Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
可视化股票市场结构#
本示例采用几种无监督学习技术,从历史报价的变化中提取股票市场结构。
我们使用的量是每日报价价格的变化:关联的报价在一天内往往会相互波动。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
从互联网检索数据#
数据来自2003年至2008年。这段时间相对平稳:(时间不算太久,因此我们可以获得高科技公司数据,并且在2008年金融危机之前)。这种历史数据可以从诸如 data.nasdaq.com 和 alphavantage.co 的API获取。
import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
symbol_dict = {
"TOT": "Total",
"XOM": "Exxon",
"CVX": "Chevron",
"COP": "ConocoPhillips",
"VLO": "Valero Energy",
"MSFT": "Microsoft",
"IBM": "IBM",
"TWX": "Time Warner",
"CMCSA": "Comcast",
"CVC": "Cablevision",
"YHOO": "Yahoo",
"DELL": "Dell",
"HPQ": "HP",
"AMZN": "Amazon",
"TM": "Toyota",
"CAJ": "Canon",
"SNE": "Sony",
"F": "Ford",
"HMC": "Honda",
"NAV": "Navistar",
"NOC": "Northrop Grumman",
"BA": "Boeing",
"KO": "Coca Cola",
"MMM": "3M",
"MCD": "McDonald's",
"PEP": "Pepsi",
"K": "Kellogg",
"UN": "Unilever",
"MAR": "Marriott",
"PG": "Procter Gamble",
"CL": "Colgate-Palmolive",
"GE": "General Electrics",
"WFC": "Wells Fargo",
"JPM": "JPMorgan Chase",
"AIG": "AIG",
"AXP": "American express",
"BAC": "Bank of America",
"GS": "Goldman Sachs",
"AAPL": "Apple",
"SAP": "SAP",
"CSCO": "Cisco",
"TXN": "Texas Instruments",
"XRX": "Xerox",
"WMT": "Wal-Mart",
"HD": "Home Depot",
"GSK": "GlaxoSmithKline",
"PFE": "Pfizer",
"SNY": "Sanofi-Aventis",
"NVS": "Novartis",
"KMB": "Kimberly-Clark",
"R": "Ryder",
"GD": "General Dynamics",
"RTN": "Raytheon",
"CVS": "CVS",
"CAT": "Caterpillar",
"DD": "DuPont de Nemours",
}
symbols, names = np.array(sorted(symbol_dict.items())).T
quotes = []
for symbol in symbols:
print("Fetching quote history for %r" % symbol, file=sys.stderr)
url = (
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/scikit-learn/examples-data/"
"master/financial-data/{}.csv"
)
quotes.append(pd.read_csv(url.format(symbol)))
close_prices = np.vstack([q["close"] for q in quotes])
open_prices = np.vstack([q["open"] for q in quotes])
# 报价的每日变化是最能传递信息的部分
variation = close_prices - open_prices
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AAPL')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AIG')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AMZN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AXP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('BA')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('BAC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CAJ')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CAT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CL')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CMCSA')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('COP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CSCO')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CVC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CVS')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CVX')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('DD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('DELL')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('F')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GE')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GS')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GSK')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('HD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('HMC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('HPQ')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('IBM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('JPM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('K')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('KMB')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('KO')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MAR')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MCD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MMM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MSFT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('NAV')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('NOC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('NVS')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('PEP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('PFE')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('PG')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('R')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('RTN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('SAP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('SNE')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('SNY')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TOT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TWX')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TXN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('UN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('VLO')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('WFC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('WMT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('XOM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('XRX')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('YHOO')
学习图结构#
我们使用稀疏逆协方差估计来找出在其他条件下哪些报价是相关的。具体来说,稀疏逆协方差为我们提供了一张图,即一个连接列表。对于每个符号,与其连接的符号是那些对解释其波动有用的符号。
from sklearn import covariance
alphas = np.logspace(-1.5, 1, num=10)
edge_model = covariance.GraphicalLassoCV(alphas=alphas)
# 标准化时间序列:使用相关性而非协方差
# 前者在结构恢复方面更高效
X = variation.copy().T
X /= X.std(axis=0)
edge_model.fit(X)
使用亲和传播的聚类#
我们使用聚类将行为相似的报价分组。在这里,在scikit-learn中可用的各种聚类技术中,我们使用了亲和传播(affinity_propagation),因为它不强制要求等大小的簇,并且可以自动从数据中选择簇的数量。
请注意,这给我们提供了与图表不同的指示,因为图表反映了变量之间的条件关系,而聚类反映了边际属性:聚类在一起的变量可以被认为在整个股票市场层面上具有类似的影响。
from sklearn import cluster
_, labels = cluster.affinity_propagation(edge_model.covariance_, random_state=0)
n_labels = labels.max()
for i in range(n_labels + 1):
print(f"Cluster {i + 1}: {', '.join(names[labels == i])}")
Cluster 1: Apple, Amazon, Yahoo
Cluster 2: Comcast, Cablevision, Time Warner
Cluster 3: ConocoPhillips, Chevron, Total, Valero Energy, Exxon
Cluster 4: Cisco, Dell, HP, IBM, Microsoft, SAP, Texas Instruments
Cluster 5: Boeing, General Dynamics, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon
Cluster 6: AIG, American express, Bank of America, Caterpillar, CVS, DuPont de Nemours, Ford, General Electrics, Goldman Sachs, Home Depot, JPMorgan Chase, Marriott, McDonald's, 3M, Ryder, Wells Fargo, Wal-Mart
Cluster 7: GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Unilever
Cluster 8: Kellogg, Coca Cola, Pepsi
Cluster 9: Colgate-Palmolive, Kimberly-Clark, Procter Gamble
Cluster 10: Canon, Honda, Navistar, Sony, Toyota, Xerox
在二维空间中的嵌入#
为了可视化,我们需要在二维画布上布置不同的符号。为此,我们使用 流形学习 技术来获取二维嵌入。 我们使用密集的特征值求解器来实现可重复性(arpack 是用我们无法控制的随机向量初始化的)。此外,我们使用大量的邻居来捕捉大规模结构。
# 为可视化寻找低维嵌入:在二维平面上找到节点(股票)的最佳位置
from sklearn import manifold
node_position_model = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(
n_components=2, eigen_solver="dense", n_neighbors=6
)
embedding = node_position_model.fit_transform(X.T).T
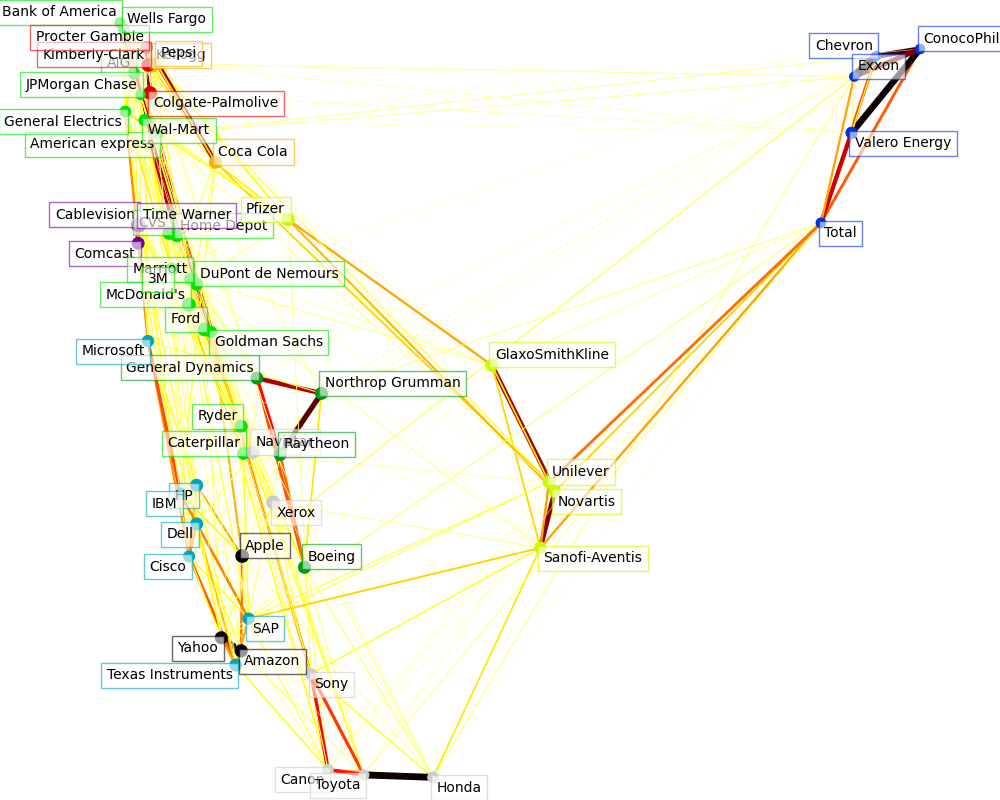
可视化#
三个模型的输出结果被组合在一个二维图中,其中节点代表股票,边代表:
聚类标签用于定义节点的颜色
稀疏协方差模型用于显示边的强度
2D嵌入用于在平面中定位节点
这个示例包含了相当多的与可视化相关的代码,因为在这里可视化对于显示图形至关重要。一个挑战是如何在最小化重叠的情况下放置标签。为此,我们使用了一种基于每个轴上最近邻方向的启发式方法。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
plt.figure(1, facecolor="w", figsize=(10, 8))
plt.clf()
ax = plt.axes([0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0])
plt.axis("off")
# 绘制偏相关图表
partial_correlations = edge_model.precision_.copy()
d = 1 / np.sqrt(np.diag(partial_correlations))
partial_correlations *= d
partial_correlations *= d[:, np.newaxis]
non_zero = np.abs(np.triu(partial_correlations, k=1)) > 0.02
# 使用嵌入的坐标绘制节点
plt.scatter(
embedding[0], embedding[1], s=100 * d**2, c=labels, cmap=plt.cm.nipy_spectral
)
# 绘制边缘
start_idx, end_idx = np.where(non_zero)
# 一个序列 (*line0*, *line1*, *line2*),其中::
#
# linen = (x0, y0), (x1, y1), ... (xm, ym)
segments = [
[embedding[:, start], embedding[:, stop]] for start, stop in zip(start_idx, end_idx)
]
values = np.abs(partial_correlations[non_zero])
lc = LineCollection(
segments, zorder=0, cmap=plt.cm.hot_r, norm=plt.Normalize(0, 0.7 * values.max())
)
lc.set_array(values)
lc.set_linewidths(15 * values)
ax.add_collection(lc)
# 为每个节点添加一个标签。这里的挑战在于我们希望将标签放置在避免与其他标签重叠的位置。
for index, (name, label, (x, y)) in enumerate(zip(names, labels, embedding.T)):
dx = x - embedding[0]
dx[index] = 1
dy = y - embedding[1]
dy[index] = 1
this_dx = dx[np.argmin(np.abs(dy))]
this_dy = dy[np.argmin(np.abs(dx))]
if this_dx > 0:
horizontalalignment = "left"
x = x + 0.002
else:
horizontalalignment = "right"
x = x - 0.002
if this_dy > 0:
verticalalignment = "bottom"
y = y + 0.002
else:
verticalalignment = "top"
y = y - 0.002
plt.text(
x,
y,
name,
size=10,
horizontalalignment=horizontalalignment,
verticalalignment=verticalalignment,
bbox=dict(
facecolor="w",
edgecolor=plt.cm.nipy_spectral(label / float(n_labels)),
alpha=0.6,
),
)
plt.xlim(
embedding[0].min() - 0.15 * np.ptp(embedding[0]),
embedding[0].max() + 0.10 * np.ptp(embedding[0]),
)
plt.ylim(
embedding[1].min() - 0.03 * np.ptp(embedding[1]),
embedding[1].max() + 0.03 * np.ptp(embedding[1]),
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 48.564 seconds)
Related examples