Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
标签传播数字:展示性能#
这个示例通过训练一个标签传播模型来分类手写数字,展示了半监督学习的强大功能,使用的标签集非常少。
手写数字数据集共有1797个点。模型将使用所有点进行训练,但只有30个点会被标记。结果将以混淆矩阵和每个类别的一系列指标的形式展示,效果会非常好。
最后,将展示最不确定的前10个预测。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
数据生成#
我们使用数字数据集。我们只使用随机选择的样本子集。
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
digits = datasets.load_digits()
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
indices = np.arange(len(digits.data))
rng.shuffle(indices)
我们选择了340个样本,其中只有40个样本会被关联到已知标签。 因此,我们存储了另外300个样本的索引,这些样本的标签我们不应该知道。
X = digits.data[indices[:340]]
y = digits.target[indices[:340]]
images = digits.images[indices[:340]]
n_total_samples = len(y)
n_labeled_points = 40
indices = np.arange(n_total_samples)
unlabeled_set = indices[n_labeled_points:]
把所有东西都打乱
y_train = np.copy(y)
y_train[unlabeled_set] = -1
半监督学习#
我们拟合一个 LabelSpreading 并使用它来预测未知标签。
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.semi_supervised import LabelSpreading
lp_model = LabelSpreading(gamma=0.25, max_iter=20)
lp_model.fit(X, y_train)
predicted_labels = lp_model.transduction_[unlabeled_set]
true_labels = y[unlabeled_set]
print(
"Label Spreading model: %d labeled & %d unlabeled points (%d total)"
% (n_labeled_points, n_total_samples - n_labeled_points, n_total_samples)
)
Label Spreading model: 40 labeled & 300 unlabeled points (340 total)
分类报告
print(classification_report(true_labels, predicted_labels))
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 27
1 0.82 1.00 0.90 37
2 1.00 0.86 0.92 28
3 1.00 0.80 0.89 35
4 0.92 1.00 0.96 24
5 0.74 0.94 0.83 34
6 0.89 0.96 0.92 25
7 0.94 0.89 0.91 35
8 1.00 0.68 0.81 31
9 0.81 0.88 0.84 24
accuracy 0.90 300
macro avg 0.91 0.90 0.90 300
weighted avg 0.91 0.90 0.90 300
混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_predictions(
true_labels, predicted_labels, labels=lp_model.classes_
)
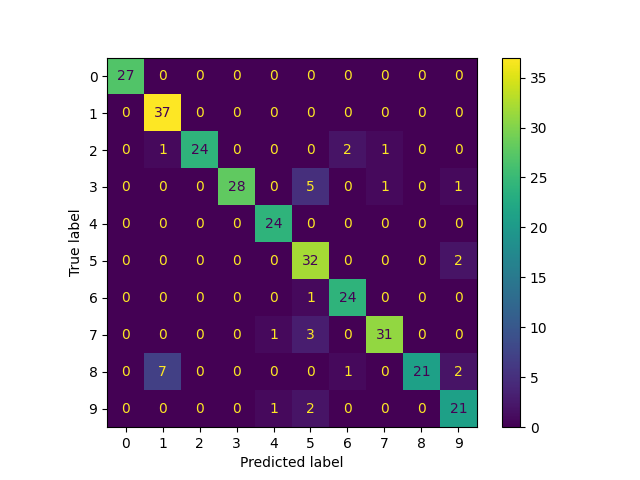
<sklearn.metrics._plot.confusion_matrix.ConfusionMatrixDisplay object at 0xffff259ae190>
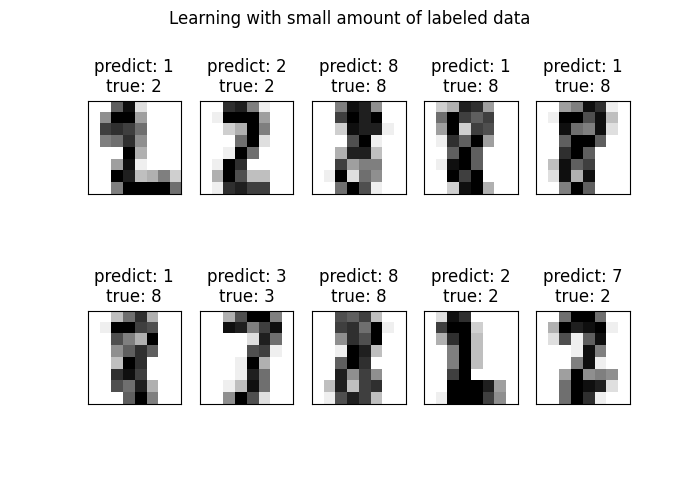
绘制最不确定的预测#
在这里,我们将挑选并展示10个最不确定的预测。
from scipy import stats
pred_entropies = stats.distributions.entropy(lp_model.label_distributions_.T)
选择最不确定的前10个标签
uncertainty_index = np.argsort(pred_entropies)[-10:]
Plot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
f = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
for index, image_index in enumerate(uncertainty_index):
image = images[image_index]
sub = f.add_subplot(2, 5, index + 1)
sub.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
sub.set_title(
"predict: %i\ntrue: %i" % (lp_model.transduction_[image_index], y[image_index])
)
f.suptitle("Learning with small amount of labeled data")
plt.show()

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.148 seconds)
Related examples