Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
转换回归模型中的目标变量的效果#
在这个示例中,我们概述了:class:~sklearn.compose.TransformedTargetRegressor 。我们使用两个示例来说明在学习线性回归模型之前转换目标变量的好处。第一个示例使用合成数据,而第二个示例基于Ames房价数据集。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier:BSD-3-Clause
print(__doc__)
合成示例
###################
#
# 生成一个合成的随机回归数据集。目标值 ``y`` 被修改为:
#
# 1. 将所有目标值平移,使得所有条目都是非负的(通过加上最小的 ``y`` 的绝对值),并且
# 2. 应用指数函数以获得无法使用简单线性模型拟合的非线性目标值。
#
# 因此,在训练线性回归模型并使用其进行预测之前,将使用对数函数( `np.log1p` )和指数函数( `np.expm1` )对目标进行转换。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=10_000, noise=100, random_state=0)
y = np.expm1((y + abs(y.min())) / 200)
y_trans = np.log1p(y)
下面我们绘制了应用对数函数前后目标的概率密度函数。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
f, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax0.hist(y, bins=100, density=True)
ax0.set_xlim([0, 2000])
ax0.set_ylabel("Probability")
ax0.set_xlabel("Target")
ax0.set_title("Target distribution")
ax1.hist(y_trans, bins=100, density=True)
ax1.set_ylabel("Probability")
ax1.set_xlabel("Target")
ax1.set_title("Transformed target distribution")
f.suptitle("Synthetic data", y=1.05)
plt.tight_layout()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
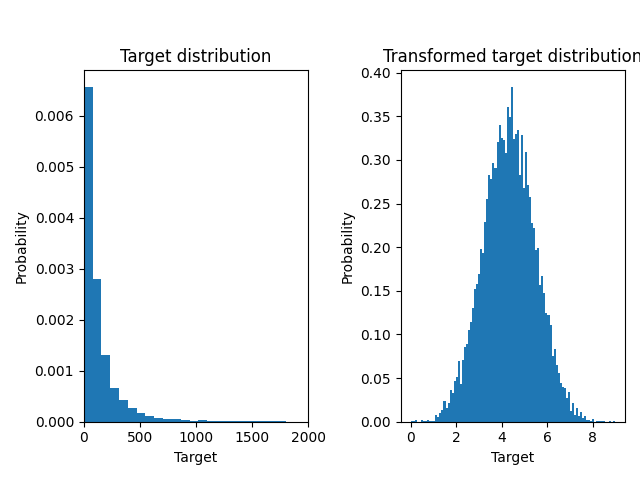
首先,将在线性模型上应用原始目标。由于非线性,训练的模型在预测时不会精确。随后,使用对数函数对目标进行线性化,即使使用类似的线性模型,也能通过中位绝对误差(MedAE)报告更好的预测结果。
from sklearn.metrics import median_absolute_error, r2_score
def compute_score(y_true, y_pred):
return {
"R2": f"{r2_score(y_true, y_pred):.3f}",
"MedAE": f"{median_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred):.3f}",
}
from sklearn.compose import TransformedTargetRegressor
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV
from sklearn.metrics import PredictionErrorDisplay
f, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharey=True)
ridge_cv = RidgeCV().fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_ridge = ridge_cv.predict(X_test)
ridge_cv_with_trans_target = TransformedTargetRegressor(
regressor=RidgeCV(), func=np.log1p, inverse_func=np.expm1
).fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target = ridge_cv_with_trans_target.predict(X_test)
PredictionErrorDisplay.from_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred_ridge,
kind="actual_vs_predicted",
ax=ax0,
scatter_kwargs={"alpha": 0.5},
)
PredictionErrorDisplay.from_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target,
kind="actual_vs_predicted",
ax=ax1,
scatter_kwargs={"alpha": 0.5},
)
# 在每个轴的图例中添加分数
for ax, y_pred in zip([ax0, ax1], [y_pred_ridge, y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target]):
for name, score in compute_score(y_test, y_pred).items():
ax.plot([], [], " ", label=f"{name}={score}")
ax.legend(loc="upper left")
ax0.set_title("Ridge regression \n without target transformation")
ax1.set_title("Ridge regression \n with target transformation")
f.suptitle("Synthetic data", y=1.05)
plt.tight_layout()
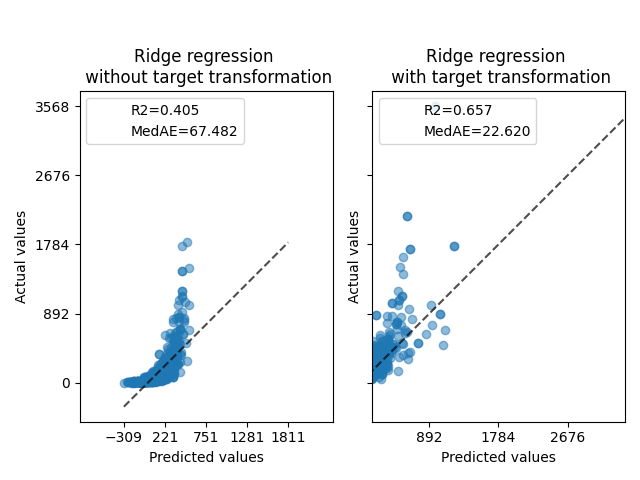
真实世界数据集
以类似的方式,Ames 房价数据集被用来展示在学习模型之前转换目标变量的影响。在这个例子中,要预测的目标是每栋房子的售价。
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.preprocessing import quantile_transform
ames = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True)
# 只保留数值列
X = ames.data.select_dtypes(np.number)
# 删除包含NaN或Inf值的列
X = X.drop(columns=["LotFrontage", "GarageYrBlt", "MasVnrArea"])
# 令价格以千美元为单位
y = ames.target / 1000
y_trans = quantile_transform(
y.to_frame(), n_quantiles=900, output_distribution="normal", copy=True
).squeeze()
一个 QuantileTransformer 被用来在应用 RidgeCV 模型之前对目标分布进行归一化。
f, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax0.hist(y, bins=100, density=True)
ax0.set_ylabel("Probability")
ax0.set_xlabel("Target")
ax0.set_title("Target distribution")
ax1.hist(y_trans, bins=100, density=True)
ax1.set_ylabel("Probability")
ax1.set_xlabel("Target")
ax1.set_title("Transformed target distribution")
f.suptitle("Ames housing data: selling price", y=1.05)
plt.tight_layout()
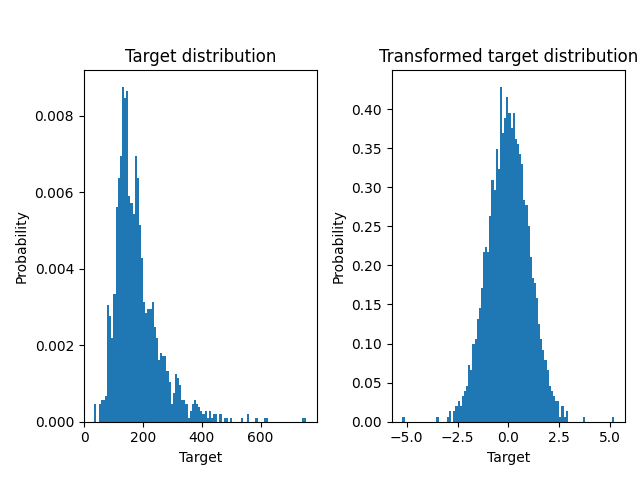
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=1)
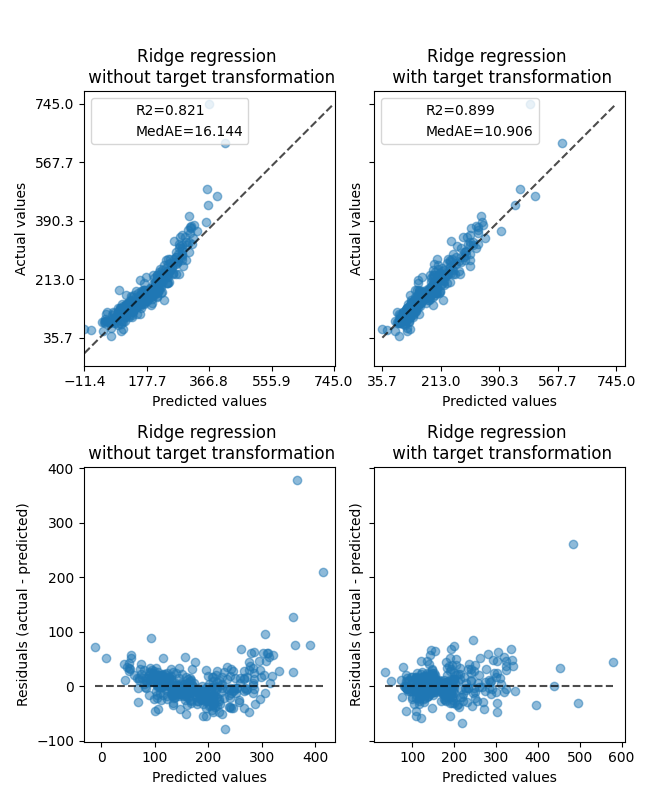
变压器的效果比在合成数据上要弱。然而,转换结果使 \(R^2\) 增加,且 MedAE 大幅减少。残差图(预测目标 - 真实目标 vs 预测目标)在没有目标转换的情况下,由于残差值随预测目标值的变化而变化,呈现出弯曲的“反向微笑”形状。通过目标转换,形状更加线性,表明模型拟合更好。
from sklearn.preprocessing import QuantileTransformer
f, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharey="row", figsize=(6.5, 8))
ridge_cv = RidgeCV().fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_ridge = ridge_cv.predict(X_test)
ridge_cv_with_trans_target = TransformedTargetRegressor(
regressor=RidgeCV(),
transformer=QuantileTransformer(n_quantiles=900, output_distribution="normal"),
).fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target = ridge_cv_with_trans_target.predict(X_test)
# 绘制实际值与预测值的对比图
PredictionErrorDisplay.from_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred_ridge,
kind="actual_vs_predicted",
ax=ax0[0],
scatter_kwargs={"alpha": 0.5},
)
PredictionErrorDisplay.from_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target,
kind="actual_vs_predicted",
ax=ax0[1],
scatter_kwargs={"alpha": 0.5},
)
# 在每个轴的图例中添加分数
for ax, y_pred in zip([ax0[0], ax0[1]], [y_pred_ridge, y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target]):
for name, score in compute_score(y_test, y_pred).items():
ax.plot([], [], " ", label=f"{name}={score}")
ax.legend(loc="upper left")
ax0[0].set_title("Ridge regression \n without target transformation")
ax0[1].set_title("Ridge regression \n with target transformation")
# 绘制残差与预测值的关系图
PredictionErrorDisplay.from_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred_ridge,
kind="residual_vs_predicted",
ax=ax1[0],
scatter_kwargs={"alpha": 0.5},
)
PredictionErrorDisplay.from_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred_ridge_with_trans_target,
kind="residual_vs_predicted",
ax=ax1[1],
scatter_kwargs={"alpha": 0.5},
)
ax1[0].set_title("Ridge regression \n without target transformation")
ax1[1].set_title("Ridge regression \n with target transformation")
f.suptitle("Ames housing data: selling price", y=1.05)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.722 seconds)
Related examples