Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
单类支持向量机与使用随机梯度下降的单类支持向量机#
本示例展示了如何在RBF核的情况下,用:class:sklearn.linear_model.SGDOneClassSVM (一种单类支持向量机的随机梯度下降版本)来近似解决:class:sklearn.svm.OneClassSVM 的问题。首先使用核近似来应用:class:sklearn.linear_model.SGDOneClassSVM ,它实现了使用SGD的线性单类支持向量机。
请注意,sklearn.linear_model.SGDOneClassSVM 的计算复杂度与样本数量呈线性关系,而核化的:class:sklearn.svm.OneClassSVM 的复杂度在最好的情况下与样本数量呈二次关系。本示例的目的不是为了说明这种近似在计算时间上的优势,而是为了展示在一个玩具数据集上我们可以获得类似的结果。
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import Nystroem
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDOneClassSVM
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.svm import OneClassSVM
font = {"weight": "normal", "size": 15}
matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
random_state = 42
rng = np.random.RandomState(random_state)
# 生成训练数据
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(500, 2)
X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# 生成一些常规的新颖观察
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(20, 2)
X_test = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# 生成一些异常的新观测值
X_outliers = rng.uniform(low=-4, high=4, size=(20, 2))
# OCSVM 超参数
nu = 0.05
gamma = 2.0
# 拟合单类支持向量机
clf = OneClassSVM(gamma=gamma, kernel="rbf", nu=nu)
clf.fit(X_train)
y_pred_train = clf.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = clf.predict(X_test)
y_pred_outliers = clf.predict(X_outliers)
n_error_train = y_pred_train[y_pred_train == -1].size
n_error_test = y_pred_test[y_pred_test == -1].size
n_error_outliers = y_pred_outliers[y_pred_outliers == 1].size
# 使用核近似和随机梯度下降法拟合单类支持向量机
transform = Nystroem(gamma=gamma, random_state=random_state)
clf_sgd = SGDOneClassSVM(
nu=nu, shuffle=True, fit_intercept=True, random_state=random_state, tol=1e-4
)
pipe_sgd = make_pipeline(transform, clf_sgd)
pipe_sgd.fit(X_train)
y_pred_train_sgd = pipe_sgd.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test_sgd = pipe_sgd.predict(X_test)
y_pred_outliers_sgd = pipe_sgd.predict(X_outliers)
n_error_train_sgd = y_pred_train_sgd[y_pred_train_sgd == -1].size
n_error_test_sgd = y_pred_test_sgd[y_pred_test_sgd == -1].size
n_error_outliers_sgd = y_pred_outliers_sgd[y_pred_outliers_sgd == 1].size
from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6))
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50), np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50))
X = np.concatenate([xx.ravel().reshape(-1, 1), yy.ravel().reshape(-1, 1)], axis=1)
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
clf,
X,
response_method="decision_function",
plot_method="contourf",
ax=ax,
cmap="PuBu",
)
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
clf,
X,
response_method="decision_function",
plot_method="contour",
ax=ax,
linewidths=2,
colors="darkred",
levels=[0],
)
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
clf,
X,
response_method="decision_function",
plot_method="contourf",
ax=ax,
colors="palevioletred",
levels=[0, clf.decision_function(X).max()],
)
s = 20
b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c="white", s=s, edgecolors="k")
b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c="blueviolet", s=s, edgecolors="k")
c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c="gold", s=s, edgecolors="k")
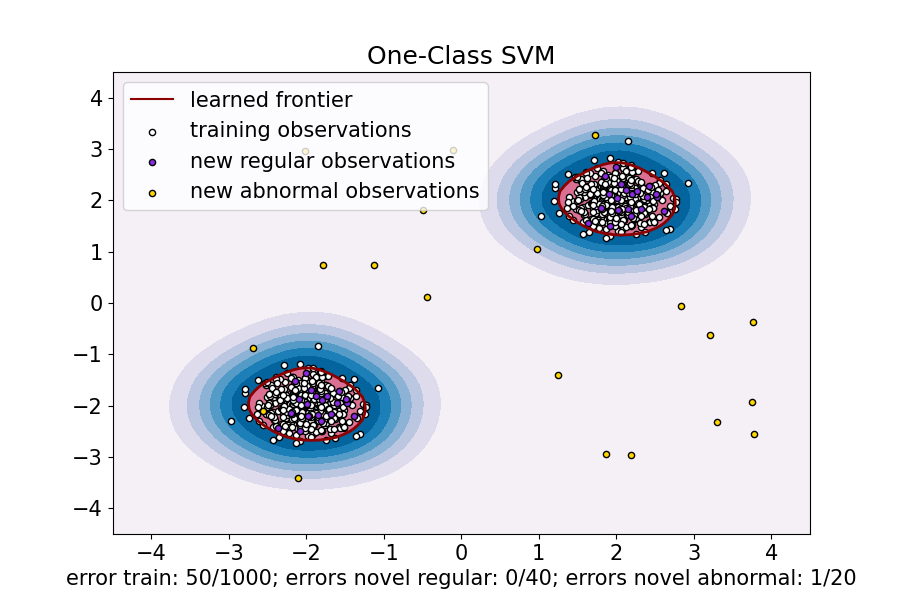
ax.set(
title="One-Class SVM",
xlim=(-4.5, 4.5),
ylim=(-4.5, 4.5),
xlabel=(
f"error train: {n_error_train}/{X_train.shape[0]}; "
f"errors novel regular: {n_error_test}/{X_test.shape[0]}; "
f"errors novel abnormal: {n_error_outliers}/{X_outliers.shape[0]}"
),
)
_ = ax.legend(
[mlines.Line2D([], [], color="darkred", label="learned frontier"), b1, b2, c],
[
"learned frontier",
"training observations",
"new regular observations",
"new abnormal observations",
],
loc="upper left",
)
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6))
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50), np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50))
X = np.concatenate([xx.ravel().reshape(-1, 1), yy.ravel().reshape(-1, 1)], axis=1)
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
pipe_sgd,
X,
response_method="decision_function",
plot_method="contourf",
ax=ax,
cmap="PuBu",
)
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
pipe_sgd,
X,
response_method="decision_function",
plot_method="contour",
ax=ax,
linewidths=2,
colors="darkred",
levels=[0],
)
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
pipe_sgd,
X,
response_method="decision_function",
plot_method="contourf",
ax=ax,
colors="palevioletred",
levels=[0, pipe_sgd.decision_function(X).max()],
)
s = 20
b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c="white", s=s, edgecolors="k")
b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c="blueviolet", s=s, edgecolors="k")
c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c="gold", s=s, edgecolors="k")
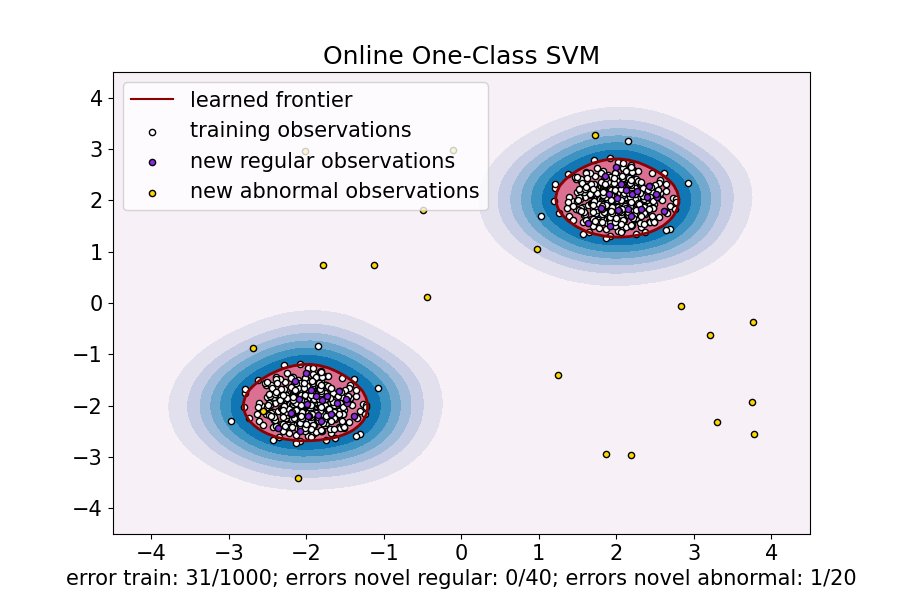
ax.set(
title="Online One-Class SVM",
xlim=(-4.5, 4.5),
ylim=(-4.5, 4.5),
xlabel=(
f"error train: {n_error_train_sgd}/{X_train.shape[0]}; "
f"errors novel regular: {n_error_test_sgd}/{X_test.shape[0]}; "
f"errors novel abnormal: {n_error_outliers_sgd}/{X_outliers.shape[0]}"
),
)
ax.legend(
[mlines.Line2D([], [], color="darkred", label="learned frontier"), b1, b2, c],
[
"learned frontier",
"training observations",
"new regular observations",
"new abnormal observations",
],
loc="upper left",
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.337 seconds)
Related examples