Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
比较 BIRCH 和 MiniBatchKMeans#
本示例比较了 BIRCH(有全局聚类步骤和无全局聚类步骤)和 MiniBatchKMeans 在一个具有 25,000 个样本和 2 个特征的合成数据集上的时间表现,该数据集使用 make_blobs 生成。
MiniBatchKMeans和BIRCH都是非常可扩展的算法,可以高效地处理数十万甚至数百万的数据点。我们选择限制此示例的数据集大小,以保持我们的持续集成资源使用在合理范围内,但感兴趣的读者可以编辑此脚本,以更大的n_samples值重新运行它。
如果 n_clusters 设置为 None,数据将从 25,000 个样本减少到 158 个聚类。这可以视为最终(全局)聚类步骤之前的预处理步骤,该步骤将这 158 个聚类进一步减少到 100 个聚类。
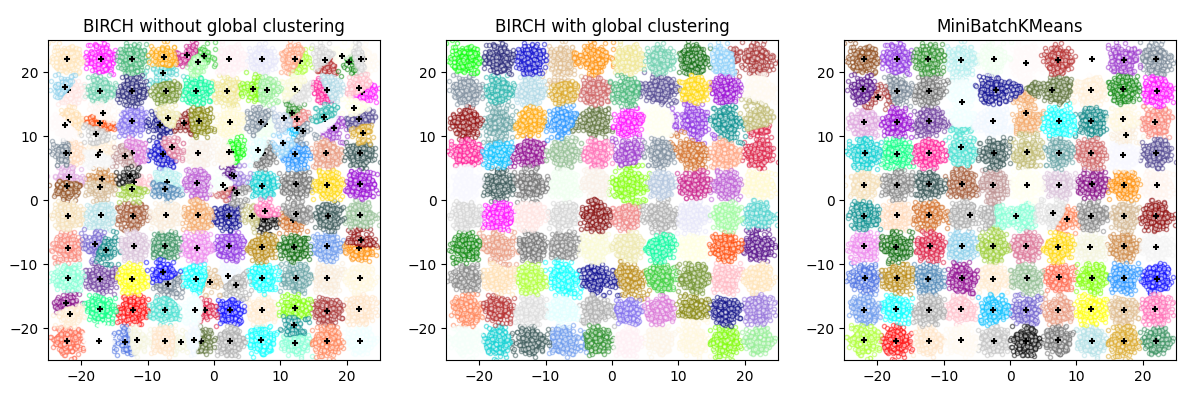
BIRCH without global clustering as the final step took 0.22 seconds
n_clusters : 158
BIRCH with global clustering as the final step took 0.21 seconds
n_clusters : 100
Time taken to run MiniBatchKMeans 0.19 seconds
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from itertools import cycle
from time import time
import matplotlib.colors as colors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from joblib import cpu_count
from sklearn.cluster import Birch, MiniBatchKMeans
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
# 生成斑点的中心,使其形成一个10 X 10的网格。
xx = np.linspace(-22, 22, 10)
yy = np.linspace(-22, 22, 10)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(xx, yy)
n_centers = np.hstack((np.ravel(xx)[:, np.newaxis], np.ravel(yy)[:, np.newaxis]))
# 生成斑点以比较 MiniBatchKMeans 和 BIRCH。
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=25000, centers=n_centers, random_state=0)
# 使用 matplotlib 默认提供的所有颜色。
colors_ = cycle(colors.cnames.keys())
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.04, right=0.98, bottom=0.1, top=0.9)
# 计算使用BIRCH算法的聚类结果(包括和不包括最终聚类步骤),并绘制图表。
birch_models = [
Birch(threshold=1.7, n_clusters=None),
Birch(threshold=1.7, n_clusters=100),
]
final_step = ["without global clustering", "with global clustering"]
for ind, (birch_model, info) in enumerate(zip(birch_models, final_step)):
t = time()
birch_model.fit(X)
print("BIRCH %s as the final step took %0.2f seconds" % (info, (time() - t)))
# Plot result
labels = birch_model.labels_
centroids = birch_model.subcluster_centers_
n_clusters = np.unique(labels).size
print("n_clusters : %d" % n_clusters)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, ind + 1)
for this_centroid, k, col in zip(centroids, range(n_clusters), colors_):
mask = labels == k
ax.scatter(X[mask, 0], X[mask, 1], c="w", edgecolor=col, marker=".", alpha=0.5)
if birch_model.n_clusters is None:
ax.scatter(this_centroid[0], this_centroid[1], marker="+", c="k", s=25)
ax.set_ylim([-25, 25])
ax.set_xlim([-25, 25])
ax.set_autoscaley_on(False)
ax.set_title("BIRCH %s" % info)
# 使用MiniBatchKMeans进行聚类计算。
mbk = MiniBatchKMeans(
init="k-means++",
n_clusters=100,
batch_size=256 * cpu_count(),
n_init=10,
max_no_improvement=10,
verbose=0,
random_state=0,
)
t0 = time()
mbk.fit(X)
t_mini_batch = time() - t0
print("Time taken to run MiniBatchKMeans %0.2f seconds" % t_mini_batch)
mbk_means_labels_unique = np.unique(mbk.labels_)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3)
for this_centroid, k, col in zip(mbk.cluster_centers_, range(n_clusters), colors_):
mask = mbk.labels_ == k
ax.scatter(X[mask, 0], X[mask, 1], marker=".", c="w", edgecolor=col, alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter(this_centroid[0], this_centroid[1], marker="+", c="k", s=25)
ax.set_xlim([-25, 25])
ax.set_ylim([-25, 25])
ax.set_title("MiniBatchKMeans")
ax.set_autoscaley_on(False)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.592 seconds)
Related examples