Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
机器学习在推断因果效应方面的失败#
机器学习模型在测量统计关联方面表现出色。 不幸的是,除非我们愿意对数据做出强假设,否则这些模型无法推断因果效应。
为了说明这一点,我们将模拟一种情况,在这种情况下,我们试图回答教育经济学中最重要的问题之一:获得大学学位对小时工资的因果效应是什么? 尽管这个问题的答案对政策制定者至关重要,但 遗漏变量偏差 (OVB) 阻止了我们识别这种因果效应。
数据集:模拟的小时工资#
数据生成过程在下面的代码中列出。工作经验(以年为单位)和能力测量值从正态分布中抽取;父母一方的小时工资从贝塔分布中抽取。然后,我们创建一个大学学位的指示变量,该变量受能力和父母小时工资的正向影响。最后,我们将小时工资建模为所有先前变量和一个随机成分的线性函数。注意,所有变量对小时工资都有正向影响。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
n_samples = 10_000
rng = np.random.RandomState(32)
experiences = rng.normal(20, 10, size=n_samples).astype(int)
experiences[experiences < 0] = 0
abilities = rng.normal(0, 0.15, size=n_samples)
parent_hourly_wages = 50 * rng.beta(2, 8, size=n_samples)
parent_hourly_wages[parent_hourly_wages < 0] = 0
college_degrees = (
9 * abilities + 0.02 * parent_hourly_wages + rng.randn(n_samples) > 0.7
).astype(int)
true_coef = pd.Series(
{
"college degree": 2.0,
"ability": 5.0,
"experience": 0.2,
"parent hourly wage": 1.0,
}
)
hourly_wages = (
true_coef["experience"] * experiences
+ true_coef["parent hourly wage"] * parent_hourly_wages
+ true_coef["college degree"] * college_degrees
+ true_coef["ability"] * abilities
+ rng.normal(0, 1, size=n_samples)
)
hourly_wages[hourly_wages < 0] = 0
模拟数据的描述#
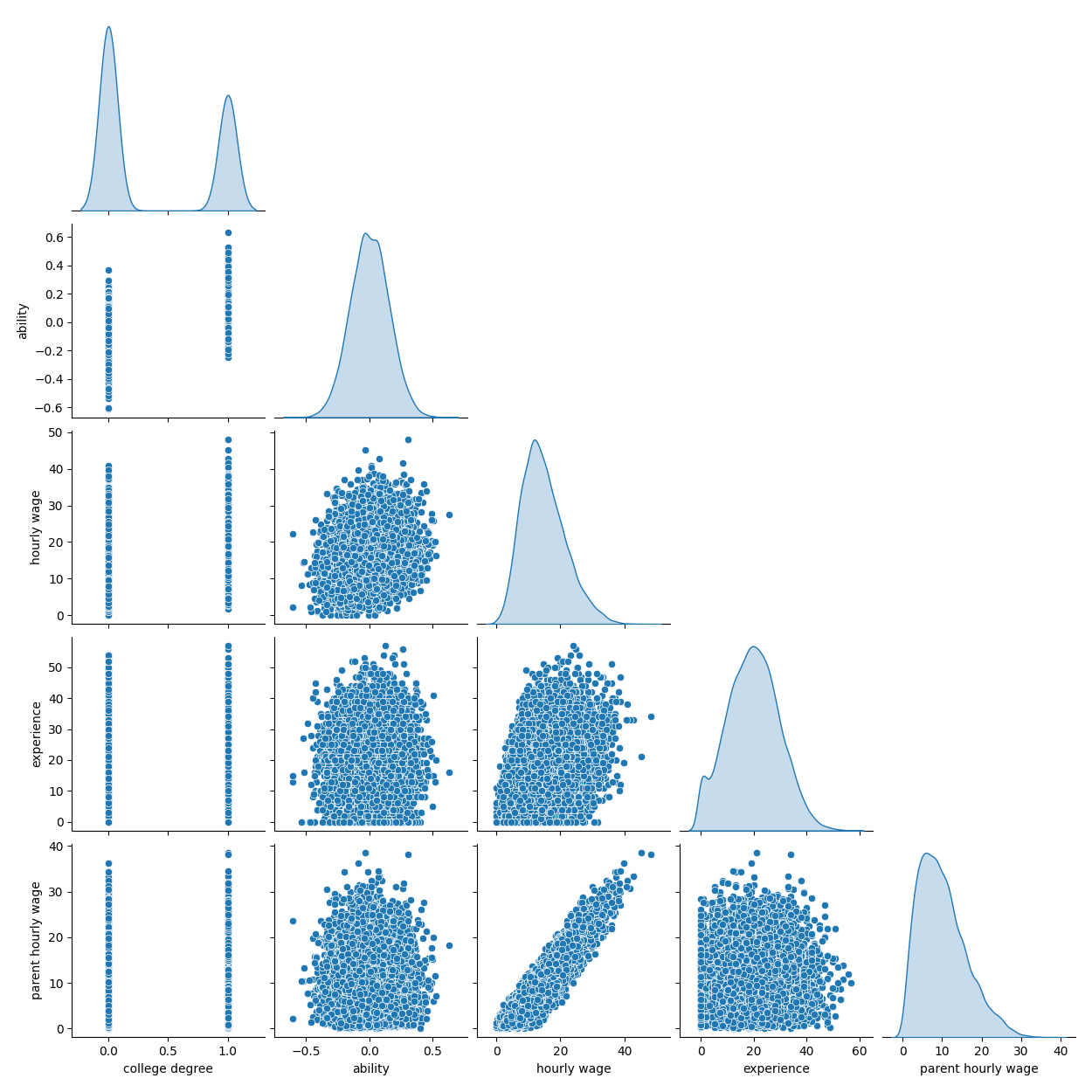
下图显示了每个变量的分布以及成对的散点图。我们OVB故事的关键是能力与大学学位之间的正相关关系。
import seaborn as sns
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"college degree": college_degrees,
"ability": abilities,
"hourly wage": hourly_wages,
"experience": experiences,
"parent hourly wage": parent_hourly_wages,
}
)
grid = sns.pairplot(df, diag_kind="kde", corner=True)
在下一节中,我们将训练预测模型,因此我们将目标列与其他特征分开,并将数据分为训练集和测试集。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
target_name = "hourly wage"
X, y = df.drop(columns=target_name), df[target_name]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
收入预测(完全观测变量)#
首先,我们训练一个预测模型,即:class:~sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression 模型。在这个实验中,我们假设真实生成模型使用的所有变量都是可用的。
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
features_names = ["experience", "parent hourly wage", "college degree", "ability"]
regressor_with_ability = LinearRegression()
regressor_with_ability.fit(X_train[features_names], y_train)
y_pred_with_ability = regressor_with_ability.predict(X_test[features_names])
R2_with_ability = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_with_ability)
print(f"R2 score with ability: {R2_with_ability:.3f}")
R2 score with ability: 0.975
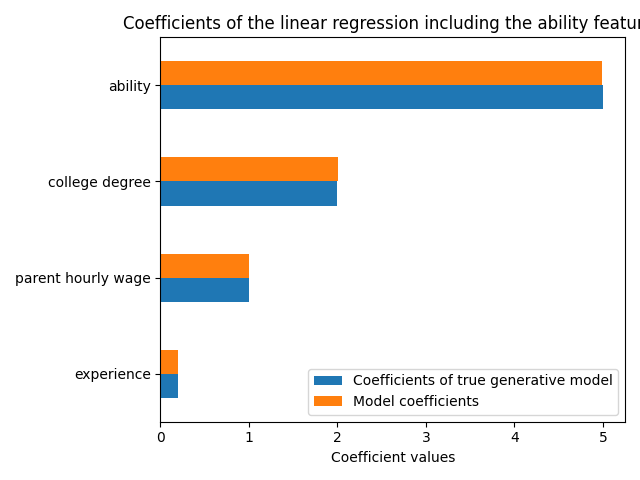
该模型很好地预测了时薪,正如高R2得分所示。我们绘制了模型系数,以表明我们准确地恢复了真实生成模型的值。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model_coef = pd.Series(regressor_with_ability.coef_, index=features_names)
coef = pd.concat(
[true_coef[features_names], model_coef],
keys=["Coefficients of true generative model", "Model coefficients"],
axis=1,
)
ax = coef.plot.barh()
ax.set_xlabel("Coefficient values")
ax.set_title("Coefficients of the linear regression including the ability features")
_ = plt.tight_layout()
收入预测(部分观测)#
在实际操作中,智力能力并未被观察到,或者仅通过一些间接指标(例如智商测试)进行估计,而这些指标也无意中测量了教育水平。但是,在线性模型中省略“能力”特征会通过正向遗漏变量偏差(OVB)导致估计值膨胀。
features_names = ["experience", "parent hourly wage", "college degree"]
regressor_without_ability = LinearRegression()
regressor_without_ability.fit(X_train[features_names], y_train)
y_pred_without_ability = regressor_without_ability.predict(X_test[features_names])
R2_without_ability = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_without_ability)
print(f"R2 score without ability: {R2_without_ability:.3f}")
R2 score without ability: 0.968
我们的模型在省略能力特征时的预测能力在R2得分方面是相似的。我们现在检查模型的系数是否与真实生成模型不同。
model_coef = pd.Series(regressor_without_ability.coef_, index=features_names)
coef = pd.concat(
[true_coef[features_names], model_coef],
keys=["Coefficients of true generative model", "Model coefficients"],
axis=1,
)
ax = coef.plot.barh()
ax.set_xlabel("Coefficient values")
_ = ax.set_title("Coefficients of the linear regression excluding the ability feature")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
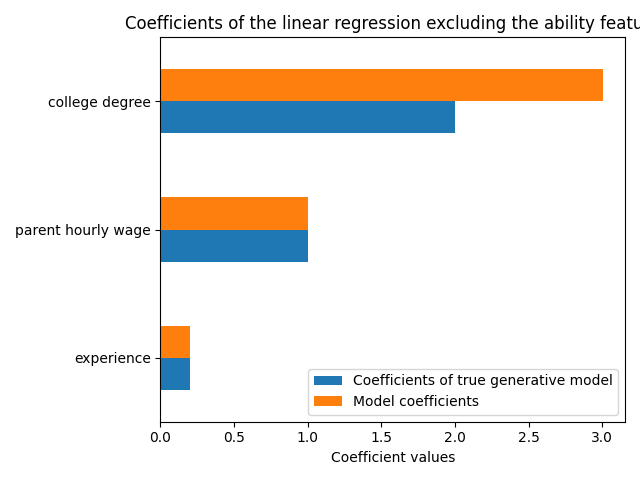
为了补偿被省略的变量,模型夸大了大学学位特征的系数。因此,将该系数值解释为真实生成模型的因果效应是不正确的。
经验教训#
机器学习模型并非用于估计因果效应。虽然我们用线性模型展示了这一点,但遗漏变量偏差(OVB)可以影响任何类型的模型。
在解释系数或由于某个特征的变化引起的预测变化时,重要的是要记住可能存在的未观察到的变量,这些变量可能与所讨论的特征和目标变量都相关。这些变量被称为 混杂变量 。为了在存在混杂的情况下仍然估计因果效应,研究人员通常会进行实验,其中处理变量(例如大学学位)是随机的。当实验费用过高或不道德时,研究人员有时可以使用其他因果推断技术,例如 工具变量 (IV) 估计。
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.170 seconds)
Related examples