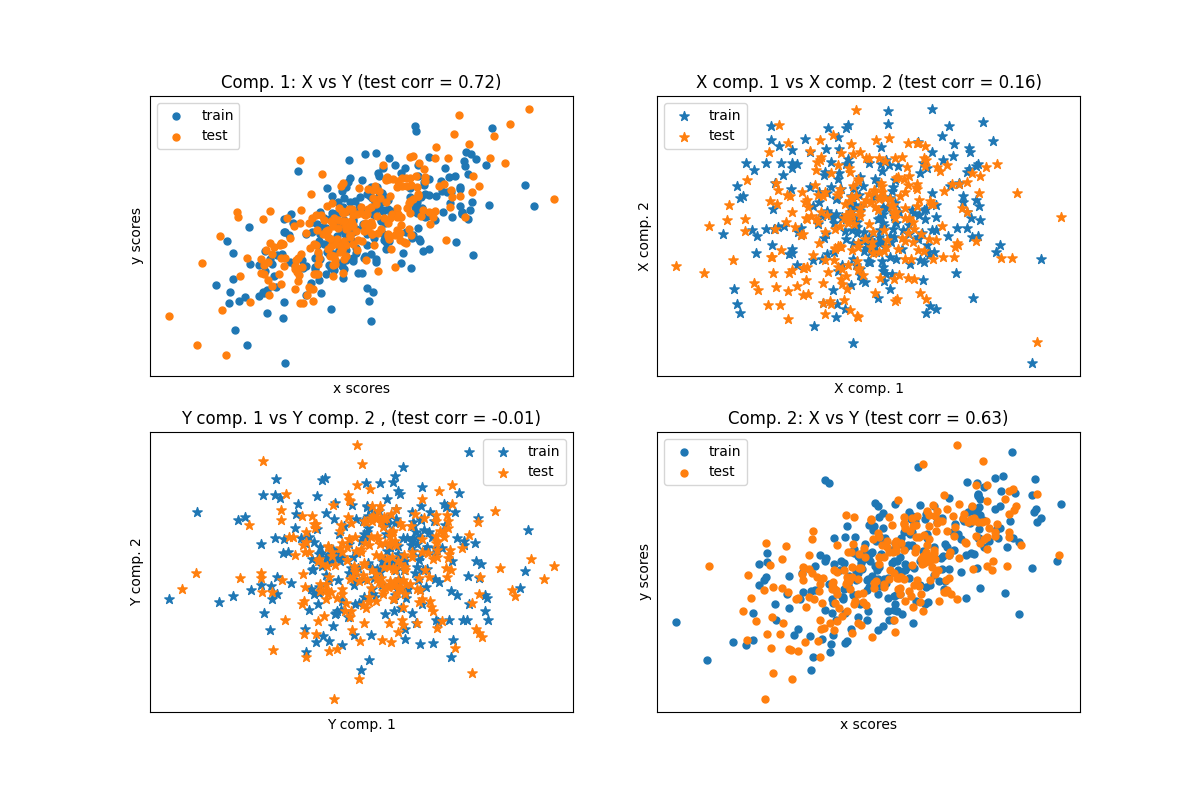
给定两个多变量协变的二维数据集X和Y,PLS提取“协方差方向”,即解释两个数据集之间最大共享方差的各个成分。这在**散点矩阵图**显示中很明显:数据集X和数据集Y中的成分1是最大相关的(点位于第一对角线附近)。对于两个数据集中的成分2也是如此,然而,不同成分之间跨数据集的相关性较弱:点云非常球形。
基于数据集的潜在变量模型#
import numpy as np
n = 500
# 2 latents vars:
l1 = np.random.normal(size=n)
l2 = np.random.normal(size=n)
latents = np.array([l1, l1, l2, l2]).T
X = latents + np.random.normal(size=4 * n).reshape((n, 4))
Y = latents + np.random.normal(size=4 * n).reshape((n, 4))
X_train = X[: n // 2]
Y_train = Y[: n // 2]
X_test = X[n // 2 :]
Y_test = Y[n // 2 :]
print("Corr(X)")
print(np.round(np.corrcoef(X.T), 2))
print("Corr(Y)")
print(np.round(np.corrcoef(Y.T), 2))
Corr(X)
[[ 1. 0.49 -0.05 -0.04]
[ 0.49 1. -0.01 -0.01]
[-0.05 -0.01 1. 0.48]
[-0.04 -0.01 0.48 1. ]]
Corr(Y)
[[ 1. 0.53 0.03 -0.02]
[ 0.53 1. 0. -0.03]
[ 0.03 0. 1. 0.5 ]
[-0.02 -0.03 0.5 1. ]]
规范(对称)PLS#
转换数据#
from sklearn.cross_decomposition import PLSCanonical
plsca = PLSCanonical(n_components=2)
plsca.fit(X_train, Y_train)
X_train_r, Y_train_r = plsca.transform(X_train, Y_train)
X_test_r, Y_test_r = plsca.transform(X_test, Y_test)
分数的散点图#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 在对角线上绘制每个成分的X与Y得分
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.scatter(X_train_r[:, 0], Y_train_r[:, 0], label="train", marker="o", s=25)
plt.scatter(X_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 0], label="test", marker="o", s=25)
plt.xlabel("x scores")
plt.ylabel("y scores")
plt.title(
"Comp. 1: X vs Y (test corr = %.2f)"
% np.corrcoef(X_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 0])[0, 1]
)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.subplot(224)
plt.scatter(X_train_r[:, 1], Y_train_r[:, 1], label="train", marker="o", s=25)
plt.scatter(X_test_r[:, 1], Y_test_r[:, 1], label="test", marker="o", s=25)
plt.xlabel("x scores")
plt.ylabel("y scores")
plt.title(
"Comp. 2: X vs Y (test corr = %.2f)"
% np.corrcoef(X_test_r[:, 1], Y_test_r[:, 1])[0, 1]
)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.legend(loc="best")
# 非对角线图组件 1 对 2 的 X 和 Y
plt.subplot(222)
plt.scatter(X_train_r[:, 0], X_train_r[:, 1], label="train", marker="*", s=50)
plt.scatter(X_test_r[:, 0], X_test_r[:, 1], label="test", marker="*", s=50)
plt.xlabel("X comp. 1")
plt.ylabel("X comp. 2")
plt.title(
"X comp. 1 vs X comp. 2 (test corr = %.2f)"
% np.corrcoef(X_test_r[:, 0], X_test_r[:, 1])[0, 1]
)
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.subplot(223)
plt.scatter(Y_train_r[:, 0], Y_train_r[:, 1], label="train", marker="*", s=50)
plt.scatter(Y_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 1], label="test", marker="*", s=50)
plt.xlabel("Y comp. 1")
plt.ylabel("Y comp. 2")
plt.title(
"Y comp. 1 vs Y comp. 2 , (test corr = %.2f)"
% np.corrcoef(Y_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 1])[0, 1]
)
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
PLS 回归,多变量响应,又称 PLS2#
from sklearn.cross_decomposition import PLSRegression
n = 1000
q = 3
p = 10
X = np.random.normal(size=n * p).reshape((n, p))
B = np.array([[1, 2] + [0] * (p - 2)] * q).T
# 每个 Yj = 1*X1 + 2*X2 + 噪声
Y = np.dot(X, B) + np.random.normal(size=n * q).reshape((n, q)) + 5
pls2 = PLSRegression(n_components=3)
pls2.fit(X, Y)
print("True B (such that: Y = XB + Err)")
print(B)
# 比较 pls2.coef_ 和 B
print("Estimated B")
print(np.round(pls2.coef_, 1))
pls2.predict(X)
True B (such that: Y = XB + Err)
[[1 1 1]
[2 2 2]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]]
Estimated B
[[ 1. 2. -0.1 -0. -0. -0. -0. -0.1 0. -0. ]
[ 1. 1.9 -0. -0. 0. 0.1 -0. 0. -0. -0. ]
[ 1. 1.9 -0. -0. -0. 0. -0. -0. -0. -0. ]]
array([[4.46260781, 4.3792903 , 4.36836896],
[5.22294138, 5.07398425, 5.06453542],
[3.2416229 , 3.5337111 , 3.43197656],
...,
[8.8168107 , 8.67329602, 8.61637485],
[9.55912109, 9.37260612, 9.3419536 ],
[6.80361268, 6.99998367, 6.88026638]])
PLS 回归,具有单变量响应,又称 PLS1#
n = 1000
p = 10
X = np.random.normal(size=n * p).reshape((n, p))
y = X[:, 0] + 2 * X[:, 1] + np.random.normal(size=n * 1) + 5
pls1 = PLSRegression(n_components=3)
pls1.fit(X, y)
# 请注意,组件的数量超过了1(y的维度)
print("Estimated betas")
print(np.round(pls1.coef_, 1))
Estimated betas
[[ 0.9 2. -0. -0. -0. -0.1 0. -0. 0. -0. ]]
CCA(对称消减的PLS模式B)#
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.103 seconds)
Related examples