Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
SVM:加权样本#
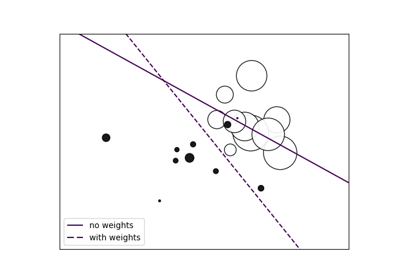
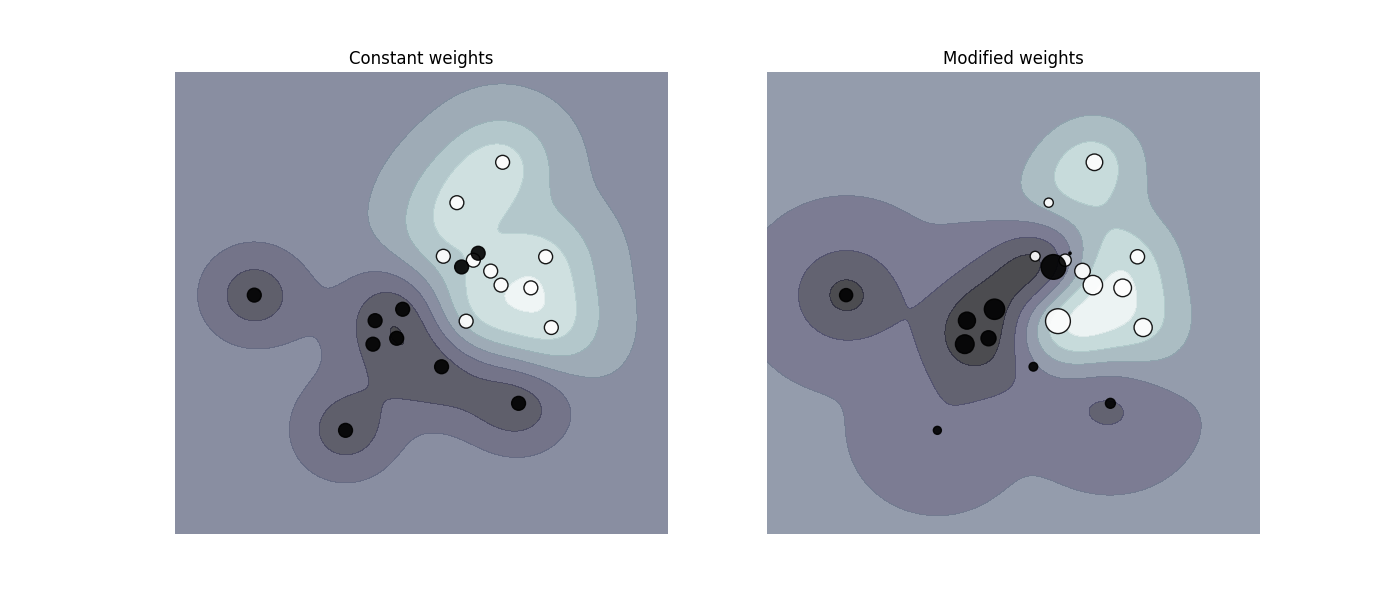
绘制加权数据集的决策函数,其中点的大小与其权重成正比。
样本加权会重新调整参数C,这意味着分类器会更加重视正确分类这些点。这个效果通常可能比较微妙。 为了强调这里的效果,我们特别对离群点进行加权,使决策边界的变形非常明显。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
def plot_decision_function(classifier, sample_weight, axis, title):
# 绘制决策函数
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4, 5, 500), np.linspace(-4, 5, 500))
Z = classifier.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# 绘制直线、点和最近的向量到平面
axis.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.75, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
axis.scatter(
X[:, 0],
X[:, 1],
c=y,
s=100 * sample_weight,
alpha=0.9,
cmap=plt.cm.bone,
edgecolors="black",
)
axis.axis("off")
axis.set_title(title)
# 我们创建了20个点
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(10, 2) + [1, 1], np.random.randn(10, 2)]
y = [1] * 10 + [-1] * 10
sample_weight_last_ten = abs(np.random.randn(len(X)))
sample_weight_constant = np.ones(len(X))
# 并且对一些异常值赋予更大的权重
sample_weight_last_ten[15:] *= 5
sample_weight_last_ten[9] *= 15
# 拟合模型。
# 此模型未考虑样本权重。
clf_no_weights = svm.SVC(gamma=1)
clf_no_weights.fit(X, y)
# 这个其他模型考虑了一些专用的样本权重。
clf_weights = svm.SVC(gamma=1)
clf_weights.fit(X, y, sample_weight=sample_weight_last_ten)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 6))
plot_decision_function(
clf_no_weights, sample_weight_constant, axes[0], "Constant weights"
)
plot_decision_function(clf_weights, sample_weight_last_ten, axes[1], "Modified weights")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.260 seconds)
Related examples
sphx_glr_auto_examples_exercises_plot_iris_exercise.py
SVM 练习