Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
使用非负矩阵分解和潜在狄利克雷分配进行主题提取#
这是一个应用 NMF 和 LatentDirichletAllocation 在文档语料库上提取语料库主题结构的加性模型的示例。输出是一个主题的图,每个主题用基于权重的前几个词表示为条形图。
非负矩阵分解应用了两种不同的目标函数:Frobenius 范数和广义 Kullback-Leibler 散度。后者等同于概率潜在语义索引。
默认参数(n_samples / n_features / n_components)应使示例在几十秒内可运行。您可以尝试增加问题的维度,但请注意,在 NMF 中时间复杂度是多项式的。在 LDA 中,时间复杂度与 (n_samples * 迭代次数) 成正比。
Loading dataset...
done in 0.704s.
Extracting tf-idf features for NMF...
done in 0.146s.
Extracting tf features for LDA...
done in 0.133s.
Fitting the NMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000...
done in 0.110s.
Fitting the NMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000...
done in 0.551s.
Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000, batch_size=128...
done in 0.062s.
Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000, batch_size=128...
done in 0.098s.
Fitting LDA models with tf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000...
done in 1.496s.
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.decomposition import NMF, LatentDirichletAllocation, MiniBatchNMF
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer
n_samples = 2000
n_features = 1000
n_components = 10
n_top_words = 20
batch_size = 128
init = "nndsvda"
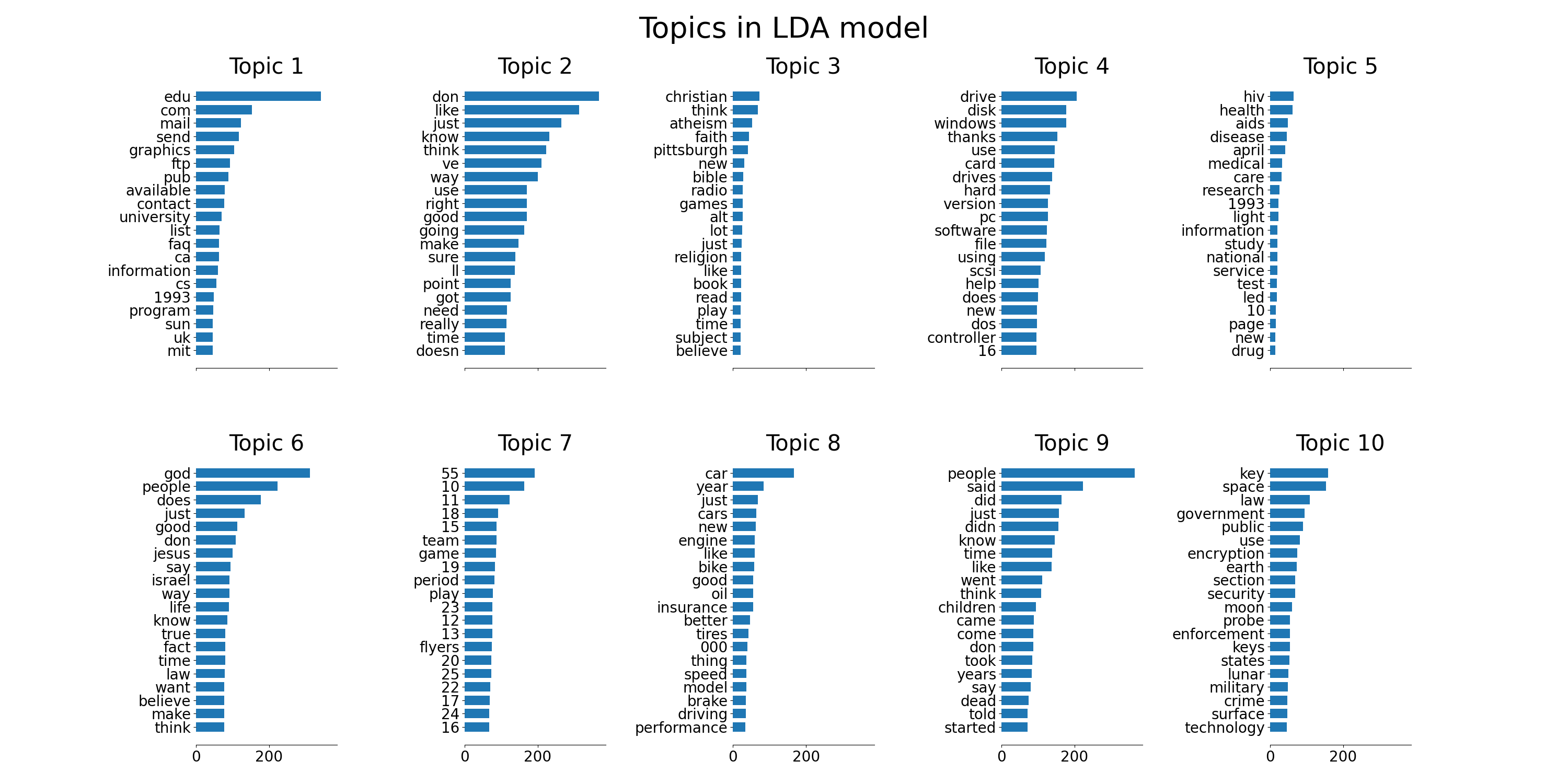
def plot_top_words(model, feature_names, n_top_words, title):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 5, figsize=(30, 15), sharex=True)
axes = axes.flatten()
for topic_idx, topic in enumerate(model.components_):
top_features_ind = topic.argsort()[-n_top_words:]
top_features = feature_names[top_features_ind]
weights = topic[top_features_ind]
ax = axes[topic_idx]
ax.barh(top_features, weights, height=0.7)
ax.set_title(f"Topic {topic_idx +1}", fontdict={"fontsize": 30})
ax.tick_params(axis="both", which="major", labelsize=20)
for i in "top right left".split():
ax.spines[i].set_visible(False)
fig.suptitle(title, fontsize=40)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.90, bottom=0.05, wspace=0.90, hspace=0.3)
plt.show()
# 加载20个新闻组数据集并对其进行向量化。我们使用了一些启发式方法来提前过滤掉无用的术语:帖子被去除了标题、页脚和引用的回复,常见的英语单词、仅出现在一个文档中或至少出现在95%文档中的单词也被移除。
print("Loading dataset...")
t0 = time()
data, _ = fetch_20newsgroups(
shuffle=True,
random_state=1,
remove=("headers", "footers", "quotes"),
return_X_y=True,
)
data_samples = data[:n_samples]
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
# 使用tf-idf特征进行NMF。
print("Extracting tf-idf features for NMF...")
tfidf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(
max_df=0.95, min_df=2, max_features=n_features, stop_words="english"
)
t0 = time()
tfidf = tfidf_vectorizer.fit_transform(data_samples)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
# 使用 tf(原始词频)特征进行 LDA。
print("Extracting tf features for LDA...")
tf_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(
max_df=0.95, min_df=2, max_features=n_features, stop_words="english"
)
t0 = time()
tf = tf_vectorizer.fit_transform(data_samples)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
print()
# 拟合NMF模型
print(
"Fitting the NMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf features, "
"n_samples=%d and n_features=%d..." % (n_samples, n_features)
)
t0 = time()
nmf = NMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
init=init,
beta_loss="frobenius",
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=1,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
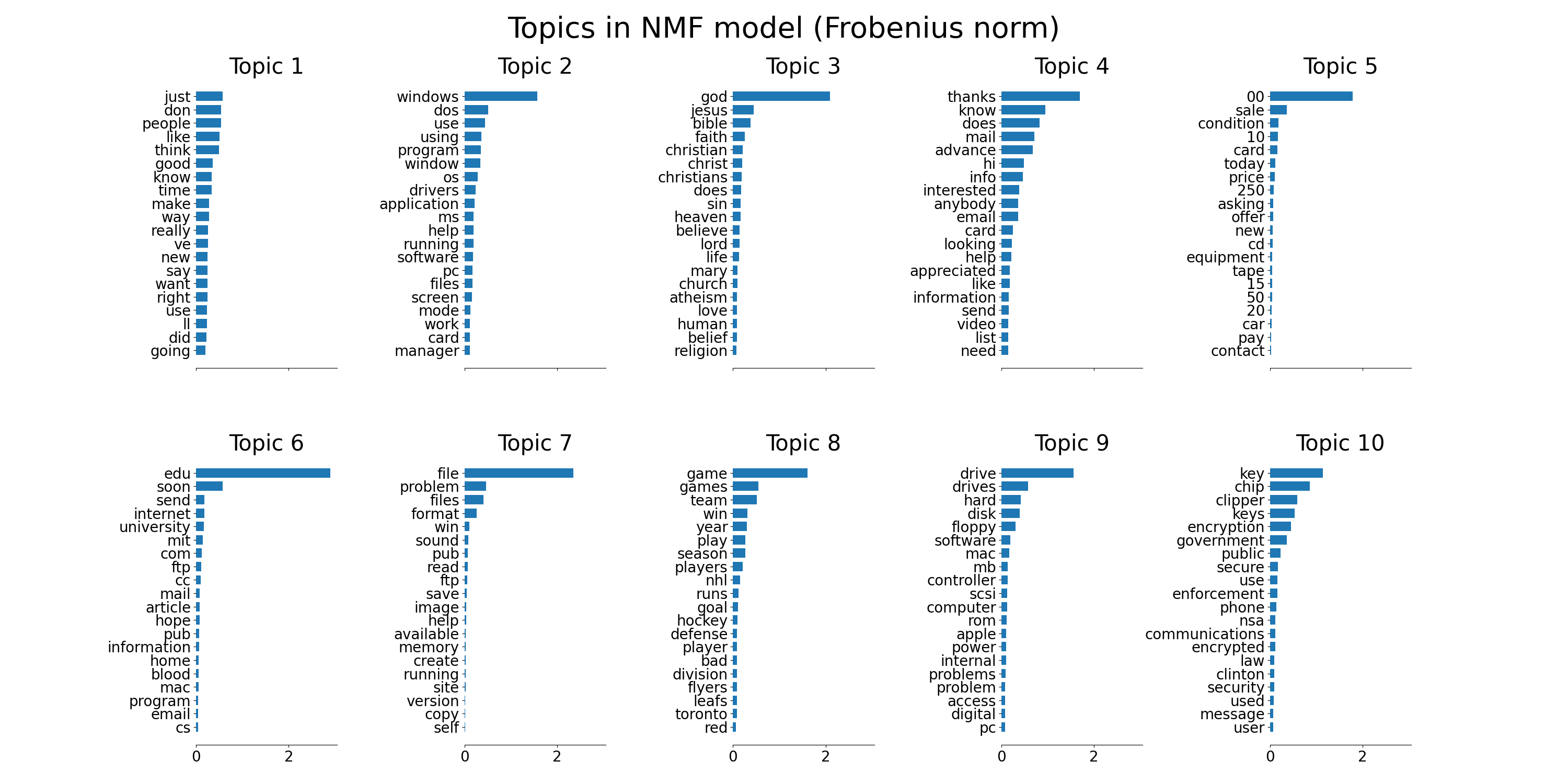
plot_top_words(
nmf, tfidf_feature_names, n_top_words, "Topics in NMF model (Frobenius norm)"
)
# 拟合NMF模型
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting the NMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler "
"divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d..."
% (n_samples, n_features),
)
t0 = time()
nmf = NMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
init=init,
beta_loss="kullback-leibler",
solver="mu",
max_iter=1000,
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=0.5,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
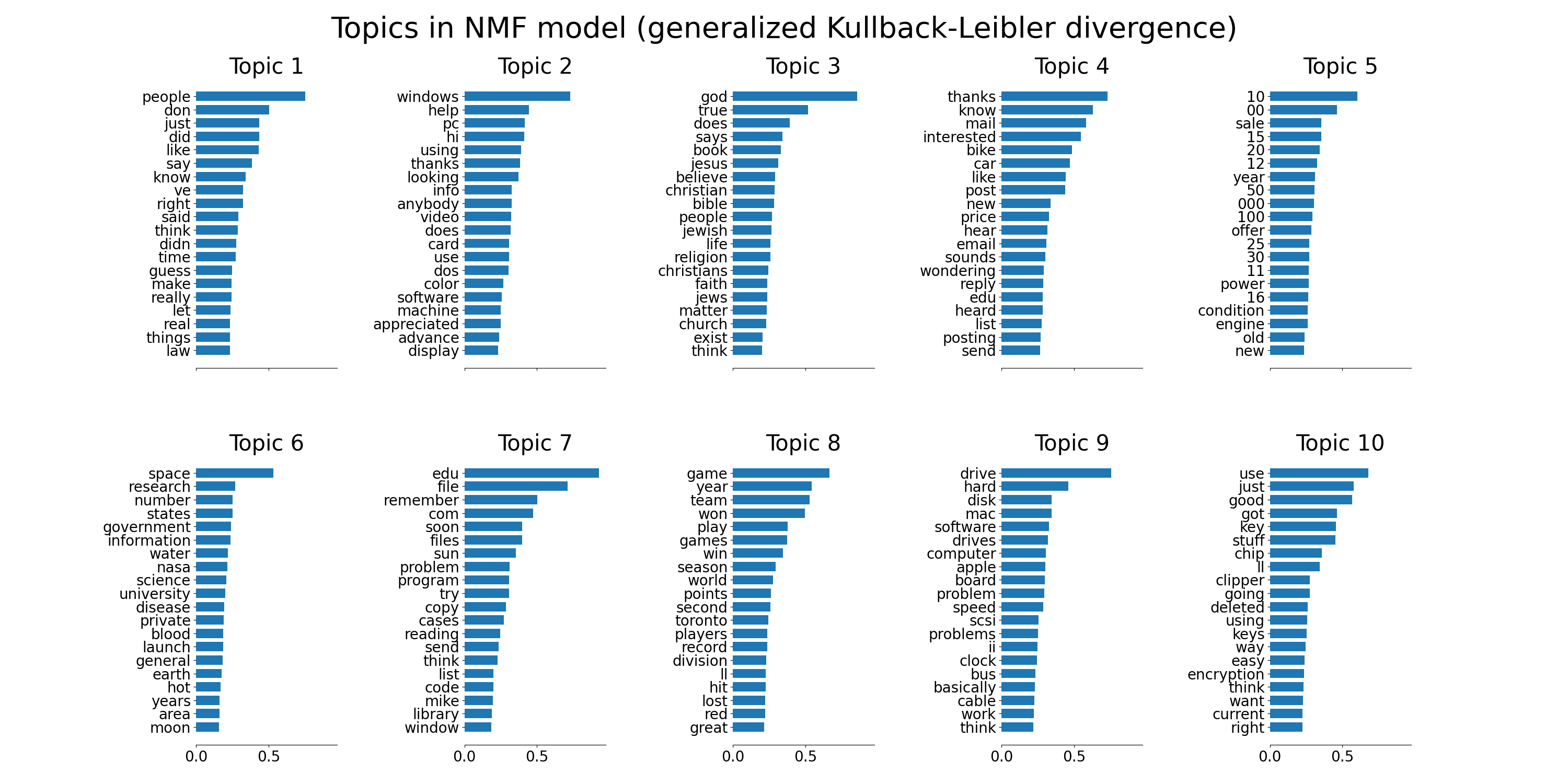
plot_top_words(
nmf,
tfidf_feature_names,
n_top_words,
"Topics in NMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence)",
)
# 拟合 MiniBatchNMF 模型
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf "
"features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d, batch_size=%d..."
% (n_samples, n_features, batch_size),
)
t0 = time()
mbnmf = MiniBatchNMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
batch_size=batch_size,
init=init,
beta_loss="frobenius",
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=0.5,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
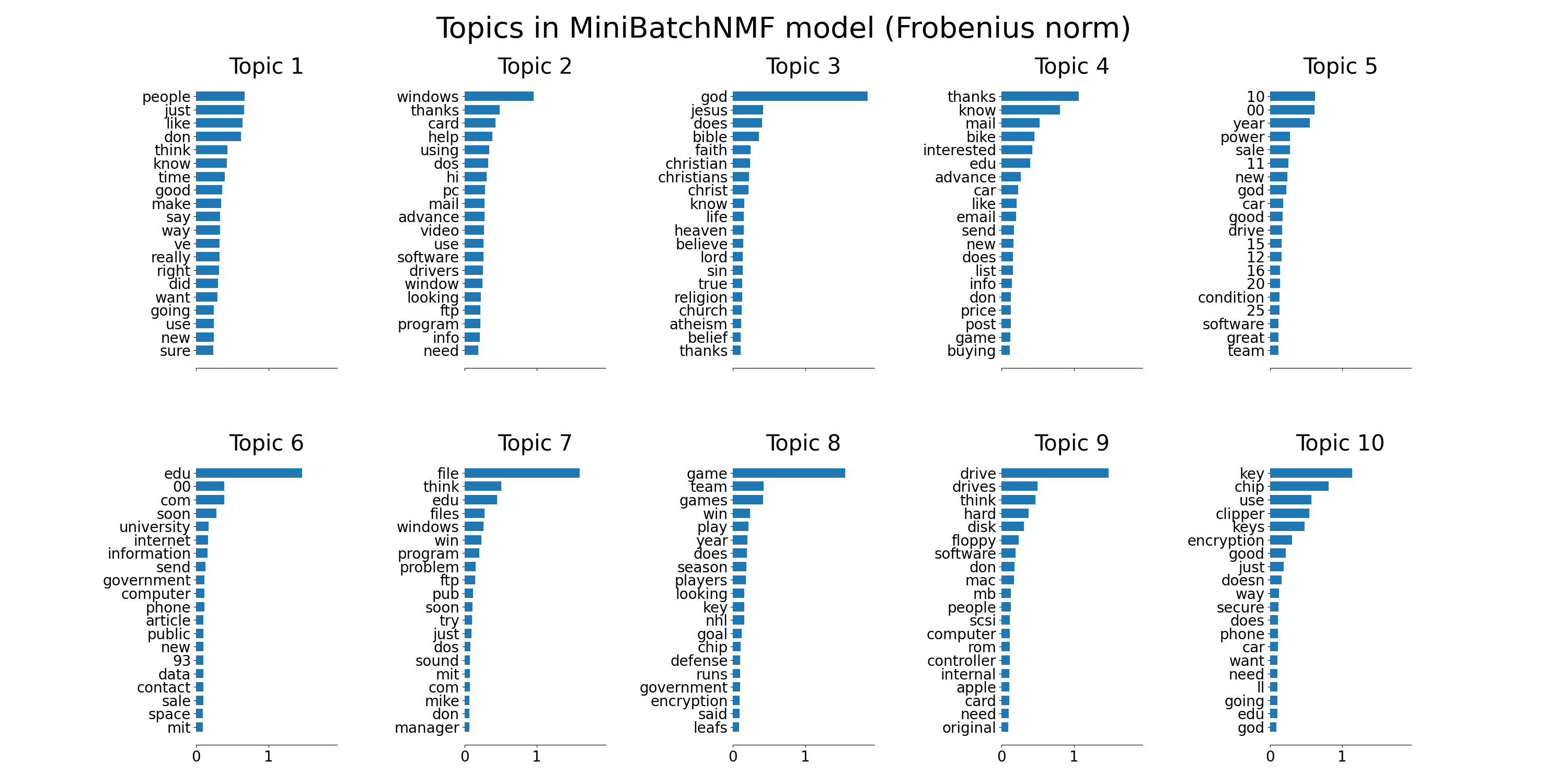
plot_top_words(
mbnmf,
tfidf_feature_names,
n_top_words,
"Topics in MiniBatchNMF model (Frobenius norm)",
)
# 拟合 MiniBatchNMF 模型
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler "
"divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d, "
"batch_size=%d..." % (n_samples, n_features, batch_size),
)
t0 = time()
mbnmf = MiniBatchNMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
batch_size=batch_size,
init=init,
beta_loss="kullback-leibler",
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=0.5,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
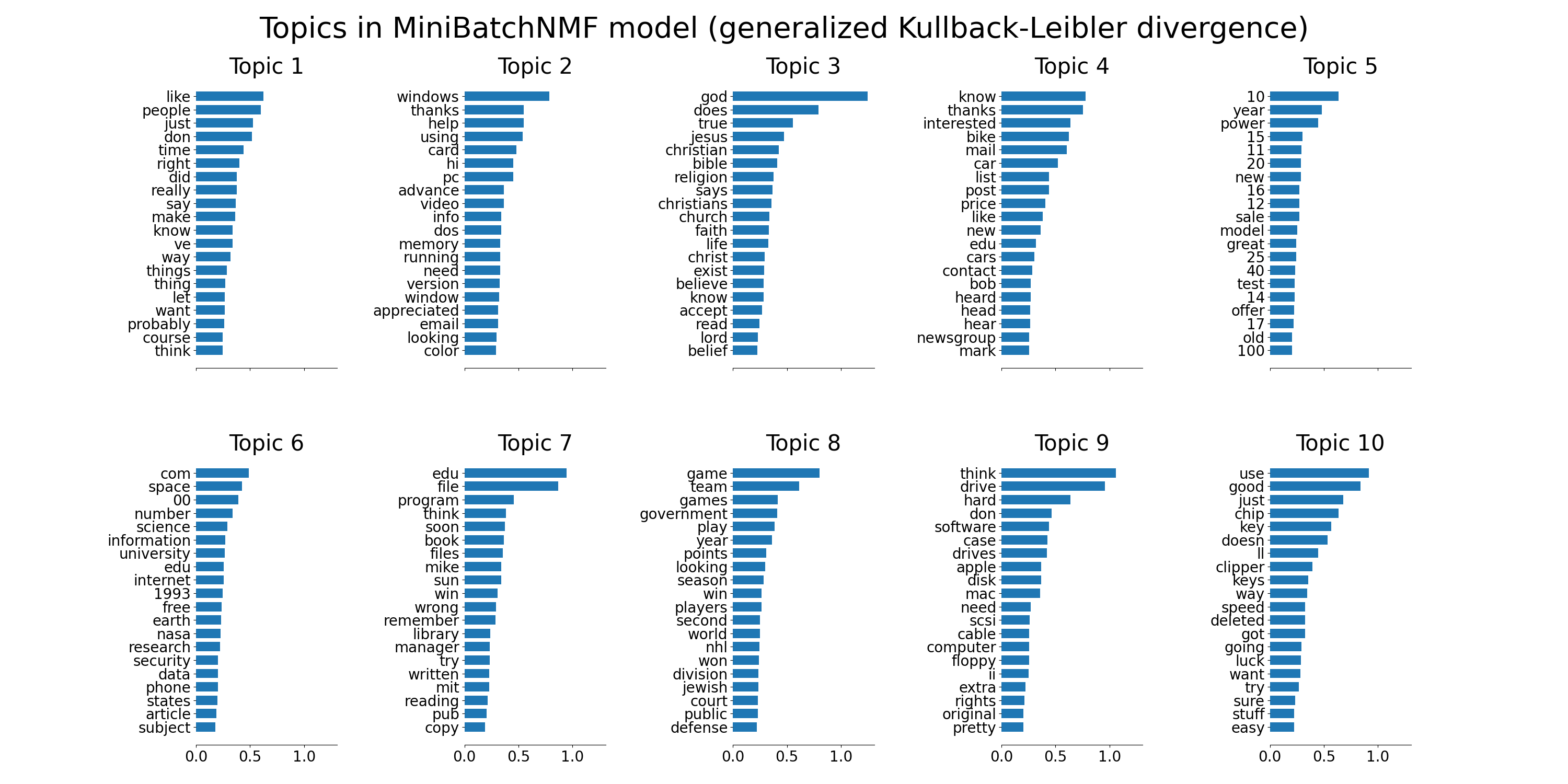
plot_top_words(
mbnmf,
tfidf_feature_names,
n_top_words,
"Topics in MiniBatchNMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence)",
)
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting LDA models with tf features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d..."
% (n_samples, n_features),
)
lda = LatentDirichletAllocation(
n_components=n_components,
max_iter=5,
learning_method="online",
learning_offset=50.0,
random_state=0,
)
t0 = time()
lda.fit(tf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tf_feature_names = tf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
plot_top_words(lda, tf_feature_names, n_top_words, "Topics in LDA model")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.812 seconds)
Related examples