Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
矢量量化示例#
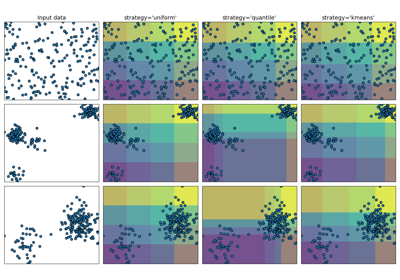
此示例展示了如何使用 KBinsDiscretizer
对一组玩具图像(浣熊脸)进行矢量量化。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX 许可证标识符:BSD-3-Clause
原始图像#
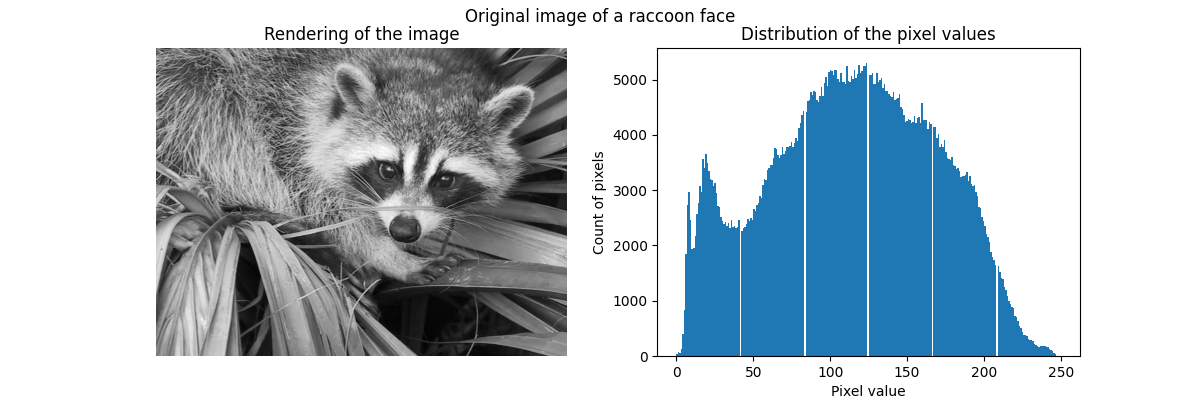
我们首先从 SciPy 加载浣熊脸图像。我们还将检查一些关于图像的信息,例如图像的形状和用于存储图像的数据类型。
请注意,根据SciPy版本的不同,我们需要调整导入方式,因为返回图像的函数所在的模块不同。此外,SciPy >= 1.10 需要安装 pooch 包。
try: # Scipy >= 1.10
from scipy.datasets import face
except ImportError:
from scipy.misc import face
raccoon_face = face(gray=True)
print(f"The dimension of the image is {raccoon_face.shape}")
print(f"The data used to encode the image is of type {raccoon_face.dtype}")
print(f"The number of bytes taken in RAM is {raccoon_face.nbytes}")
The dimension of the image is (768, 1024)
The data used to encode the image is of type uint8
The number of bytes taken in RAM is 786432
因此,该图像是一个高度为768像素、宽度为1024像素的二维数组。每个值是一个8位无符号整数,这意味着图像使用每像素8位进行编码。图像的总内存使用量为786千字节(1字节等于8位)。
使用8位无符号整数意味着图像最多使用256种不同的灰度级进行编码。我们可以检查这些值的分布。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(12, 4))
ax[0].imshow(raccoon_face, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].axis("off")
ax[0].set_title("Rendering of the image")
ax[1].hist(raccoon_face.ravel(), bins=256)
ax[1].set_xlabel("Pixel value")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Count of pixels")
ax[1].set_title("Distribution of the pixel values")
_ = fig.suptitle("Original image of a raccoon face")
通过矢量量化进行压缩#
通过矢量量化进行压缩的思想是减少表示图像的灰度级数量。例如,我们可以使用8个值代替256个值。因此,这意味着我们可以有效地使用3位而不是8位来编码单个像素,从而将内存使用量减少大约2.5倍。我们稍后将讨论这种内存使用情况。
编码策略
可以使用 KBinsDiscretizer 进行压缩。我们需要选择一种策略来定义 8 个灰度值进行子采样。最简单的策略是将它们等距定义,这对应于设置 strategy="uniform" 。从之前的直方图中,我们知道这种策略肯定不是最优的。
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
n_bins = 8
encoder = KBinsDiscretizer(
n_bins=n_bins,
encode="ordinal",
strategy="uniform",
random_state=0,
)
compressed_raccoon_uniform = encoder.fit_transform(raccoon_face.reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(
raccoon_face.shape
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(12, 4))
ax[0].imshow(compressed_raccoon_uniform, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].axis("off")
ax[0].set_title("Rendering of the image")
ax[1].hist(compressed_raccoon_uniform.ravel(), bins=256)
ax[1].set_xlabel("Pixel value")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Count of pixels")
ax[1].set_title("Sub-sampled distribution of the pixel values")
_ = fig.suptitle("Raccoon face compressed using 3 bits and a uniform strategy")
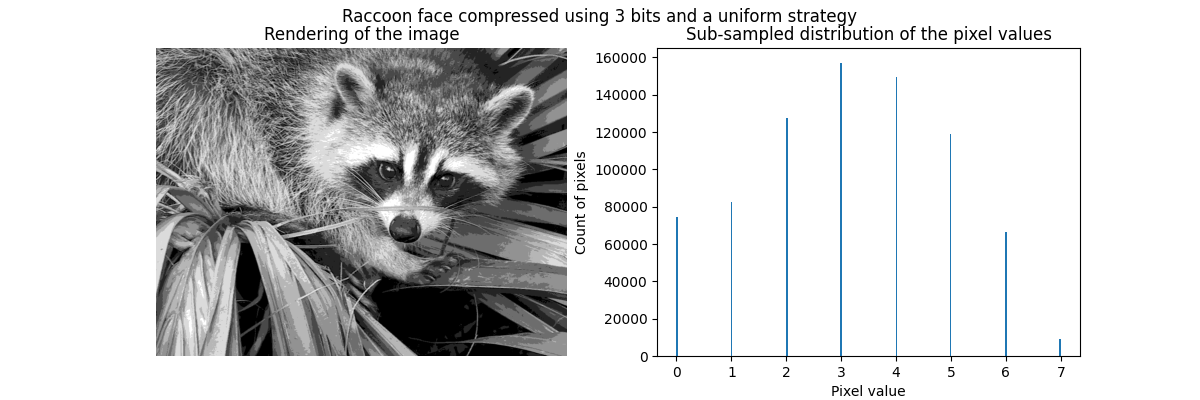
从定性上看,我们可以发现一些小区域在压缩后有影响(例如右下角的叶子)。但总的来说,生成的图像仍然看起来不错。
我们观察到像素值的分布已被映射到8个不同的值。我们可以检查这些值与原始像素值之间的对应关系。
bin_edges = encoder.bin_edges_[0]
bin_center = bin_edges[:-1] + (bin_edges[1:] - bin_edges[:-1]) / 2
bin_center
array([ 15.625, 46.875, 78.125, 109.375, 140.625, 171.875, 203.125,
234.375])
_, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.hist(raccoon_face.ravel(), bins=256)
color = "tab:orange"
for center in bin_center:
ax.axvline(center, color=color)
ax.text(center - 10, ax.get_ybound()[1] + 100, f"{center:.1f}", color=color)
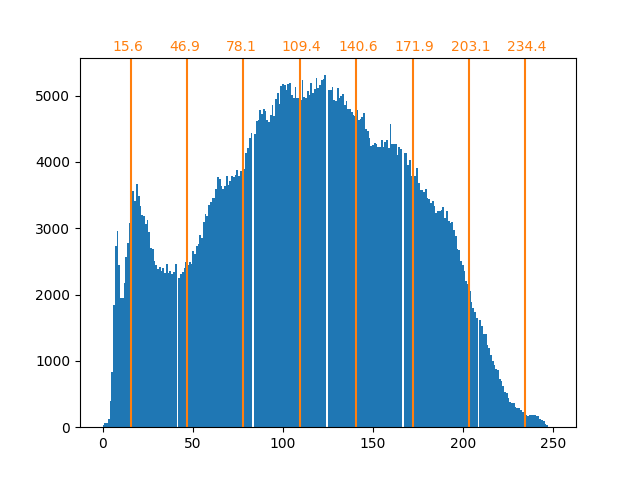
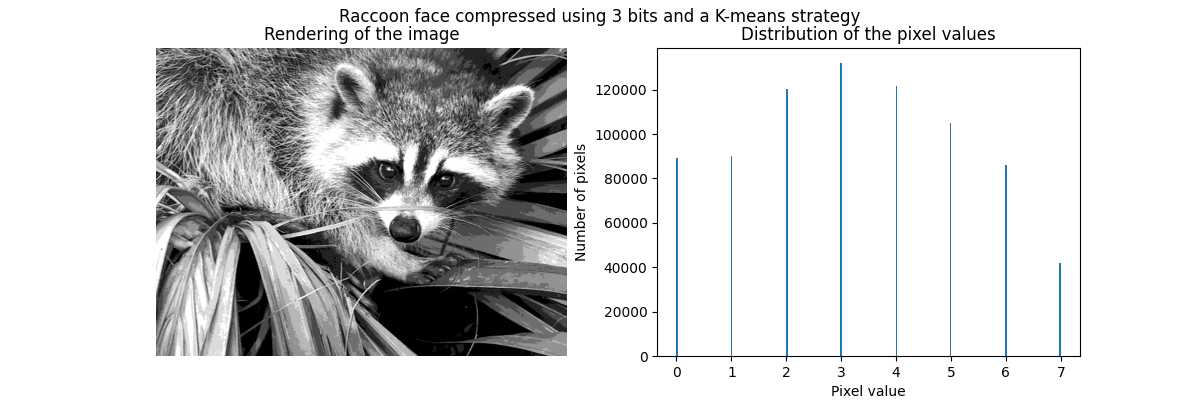
正如前面所述,均匀采样策略并不是最优的。请注意,例如映射到值7的像素将编码相当少量的信息,而映射到值3的像素将表示大量的计数。我们可以改用诸如k-means之类的聚类策略来找到更优的映射。
encoder = KBinsDiscretizer(
n_bins=n_bins,
encode="ordinal",
strategy="kmeans",
random_state=0,
)
compressed_raccoon_kmeans = encoder.fit_transform(raccoon_face.reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(
raccoon_face.shape
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(12, 4))
ax[0].imshow(compressed_raccoon_kmeans, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].axis("off")
ax[0].set_title("Rendering of the image")
ax[1].hist(compressed_raccoon_kmeans.ravel(), bins=256)
ax[1].set_xlabel("Pixel value")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Number of pixels")
ax[1].set_title("Distribution of the pixel values")
_ = fig.suptitle("Raccoon face compressed using 3 bits and a K-means strategy")
bin_edges = encoder.bin_edges_[0]
bin_center = bin_edges[:-1] + (bin_edges[1:] - bin_edges[:-1]) / 2
bin_center
array([ 18.90885631, 53.34346583, 82.64447187, 109.28225276,
134.70763101, 159.78681467, 185.17226834, 224.02069427])
_, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.hist(raccoon_face.ravel(), bins=256)
color = "tab:orange"
for center in bin_center:
ax.axvline(center, color=color)
ax.text(center - 10, ax.get_ybound()[1] + 100, f"{center:.1f}", color=color)
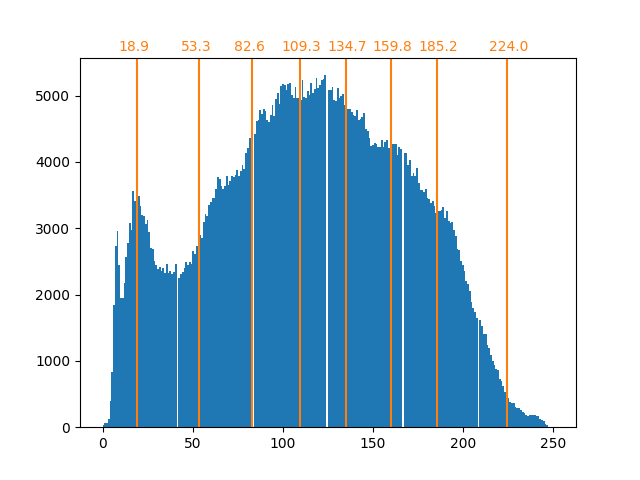
现在,各个箱中的计数更加均衡,并且它们的中心不再是等距的。请注意,我们可以通过使用 strategy="quantile" 而不是 strategy="kmeans" 来强制每个箱中的像素数量相同。
内存占用
我们之前说过,我们应该节省8倍的内存。让我们来验证一下。
print(f"The number of bytes taken in RAM is {compressed_raccoon_kmeans.nbytes}")
print(f"Compression ratio: {compressed_raccoon_kmeans.nbytes / raccoon_face.nbytes}")
The number of bytes taken in RAM is 6291456
Compression ratio: 8.0
令人惊讶的是,我们的压缩图像占用了比原始图像多8倍的内存。这确实与我们的预期相反。其主要原因在于用于编码图像的数据类型。
print(f"Type of the compressed image: {compressed_raccoon_kmeans.dtype}")
Type of the compressed image: float64
确实,KBinsDiscretizer 的输出是一个64位浮点数组。这意味着它占用了8倍的内存。然而,我们使用这种64位浮点表示来编码8个值。实际上,只有当我们将压缩图像转换为3位整数数组时,才能节省内存。我们可以使用 numpy.ndarray.astype 方法。然而,3位整数表示并不存在,并且为了编码这8个值,我们也需要使用8位无符号整数表示。
实际上,观察到内存增益需要原始图像是64位浮点表示。
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.967 seconds)
Related examples