Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
带交叉验证的递归特征消除#
一个递归特征消除(RFE)的示例,通过交叉验证自动调整所选特征的数量。
数据生成#
我们使用3个信息特征构建一个分类任务。引入2个额外的冗余(即相关)特征会导致所选特征因交叉验证折叠而异。其余特征是随机抽取的,因此是无信息的。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=500,
n_features=15,
n_informative=3,
n_redundant=2,
n_repeated=0,
n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
class_sep=0.8,
random_state=0,
)
模型训练与选择#
我们创建了RFE对象并计算了交叉验证得分。评分策略“准确性”优化了正确分类样本的比例。
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
min_features_to_select = 1 # Minimum number of features to consider
clf = LogisticRegression()
cv = StratifiedKFold(5)
rfecv = RFECV(
estimator=clf,
step=1,
cv=cv,
scoring="accuracy",
min_features_to_select=min_features_to_select,
n_jobs=2,
)
rfecv.fit(X, y)
print(f"Optimal number of features: {rfecv.n_features_}")
Optimal number of features: 3
在当前情况下,具有3个特征的模型(对应于真实生成模型)被认为是最优的。
绘制特征数量与交叉验证得分的关系图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
cv_results = pd.DataFrame(rfecv.cv_results_)
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel("Number of features selected")
plt.ylabel("Mean test accuracy")
plt.errorbar(
x=cv_results["n_features"],
y=cv_results["mean_test_score"],
yerr=cv_results["std_test_score"],
)
plt.title("Recursive Feature Elimination \nwith correlated features")
plt.show()
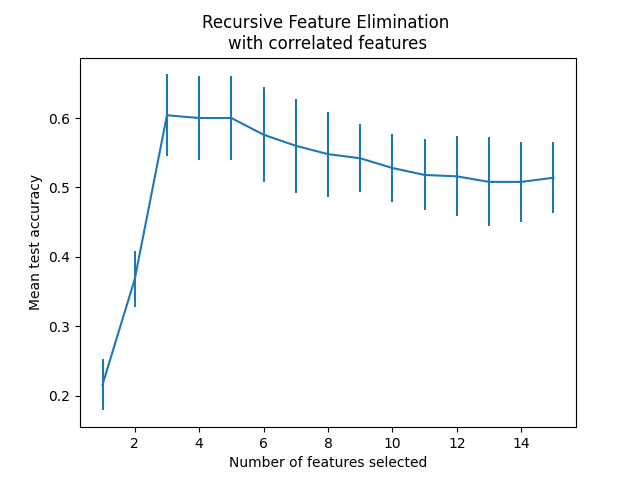
从上图可以进一步注意到,对于选择的3到5个特征,得分出现了一个平台期(平均值相似且误差条重叠)。这是引入相关特征的结果。实际上,由RFE选择的最优模型可能位于这个范围内,具体取决于交叉验证技术。选择超过5个特征时,测试准确率下降,也就是说,保留无信息特征会导致过拟合,因此对模型的统计性能有害。
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.329 seconds)
Related examples