Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
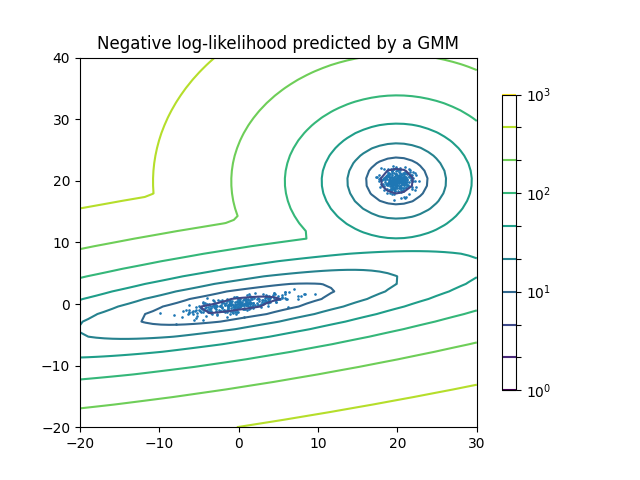
高斯混合模型的密度估计#
绘制两个高斯分布混合的密度估计。数据是从两个具有不同中心和协方差矩阵的高斯分布生成的。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
from sklearn import mixture
n_samples = 300
# 生成随机样本,两个成分
np.random.seed(0)
# 生成以 (20, 20) 为中心的球形数据
shifted_gaussian = np.random.randn(n_samples, 2) + np.array([20, 20])
# 生成零中心拉伸高斯数据
C = np.array([[0.0, -0.7], [3.5, 0.7]])
stretched_gaussian = np.dot(np.random.randn(n_samples, 2), C)
# 将这两个数据集合并成最终的训练集
X_train = np.vstack([shifted_gaussian, stretched_gaussian])
# 拟合一个具有两个成分的高斯混合模型
clf = mixture.GaussianMixture(n_components=2, covariance_type="full")
clf.fit(X_train)
# 显示模型预测分数的等高线图
x = np.linspace(-20.0, 30.0)
y = np.linspace(-20.0, 40.0)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
XX = np.array([X.ravel(), Y.ravel()]).T
Z = -clf.score_samples(XX)
Z = Z.reshape(X.shape)
CS = plt.contour(
X, Y, Z, norm=LogNorm(vmin=1.0, vmax=1000.0), levels=np.logspace(0, 3, 10)
)
CB = plt.colorbar(CS, shrink=0.8, extend="both")
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], 0.8)
plt.title("Negative log-likelihood predicted by a GMM")
plt.axis("tight")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.057 seconds)
Related examples